
Oracle® Communications
ASAP
Service Request Translator User's Guide
Release 7.2
E18882-01
April 2012
Oracle Communications ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide, Release 7.2
E18882-01
Copyright © 2012, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
This software and related documentation are provided under a license agreement containing restrictions on
use and disclosure and are protected by intellectual property laws. Except as expressly permitted in your
license agreement or allowed by law, you may not use, copy, reproduce, translate, broadcast, modify, license,
transmit, distribute, exhibit, perform, publish, or display any part, in any form, or by any means. Reverse
engineering, disassembly, or decompilation of this software, unless required by law for interoperability, is
prohibited.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice and is not warranted to be error-free. If
you find any errors, please report them to us in writing.
If this is software or related documentation that is delivered to the U.S. Government or anyone licensing it
on behalf of the U.S. Government, the following notice is applicable:
U.S. GOVERNMENT RIGHTS Programs, software, databases, and related documentation and technical data
delivered to U.S. Government customers are "commercial computer software" or "commercial technical data"
pursuant to the applicable Federal Acquisition Regulation and agency-specific supplemental regulations. As
such, the use, duplication, disclosure, modification, and adaptation shall be subject to the restrictions and
license terms set forth in the applicable Government contract, and, to the extent applicable by the terms of
the Government contract, the additional rights set forth in FAR 52.227-19, Commercial Computer Software
License (December 2007). Oracle America, Inc., 500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood City, CA 94065.
This software or hardware is developed for general use in a variety of information management
applications. It is not developed or intended for use in any inherently dangerous applications, including
applications that may create a risk of personal injury. If you use this software or hardware in dangerous
applications, then you shall be responsible to take all appropriate fail-safe, backup, redundancy, and other
measures to ensure its safe use. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates disclaim any liability for any damages
caused by use of this software or hardware in dangerous applications.
Oracle and Java are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of
their respective owners.
Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. All SPARC trademarks
are used under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. AMD,
Opteron, the AMD logo, and the AMD Opteron logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Advanced
Micro Devices. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This software or hardware and documentation may provide access to or information on content, products,
and services from third parties. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates are not responsible for and expressly
disclaim all warranties of any kind with respect to third-party content, products, and services. Oracle
Corporation and its affiliates will not be responsible for any loss, costs, or damages incurred due to your
access to or use of third-party content, products, or services.

iii
Contents
Preface ................................................................................................................................................................. v
Audience....................................................................................................................................................... v
Related Documents ..................................................................................................................................... v
1 The Service Request Translator
Process Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 1-1
2 Installing the SRT
Installing and Managing the SRT......................................................................................................... 2-1
Upgrading the SRT................................................................................................................................... 2-3
3 Working with SRT Components
Translation Process................................................................................................................................... 3-1
SRT and SRP Message Queues.............................................................................................................. 3-7
Logging with log4j ................................................................................................................................... 3-8
Configuring Event Templates ................................................................................................................ 3-8
SRT Translation ........................................................................................................................................ 3-8
Sample SrtTranslation.xsd ................................................................................................................ 3-9
XSLT Conversions ................................................................................................................................. 3-10
Sample Transformation.................................................................................................................. 3-11
Lookups ............................................................................................................................................ 3-12
Configuring srtServiceModel.xsd ...................................................................................................... 3-16
serviceBundle................................................................................................................................... 3-17
serviceAction ................................................................................................................................... 3-18
querySpawningLogic...................................................................................................................... 3-18
Manually Deploying SRT Data .......................................................................................................... 3-19
External Adapters .................................................................................................................................. 3-20
JDBCAdapter ................................................................................................................................... 3-20
Class Name ............................................................................................................................... 3-21
Parameters................................................................................................................................. 3-21
Example..................................................................................................................................... 3-21
BSF Adapter ..................................................................................................................................... 3-21
Class Name ............................................................................................................................... 3-21
Parameters................................................................................................................................. 3-21
iv
A Sample XML Files, Schemas, and Transformations
Sample activationModel.xml ................................................................................................................ A-1
Sample srt.xml.......................................................................................................................................... A-2
Sample translation.xml .......................................................................................................................... A-8
Sample translation.xslt........................................................................................................................... A-9
Sample Usage of XML and XPATH Parameters .............................................................................. A-10

v
Preface
This guide provides an overview of Oracle Communications ASAP Service Request
Translator (SRT), contains instructions for installing SRT, and describes its
components.
Audience
This document is intended for system administrators, system integrators, and other
individuals who need to maintain and work with ASAP.
Related Documents
For more information, see the following documents in the ASAP documentation set:
■ Oracle Communications ASAP Release Notes
■ Oracle Communications ASAP Concepts
■ Oracle Communications ASAP Installation Guide
■ Oracle Communications ASAP System Administrator's Guide
■ Oracle Communications ASAP Order Control Application User's Guide
■ Oracle Communications ASAP Server Configuration Guide
■ Oracle Communications ASAP Security Guide
■ Oracle Communications ASAP Cartridge Development Guide
■ Oracle Communications ASAP Developer’s Guide
Note: To download the Oracle Communications ASAP Developer’s
Guide from the Oracle software delivery Web site, you must select
Oracle Communications Service Activation Developer
Documentation Pack. You can visit the Oracle software delivery Web
site at:
http://edelivery.oracle.com
vi
1
The Service Request Translator 1-1
1The Service Request Translator
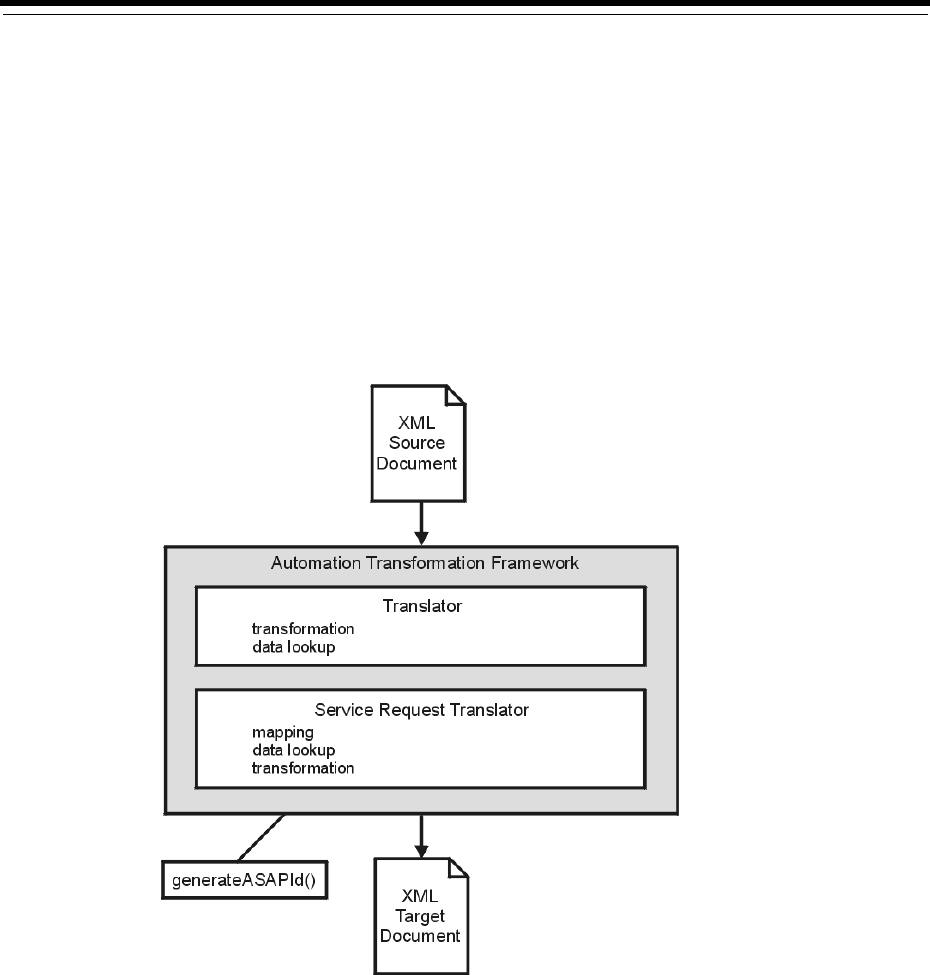
The Oracle Communications ASAP Service Request Translator (SRT) enables a variety
of tasks within a transformation computation, including mapping, data lookup, and
message transformation. Mapping tasks allow upstream requests to be decomposed
into one or more downstream requests. Data lookup functions can involve retrieving
data from external systems (such as databases). Transformation actions can involve
presentation formatting. The SRT is triggered by an XML source document and
generates an XML target document as its output.
Figure 1–1 Service Request Translator Context
Process Overview
Figure 1–2 illustrates an end-to-end process flow for a service activation in which the
SRT provisions a service.

Process Overview
1-2 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
Figure 1–2 SRT Process Flow
1. A customer service representative (CSR) receives a request.
2. The CSR creates a service order and enters it into the customer relationship
management (CRM) system. The service order includes information about the
subscriber and the selected services.
3. The CRM submits the service order to the Enterprise Application Integration
(EAI).
4. Other Operations Support Systems (OSS)/ Business Support Systems (BSS)
interact with the EAI to process the order and contribute additional provisioning
information to the order. For example, an order may include the following
information before it is submitted to ASAP:
■ MSISDN
■ IMSI (SIM details)
■ GSM bearer service details
■ Supplementary services list (CFD, CWT)
■ KI (SIM details)
■ Algorithm (SIM details)
■ Carrier Code
■ Profile
■ OIC
■ Welcome message

Process Overview
The Service Request Translator 1-3
5.
The SRT receives notification from the upstream EAI bus that a message is
available and an order is ready to be processed. The SRT determines that this
notification represents a new service order.
6. The message headers are saved in the database and managed by the SRT
application logic. The actual Java Message Service (JMS) message (including
headers and payload) is saved in the database by Oracle WebLogic Server, by
configuring the JMS destination (in this case, a queue) to be saved in the database.
The system translates the new service order by performing the following actions:
■ ASAP creates a new work order template to handle the service order.
■ A new unique work order ID is generated by the system using either a field on
the incoming request or predefined custom logic. For example, if multiple
CRM systems are used, it may not be possible to find unique IDs from
incoming requests because each CRM system may generate duplicate IDs.
This possible duplication of IDs may make it difficult to correlate work order
IDs. However, the system can be configured to generate a new unique work
order ID based on the Originator work order property (to identify which CRM
system submitted the request) and the Service Order ID.
■ The system extracts each generic service from the incoming service order. For
each generic service, the system does the following:
– Executes optional custom logic (such as composing one or more ASAP
services based on a combination of input parameters and/or tokens and
places any derived ASAP services on the ASAP work order. For example:
"C_", action, service, technology, softwareLoad
– Determines if there are statically-defined ASAP service mappings,
executes any optional spawning logic for each (for example, if a network
element identifier was not present on the work order, a certain CSDL may
be excluded from the ASAP order), and places the appropriate ASAP
services on the ASAP work order.
– Executes optional custom logic for each statically-defined ASAP service
and places any derived ASAP services on the ASAP work order.
■ Using predefined mappings (including optional/required parameter
configurations), the system identifies the parameters associated with each
ASAP service that has been placed on the order and extracts values from the
parameters received on the service order. The ASAP parameters are added to
the ASAP work order. Incoming parameters are mapped to outgoing
parameters.
■ Using a predefined configuration, the system identifies the default values for
parameters whose values are not available on the generic service order. The
default values are added to the ASAP work order.
■ Using a predefined configuration, the system executes any custom logic that is
defined for any ASAP parameters. For example, network element ID
parameters (in this case having no incoming service order value) will have
preconfigured logic defined that will be used to retrieve a set of (possibly
indexed) network element IDs.

Process Overview
1-4 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
7.
After successfully receiving the generic service order, generating the ASAP work
order, and performing the service translation, the system submits the work order
to ASAP and waits for a response.
8. The system receives a response from ASAP indicating that the work order has
been successfully submitted.
9. The system notifies the EAI that the associated generic service order has been
successfully submitted to ASAP.
10. Externally (downstream), the ASAP work order is decomposed into atomic
actions.
11. The system receives notification from ASAP that the work order has either
succeeded or failed.
12. The system retrieves any related information/error messages associated with the
work order from ASAP.
13. The system notifies the EAI that the corresponding generic service order has either
succeeded or failed and provides the corresponding information/error message.
14. The EAI notifies the CRM of the success or failure of the order.
Note: If the data required to provision the service is not provided by
the original service request application, the SRT can retrieve data from
external systems other than the order entry or CRM system. You can
use these extensions to access external data from another system such
as an inventory system. For example, the extension could retrieve the
NE ID of a switch and then update a CSDL parameter.
Note: If the SRT goes down after saving the message context and
creating the work order in SARM, it is not necessary to send another
CreateOrderByValueRequest. After a message has been received from
upstream and the transformed createOrderByValueRequest has been
delivered to the Java SRP’s queue, that transaction is complete and
does not need to be repeated in the event of SRT failure. When the
SRT starts again, the next message will be an ASAP event. This event
will be picked up by SRT, the appropriate plug-in launched, the
context loaded from the database by using the work order ID, and
then a transformation of the event to the upstream’s format is
executed and delivered back upstream.
Note: If the SRT goes down while it is processing orderComplete or
OrderFailEvent, when the SRT starts back up, it will identify
unprocessed messages in the topic and will launch the appropriate
plug-in to handle these messages, as though the events had just been
delivered.

2
Installing the SRT 2-1
2Installing the SRT
This chapter describes how to install and uninstall, configure and unconfigure, deploy
and undeploy the Oracle Communications ASAP Service Request Translator (SRT).
The installation for the SRT consists of an ant build file in the install directory
SRT/install.xml.
When you use ant (supplied with the ASAP environment) to run the installation, you
can obtain help with the ant command as follows:
ant -projecthelp -buildfile install.xml
The project Help includes a description of the installation file, how to run it, and all
available targets.
Installing and Managing the SRT
Install the SRT by doing the following:
Installing the SRT
1. Go to the Oracle Web site:
https://edelivery.oracle.com
2. Download the ASAP.R7_2_0.BXXX.srt.tar file.
3. Put the ASAP.R7_2_0.bXXX.srt.tar file in ASAP_Home directory, where ASAP_
Home is the directory in which ASAP is installed.
4. Source the ASAP_Home/Environment_Profile.
5. Run the following command:
tar xvf ASAP.R7_2_0.BXXX.srt.tar
This creates two tar files srt.tar and srt_docs.tar.
6. Run the following command:
tar xvf srt.tar
This creates the SRT directory.
7. Go to the SRT directory.
8. Run the following command:
ant -buildfile install.xml

Installing and Managing the SRT
2-2 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
This runs the default 'install' target identified in install.xml. This command customizes
the SRT.ear file with the ASAP environment ID, creates all required resources, and
deploys the SRT into the Oracle WebLogic Server.
Other targets are listed in Table 2–1:
Table 2–2 lists resources created by the 'configure' target. If a target already exists, the
script will continue processing. These same resources will be deleted with the
'unconfigure' target, except for the JMSServer, which is assumed to have been created
as part of an ASAP installation.
Note: If you enabled SSL when you installed ASAP, SRT will also use
SSL.
Table 2–1 Ant Target
Ant Target Functionality
install Configures the Oracle WebLogic Server, customizes the SRT.ear file, and
deploys it to a server. Temporary files are deleted after completion. If no
targets are specified, the ant command default to this value.
uninstall Removes the SRT.ear file from the Oracle WebLogic Server, and deletes
Oracle WebLogic Server resources created during installation.
configure Creates resources on the Oracle WebLogic Server.
unconfigure Removes resources on the Oracle WebLogic Server.
deploy Deploys the SRT.
query Checks WebLogic resources for the SRT.
undeploy Undeploys the SRT
Table 2–2 Created Resources
Resource Name Resource JNDI Type Purpose
asap.env_id.JMSServer None. JMSServer Hosts all JMS queues and topics.
This is normally created by an
ASAP installation.
SRT.MessageQueue System.asap_envid.ApplicationType.
ServiceActivation.Application.1-0;7-2;
ASAP.Comp.SRT.MessageQueue
JMSQueue The SRT processes all messages
placed in this queue.
SRT.ResponseQueue System.asap_envid.ApplicationType.
ServiceActivation.Application.1-0;7-2;
ASAP.Comp.SRT.ResponseQueue
JMSQueue If 'reply-to' is not specified for
an inbound message, the
response will be placed in this
queue.
SRT.MessageErrorQueue System.asap_envid.ApplicationType.
ServiceActivation.Application.1-0;7-2;
ASAP.Comp.SRT.MessageErrorQueue
JMSQueue The queue that stores messages
from the SRTMessageQueue that
cannot be processed.
SRT.JSRPResponseQueue System.asap_envid.ApplicationType.
ServiceActivation.Application.1-0;7-2;
ASAP.Comp.SRT.JSRPResponseQueue
JMSQueue The queue that SRT uses to
listens for responses from the
JSRP.
SRT.EventErrorQueue System.asap_envid.ApplicationType.
ServiceActivation.Application.1-0;7-2;
ASAP.Comp.SRT.EventErrorQueue
JMSQueue The queue that stores messages
from the JSRPEventTopic that
cannot be processed.

Upgrading the SRT
Installing the SRT 2-3
Upgrading the SRT
To upgrade an existing SRT installation with a newer version, do the following:
1. Go to the Oracle Web site:
https://edelivery.oracle.com
2. Download the patch (for example, ASAP.R7_n_n.SRT.Bn.tar, where R7_n_n
represents the ASAP release and bn represents the build number).
3. Put the ASAP.R7_n_n.SRT.Bn.tar file in ASAP_Home directory, where ASAP_Home
is the directory in which ASAP is installed.
4. Source the ASAP_Home/Environment_Profile.
5. Un-tar the patch:
tar xvf patch
This creates two tar files srt.tar and srt_docs.tar.
6. Un-tar the srt.tar file.
tar xvf srt.tar
This creates the SRT directory.
7. Change the directory to the SRT directory:
cd ASAP_Home/SRT
8. Run the following command:
ant -buildfile install.xml undeploy
9. Run the following command:
ant -buildfile install.xml customize deploy clean

Upgrading the SRT
2-4 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide

3
Working with SRT Components 3-1
3Working with SRT Components
This chapter describes the end-to-end translation process, with particular emphasis on
the components of the translation that you must configure.
Translation Process
An example of a typical translation process follows:
1. A customer service representative (CSR) receives a request to add a new
subscriber with Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) bearer service,
several basic supplementary services such as call forwarding (CFD) and call
waiting (CWT) and voicemail service.
2. The CSR creates a service order and enters it into the customer relationship
management system (CRM). The service order includes information about the
subscriber and the services they have selected.
3. The CRM submits the service order to the Enterprise Application Integration
(EAI).
4. Other Operations Support Systems (OSS)/ Business Support Systems (BSS)
interact with the EAI to process the order and contribute additional provisioning
information to the order. For example, an order may include the following
information before it is submitted to ASAP:
■ MSISDN
■ IMSI (SIM details)
■ GSM bearer service details
■ Supplementary services list (CFD, CWT)
■ KI (SIM details)
■ Algorithm (SIM details)
■ Carrier Code
■ Profile
■ OIC
■ Welcome Message
5. The EAI publishes a message (XML document) containing the following
information:
■ The parameters listed above
■ Service bundle name or Service action name

Translation Process
3-2 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
■ Action (for example, ADD)
■ Provisioning parameters (label, value)
■ System ID
■ Work order properties such as due date and time, priority etc.
When an incoming message is published by the upstream system, it is received by the
SRT.MessageQueue and a service request order is created that will serve as the source
of the translation.
The following is an example of an incoming message.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<UPSTREAM_Order_Value xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<OrderLevelInfo>
<ApplicationClientId>Upstream</ApplicationClientId>
<ServiceOrderId>ADDFEAT</ServiceOrderId>
<ScheduleActivationDate>2005-01-13T12:00:00</ScheduleActivationDate>
<OrderType>ChangeSubscriberService</OrderType>
<PayMethod>Pre-Paid</PayMethod>
<SIM>
<!--The first 5 character of region (55555)-->
<IMSI>5555510007</IMSI>
<KI>0</KI>
<Algorithm>None</Algorithm>
</SIM>
<Old_SIM>
<Old_IMSI>5555510009</Old_IMSI>
<Old_KI>0</Old_KI>
<Old_Algorithm>String</Old_Algorithm>
</Old_SIM>
<OrderPriority>5</OrderPriority>
<ParentKey/>
<ExternalSystemId>ExternalSysId-Upstream</ExternalSystemId>
</OrderLevelInfo>
<Products>
<ProductCode>CW</ProductCode>
<ProductDescription>Add subscriber features</ProductDescription>
<Action>NEW</Action>
<MSISDN>6425259999</MSISDN>
<ServiceAttributes>
<AttributeName>3WC</AttributeName>
<AttributeValue>1</AttributeValue>
</ServiceAttributes>
<ServiceAttributes>
<AttributeName>CLI</AttributeName>
<AttributeValue>1</AttributeValue>
</ServiceAttributes>
<ServiceAttributes>
<AttributeName>CWT</AttributeName>
<AttributeValue>0</AttributeValue>
</ServiceAttributes>
<Old_MSISDN>0</Old_MSISDN>
<Profile>None</Profile>
<NetworkID>None</NetworkID>
</Products>
</UPSTREAM_Order_Value>
...

Translation Process
Working with SRT Components 3-3
Based on a value in the service request order (UPSTREAM_Order_Value in the
example), the SrtTranslation.xsd file is called to perform a translation. At this point,
the translation includes the work order’s header portion.
Work order headers are also mapped based on the mapping defined in the message
type. For example, if the incoming order contains a priority, purchase order number,
and due date, these values will be included in the translation, provided they are
incorporated in the SrtServiceModel.xsd file as lookups or are provided by means of a
translation. For more information on work order headers, refer to the ASAP work
order header and work order properties section of ASAP System Administrator’s Guide.
The headers that are populated are independent of the service actions selected to
appear on the work order.
In addition to work order headers, the SRT allows for any combination of service
bundle parameters to be used to compose ASAP work order header parameters (for
example, allowing for the upstream work order ID and external system ID to be used
to generate a work order ID).
Oracle Professional Services or other qualified personnel are responsible for
translations. Translations are defined in SrtTranslation.xsd. For more information, see
"SRT Translation".
Parameter mappings can be achieved by means of XSLT conversions or lookups.
Lookups are performed by external instance adaptors. See "External Adapters" for
more information.
After the Automation Transformation Framework produces the interim work order,
the order is passed to the SRT to perform additional mappings, data lookups, and
transformations. The interim work order is validated against the
SRTServiceActivation.xsd file. For more information on this schema, refer to SRT
Online Reference installed with the SRT software.
If the inbound work order contains a parameter that identifies a service bundle such as
bundle ID, order type, or product code, as in the previous example, the SRT generates
the service bundles and associated CSDLs (service actions) on the ASAP work order.
Inbound work orders can also contain service actions with parameter mappings and
lookup definitions, without the need to model these as a service bundle. This allows
the support of service actions directly during the translation of service orders from
upstream.
The basic format of the XML that is validated against the schema appears as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<srtServiceModel xmlns="http://www.metasolv.com/ServiceActivation/2004/
ServiceBundle" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.metasolv.com/ServiceActivation/2004/ ServiceBundle
C:\ASAP\srt\srtServiceModel.xsd">
<serviceBundle>
<serviceBundleActionName>String</serviceBundleActionName>
<serviceBundleSpawning>
<parameterName>Text</parameterName>
<parameterValue>Text</parameterValue>
</serviceBundleSpawning>
<description>String</description>
<serviceAction>
<serviceActionName>String</serviceActionName>
<serviceActionSpawningLogic>
<alwaysCondition>1</alwaysCondition>
<expression>Text</expression>

Translation Process
3-4 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
</serviceActionSpawningLogic>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>String</parameterName>
<parameterValue>String</parameterValue>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<includeOrderDataInResponse>true</includeOrderDataInResponse>
<description>String</description>
</serviceAction>
</serviceBundle>
<serviceAction>
<serviceActionName>C_CALLFWD_BUSY_ADD_POTS-OPTIONS</serviceActionName>
<serviceActionSpawning>
<parameterName>ServiceName</parameterName>
<parameterValue>CallForwardBusy</parameterValue>
</serviceActionSpawning>
<description/>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LINE</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LINE</parameterName>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>NE_ID</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>NEID</parameterName>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>NPA</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>NPA</parameterName>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>NXX</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>NXX</parameterName>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
</serviceAction>
<querySpawningLogic>
<northBoundMapping>
<parameterName>String</parameterName>
</northBoundMapping>
<returnDataOnParameter>
<regularExpression>String</regularExpression>
<evaluateCondition>true</evaluateCondition>
</returnDataOnParameter>
</querySpawningLogic>
</srtServiceModel>
A more detailed sample of the XML appears in "Sample srt.xml". See also "Configuring
srtServiceModel.xsd".
For detailed information on the schema, refer to SRT Online Reference.
For each service request on the service request order, the mapping definition is queried
for the ordered set of possible service actions. The SRT then evaluates the spawning
logic of each service action for input parameters (contained on the service request
source). All true evaluations become service actions on the work order. All false

Translation Process
Working with SRT Components 3-5
actions are not added to the order. The service request must conform to
srtServiceModel.xsd schema.
After the SRT has determined all work order service actions, the SRT performs
parameter mapping. The SRT obtains all required and optional parameters from the
service request source and adds them to the work order. If a parameter has no value,
but a default is defined in srtServiceModel.xsd, the default is used. If there is no
default for a missing required parameter, this is considered a translation error.
Once the mapping has completed, an orderValueRequest is created and is posted to
the JSRP RequestQueue.
You need to ensure that the services (CSDLs and ASDLs) contained in the work order
conform to the content and structure set out in the ServiceModel.xsd schema.
ServiceModel.xsd defines the content and structure of one or more ServiceModel.xml
files. This file ensures that the element hierarchy and document structure of
ServiceModel.xml are correct and ensures element and attribute content adheres to the
defined datatype.
ServiceModel.xsd contains the elements and structure to define:
■ Network actions (ASDLs) and their associated rollback conditions, parameters,
and associated devices/software loads.
■ Device mappings (atomicDeviceMap), which provide a type definition to map
ASDLs to network element types.
■ CSDLs and their associated rollback conditions, priorities, provisioning events,
and mappings to ASDLs.

Translation Process
3-6 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
Figure 3–1 ServiceModel.xsd
ServiceModel.xsd is fully annotated. Online documentation related to this schema is
located in ASAP Online Reference. Detailed instructions on constructing a valid service
model are contained in ASAP System Administrator’s Guide. The ASAP_
Home/samples/sadt directory contains sample service models.
The XML files you create that contain the service models can have any name, provided
the <ServiceModel> element in the activation model deployment descriptor
(activation-model.xml) correctly references it.

SRT and SRP Message Queues
Working with SRT Components 3-7
SRT and SRP Message Queues
The processing of messages to and from the SRT and SRP involves the message queues
illustrated in Figure 3–2.
Figure 3–2 Message Queues
The SRT and SRP process messages as follows:
1. The upstream XML is received in the SRT.MessageQueue (1). If the message is
flawed, an error message is sent to the MessageErrorQueue (10).
2. SRT creates a CreateOrderByValueRequest, which is sent to the SRP (2).
3. The SRP sends the request to the SARM (3), which acknowledges the request.
4. The SRP sends a CreateOrderByValueResponse to the SRT.JSRPResponse queue
(4).
5. The response is processed by the SRT (5) and is passed to the SRT.ResponseQueue
(6).
Note: SRT orders the service bundles (that is, CSDLs) according to
the order of service request, rather than the configuration in the SRT.
If CSDL level/priority is specified for an individual CSDL, the SARM
still adjusts the CSDL execution order. Therefore, in order to ensure
the execution of service bundles, CSDL level should not be used when
modelling CSDLs.

Logging with log4j
3-8 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
6.
All I/O events from the SARM that are sent to the SRP’s XVTEventTopic (7). These
events include soft error events, rollback events, timeout events, failure events,
and complete events, among others.
7. These events are sent to the SRT (8). Event errors are sent to the EventErrorQueue
(9).
Logging with log4j
Message logging in ASAP and the SRT is performed through log4j. For details on how
to manage logging settings, refer to ASAP System Administrator’s Guide.
Configuring Event Templates
Extended information such as work order properties, information parameters, global
work order parameters, and CSDL return parameters can be returned on an ASAP
event. The details returned are controlled by template entries.
For more information refer to the descriptions of the tbl_event_dataset, tbl_event_
template, and srt_header_mapping tables in ASAP Developer’s Guide.
Templates and parameters that are defined in the tbl_event_dataset and tbl_event_
template tables are referenced as XPaths in the srt_header_mapping table. The SRT
iterates through the table entries and runs the configured XPaths. The returned
name/value pairs are added to the JMS header properties.
To configure the event templates to be applied to events and actions from the SRT,
specify XPaths as in the examples below.
Examples
To return a specific information parameter on all event types, create a record with
values similar to the following:
Name: 'IMSI'
Value:
/*[name()=mslv-sa:completeEvent]//extendedWoProperties/extendedWoProperty[na
me='IMSI']/value
To return all extendedWoProperties on a completed event, create a record with values
similar to the following:
Name: /*[name()=mslv-sa:completeEvent]//extendedWoProperties//name
Value: /*[name()=mslv-sa:completeEvent]//extendedWoProperties//value
SRT Translation
SrtTranslation.xsd enables Oracle Professional Services personnel or other users to
specify the mapping logic between the parameters contained in upstream XML files
and those required for srtServiceModel.xsd. The parameters included in
SrtTranslation.xsd must match those referenced in the XML service activation schema.

SRT Translation
Working with SRT Components 3-9
Figure 3–3 SRT Translation
Sample SrtTranslation.xsd
The translation takes the form of an XSLT transformation (identified in
<translationScript>translation.xslt</translationScript> below). This translation
produces an interim XML that is then passed to the SRT. This interim XML contains
work order header information. The SRT initializes an ASAP work order and
populates the ASAP work order header information using the SRT work order header
and, in some cases, the SRT work order parameters that are pertinent to the
provisioning process. In the previous example, work order header parameters are
represented in the <OrderLevelInfo> element. As well, the <translationScript> element
references the XSLT conversion, and the <lookup> elements identify the external
adaptors. For more information, see "External Adapters".
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<northBoundIntegration
xmlns="http://www.metasolv.com/ServiceActivation/2004/Translation"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.metasolv.com/ServiceActivation/2004/Translation
C:\ASAP\srt\SrtTranslation.xsd">
<translation>

XSLT Conversions
3-10 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
<translationName>Text</translationName>
<translationScript>translation.xslt</translationScript>
<translationDispatch>
<xpath>
<xpath>//cm:ApplicationClientID</xpath>
1
<xpathReturn>Upstream</xpathReturn>
</xpath>
</JMSHeader>
</translationDispatch>
</translation>
<externalMethodLibrary>
<fileName>Text</fileName>
<libraryName>Text</libraryName>
<type enabled="true" id="String">
<sql>Text</sql>
</type>
</externalMethodLibrary>
<lookup>
<lookupName>Text</lookupName>
<lookupType>Text</lookupType>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>Text</parameterName>
<parameterValue>Text</parameterValue>
</inputParameter>
<outputParameter>
<parameterName>Text</parameterName>
<xpath>Text</xpath>
</outputParameter>
<cache id="String">
<scope>NODE</scope>
<timeout>60000</timeout>
<maxSize>100</maxSize>
</cache>
</lookup>
</northBoundIntegration>
XSLT Conversions
XSLT conversions enable XML transformations by means of an XSLT stylesheet. The
XSLT stylesheet takes the input XML document and converts it into an output XML
document.
The XSLT conversion produces a document that conforms to the
SRTServiceActivation.xsd schema.
The XSLT stylesheet identifies the following:
■ translationName – A unique name given to the translation script as an identifier.
■ translationScript – The XSLT file that implements the translation. This file must be
included in the SAR file under SRT/Translations.
■ translationDispatch – The condition under which this translation is applied to the
XML upstream document. It can either be based on a JMSHeader or be based on
an XPath in the upstream document.
1
Ensure that the XPath contains a namespace prefix for use with the incoming schema
(represented here by cm:).

XSLT Conversions
Working with SRT Components 3-11
Sample Transformation
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/products/oss/xml/ServiceActivation"
xmlns:sa="http://java.sun.com/products/oss/xml/ServiceActivation"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mslv-sa="http://www.metasolv.com/oss/ServiceActivation/2003"
xmlns:co="http://java.sun.com/products/oss/xml/Common"
xmlns:fo="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Format">
<xsl:output method="xml" indent="yes" standalone="yes" media-type="xml"/>
<xsl:template match="UPSTREAM_Order_Value">
2
<createOrderByValueRequest
3
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/products/oss/xml/ServiceActivation"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mslv-sa="http://www.metasolv.com/oss/ServiceActivation/2003"
xmlns:co="http://java.sun.com/products/oss/xml/Common">
<orderValue xsi:type="mslv-sa:ASAPOrderValue">
<apiClientId>SRT</apiClientId>
<orderKey>
<co:applicationContext>
<co:factoryClass/>
<co:url/>
<co:systemProperties/>
</co:applicationContext>
<co:applicationDN>System/ENV_
ID/ApplicationType/ServiceActivation/Application/1-0;4-7;ASAP/Comp/</co:applicatio
nDN>
<co:type>javax.oss.order.CreateOrderValue</co:type>
<primaryKey>
<xsl:value-of select="//@serviceOrderId"/>
4
</primaryKey>
</orderKey>
<priority>3</priority>
<requestedCompletionDate>2003-06-11T12:00:00</requestedCompletionDate>
5
<services>
<parameter>
<name>NE_ID</name>
6
<value>TOR_REM2</value>
</parameter>
<parameter>
<name>DN</name>
7
<value>
<xsl:value-of select="//number"/>
</value>
</parameter>
<parameter>
<name>LDATA</name>
<value>236</value>
2
Referenced in the <translationDispatch> element in SrtTranslation.xsd.
3
The action identified by the interim work order to be processed by the JSRP.
4
Extracts the serviceOrderId from the incoming work order to serve as the primary key for the
ASAP work order.
5
If <requestedCompletionDate> is set, you do not need to send <startOrderByKeyRequest>;
ASAP will start the order automatically when <requestedCompeltionDate> is due. If
<requestedCompletionDate> is not set, you have to send <startOrderByKeyRequest> to start
the order.
6
The default NE_ID provided to the ASAP work order by this transformation for this service.
7
The value for DN, required by the ASAP work order, is extracted from the incoming work
order’s number parameter.

XSLT Conversions
3-12 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
</parameter>
<parameter>
<name>LCC</name>
<value>1</value>
</parameter>
<parameter>
<name>LTG</name>
<value>1</value>
</parameter>
<parameter>
<name>LEN</name>
<value>
<mslv-sa:value>
<xsl:value-of select="//len"/>
</mslv-sa:value>
</value>
</parameter>
</services>
...
The complete sample XSLT is located on "Sample translation.xslt".
Lookups
If the incoming XML does not contain the required parameters, you can include
lookups in SrtTranslation.xsd. For example, if the incoming work order does not
include the parameter NE_ID, a lookup can determine the NE_ID based on another
value on the work order, such as the IMSI.
■ lookupName – A unique lookup name.
■ lookupType – The lookup type. Can be SQL or Javascript or any other fully
qualified Java class name.
■ inputParameter – Defines the name a parameter will be given when passed to the
lookup and its value. These parameters can either be statically defined or
dynamically derived from other lookups or the upstream order.
■ outputParameter – The parameter that is the result of the lookup and the XPath to
use on the output of the lookup.
■ cache – Identifies the scope, timeout, and maximum size (in MB) of the lookup
results.
Three levels of cache are supported and set using the scope child element
■ NONE: External instances are not cached.
■ NODE: (default) Lookup results are cached at the order level. This means the
same lookup will be performed only once regardless of how many times it is
called in the order. This setting is useful if it is moderately expensive to
retrieve the external instance and the field referencing the external instance is
a multi-instance node. Cached instances are only reused across multi-instance
nodes if the actual resolved values of all parameters are identical and the
lookup adapter class is the same.
■ SYSTEM: External instances are cached and reused system wide. This is useful
if retrieving the external instance is expensive and it is performed frequently.
Cached instances results are only reused if the actual resolved values of all
parameters are identical and the lookup adapter class is the same.
If <scope> is set to SYSTEM, two additional elements are supported. <timeout> is
the number of milliseconds for which a cached external instance is valid.

XSLT Conversions
Working with SRT Components 3-13
<maxSize> is the maximum number of actual entries in the cache that will be
maintained at any one time for this defined external instance. The default value for
<timeout> is 15000 (15 seconds). The default value for <maxSize> is 50.
The SRT supports the splitting and concatenation of upstream parameters. Each
lookup input parameter has an attribute sourceDocument, which indicates to the SRT
which XML document source to use when resolving the input parameter value. If
multiple lookups are chained together, the SRT ensures they are executed in correct
sequence. The sourceDocument attribute defaults to ASAP_SRT_ORDER.
The <lookupParameterName> element indicates where to perform the lookup. This
element can contain the value ASAP_SRT_ORDER or a lookup instance name.
The InputParameterType as defined in SrtTranslation.xsd appears as follows:
<xs:complexType name="InputParameterType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="parameterName">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The name used to pass this parameter to the
lookup implementation</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:choice>
<xs:element name="parameterValue">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A static value for the
parameter.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="lookupParameterName">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The name of a output parameter from either
another lookup or the order.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:attribute name="sourceDocument" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:element>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
The following is an example of SrtTranslation.xsd with multiple lookups chained
together.
HOST_CLLI_LOOKUP is an SQL type lookup that takes one input parameter,
NPANXX_CLLI, for its select SQL statement.
NPANXX_CLLI is the lookup result from NPANXX_CLLI_LOOKUP, which will
concatenate the two input parameters NPANXX and CLLI.
NPANXX is the result from NPANXX_LOOKUP, and the CLLI is coming from order
data parameter NE_ID.
NPANXX_LOOKUP takes the NPA and NXX from NPA_LOOKUP and NXX_
LOOKUP and concatenates them as one single value. The NPA is the lookup result
from NPA_LOOKUP and NXX is the lookup result from NXX_LOOKUP. Both of these
are substrings from the order data parameter PHONE. At the end of lookup execution,
the value will be populated back the order data parameter name HOST_CLLI.
<northBoundIntegration xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.metasolv.com/ServiceActivation/2004/Translation"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="C:\parameterMap.xsd">

XSLT Conversions
3-14 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
<translation>
<translationName>POTSTranslation</translationName>
<translationScript>POTSTranslation.xslt</translationScript>
<translationDispatch>
<xpath>
<xpath>//@name</xpath>
<xpathReturn>POTS-Sample</xpathReturn>
</xpath>
</translationDispatch>
</translation>
<lookup>
<lookupName>NPA_LOOKUP</lookupName>
<lookupType>XPATH</lookupType>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>xpath:function</parameterName>
<parameterValue>substring-before</parameterValue>
</inputParameter>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>in:1</parameterName>
<lookupParameterName sourceDocument="ASAP_SRT_
ORDER">TELEPHONE</lookupParameterName>
</inputParameter>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>in:2</parameterName>
<parameterValue>3</parameterValue>
</inputParameter>
<outputParameter>
<parameterName>NPA</parameterName>
<xpath>/result/text()</xpath>
</outputParameter>
<cache id="NPA_LOOKUP_cache">
<scope>NODE</scope>
<timeout></timeout>
<maxSize></maxSize>
</cache>
</lookup>
<lookup>
<lookupName>NXX_LOOKUP</lookupName>
<lookupType>XPATH</lookupType>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>xpath:function</parameterName>
<parameterValue>substring</parameterValue>
</inputParameter>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>in:1</parameterName>
<lookupParameterName sourceDocument="ASAP_SRT_
ORDER">TELEPHONE</lookupParameterName>
</inputParameter>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>in:2</parameterName>
<parameterValue>3</parameterValue>
</inputParameter>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>in:3</parameterName>
<parameterValue>3</parameterValue>
</inputParameter>
<outputParameter>
<parameterName>NXX</parameterName>
<xpath>/result/text()</xpath>
</outputParameter>

XSLT Conversions
Working with SRT Components 3-15
<cache id="NXX_LOOKUP_cache">
<scope>NODE</scope>
<timeout></timeout>
<maxSize></maxSize>
</cache>
</lookup>
<lookup>
<lookupName>NPANXX_LOOKUP</lookupName>
<lookupType>XPATH</lookupType>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>xpath:function</parameterName>
<parameterValue>concat</parameterValue>
</inputParameter>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>in:1</parameterName>
<lookupParameterName sourceDocument="NPA_LOOKUP">NPA</lookupParameterName>
</inputParameter>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>in:2</parameterName>
<lookupParameterName source-document="NXX_LOOKUP">NXX</lookupParameterName>
</inputParameter>
<outputParameter>
<parameterName>NPANXX</parameterName>
<xpath>/result/text()</xpath>
</outputParameter>
<cache id="NPANXX_LOOKUP_cache">
<scope>NODE</scope>
<timeout></timeout>
<maxSize></maxSize>
</cache>
</lookup>
<lookup>
<lookupName>NPANXX_CLLI_LOOKUP</lookupName>
<lookupType>XPATH</lookupType>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>xpath:function</parameterName>
<parameterValue>concat</parameterValue>
</inputParameter>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>in:1</parameterName>
<lookupParameterName sourceDocument="NPANXX_
LOOKUP">NPANXX</lookupParameterName>
</inputParameter>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>in:2</parameterName>
<lookupParameterName sourceDocument="ASAP_SRT_ORDER">NE_
ID</lookupParameterName>
</inputParameter>
<outputParameter>
<parameterName>NPANXX_CLLI</parameterName>
<xpath>/result/text()</xpath>
</outputParameter>
<cache id="NPA_LOOKUP_cache">
<scope>NODE</scope>
<timeout></timeout>
<maxSize></maxSize>
</cache>
</lookup>
<lookup>
<lookupName>HOST_CLLI_LOOKUP</lookupName>

Configuring srtServiceModel.xsd
3-16 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
<lookupType>SQL</lookupType>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>jdbc:sqlStatement</parameterName>
<parameterValue>SELECT HOST_CLLI FROM tbl_clli_route WHERE NPANXX_CLLI =
?</parameterValue>
</inputParameter>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>jdbc:dataSource</parameterName>
<parameterValue>System.en08.ApplicationType.ServiceActivation.Application.1-0;5-0;
ASAP.Comp.SARMDataSource</parameterValue>
</inputParameter>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>in:1</parameterName>
<lookupParameterName sourceDocument="NPANXX_CLLI_LOOKUP">NPANXX_
CLLI</lookupParameterName>
</inputParameter>
<outputParameter>
<parameterName>HOST_CLLI</parameterName>
<xpath>/sql/row-set/row/col</xpath>
</outputParameter>
<cache id="HOST_CLLI_LOOKUP_cache">
<scope>NODE</scope>
<timeout></timeout>
<maxSize></maxSize>
</cache>
</lookup>
</northBoundIntegration>
Configuring srtServiceModel.xsd
The srtServiceModel.xsd schema identifies the service bundles, service actions
(CSDLs), and spawning logic.

Configuring srtServiceModel.xsd
Working with SRT Components 3-17
Figure 3–4 srtServiceModel.xsd Schema
serviceBundle
The <serviceBundle> element is described as follows:
■ serviceBundleName – The name of the service bundle.
■ serviceBundleSpawning – Identifies the condition under which this service bundle
will be added to the work order. The condition is identified by the following:
■ parameterName
■ parameterValue
■ description – A description of the service bundle.
■ serviceAction – One or more service actions (CSDLs) that are included in the
service bundle.
■ serviceActionName – The name of the service action (CSDL).

Configuring srtServiceModel.xsd
3-18 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
■ serviceActionSpawningLogic – For each CSDL associated with a service
bundle, the SRT verifies whether the CSDL should be spawned.
When the SRT receives a service bundle and its associated service actions, the
SRT refers to the following conditional logic:
– Always generate the service action – The SRT always generates the service
action for this service action.
– Generate service action if parameter defined – The SRT generates a
particular service action only if the stated parameter is defined.
– Generate service action if parameter not defined – The SRT generates a
particular service action only if the stated parameter is not defined.
– Generate service action if parameter defined and equal – The SRT
generates a particular service action only if the stated parameter is defined
and has a particular parameter value.
■ serviceActionParameterMapping – Maps the parameter name on the interim
order to the parameter name on the service action.
■ includeOrderDataInResponse – If TRUE, order data is included in SRT
responses.
serviceAction
The <serviceAction> element is used to support service actions (CSDLs) directly
during the translation of service orders from upstream.
■ serviceActionName – The name of the service action.
■ serviceActionSpawning – Identifies the condition under which this service action
will be added to the work order. The condition is identified by the following:
■ parameterName
■ parameterValue
■ description – A description of the service action.
■ serviceActionParameterMapping – Maps the parameter name on the interim order
to the parameter name on the service action.
■ includeOrderDataInResponse – If TRUE, order data is included in SRT responses.
querySpawningLogic
The <querySpawningLogic> element is described as follows:
■ northBoundMapping – Enables the querying of completed orders for additional
work order information.
■ parameterName – A parameter on the work order that identifies whether
work order data is returned to an upstream system on completion.
■ returnDataOnParameter – Enables the querying of completed orders for additional
work order information provided the evaluate condition is met.
■ regularExpression – The condition that must be met in order for the data on
the work order to be returned to an upstream system.
■ evaluateCondition – The regularExpression must evaluate to this condition for
the data on the work order to be returned to an upstream system.

Manually Deploying SRT Data
Working with SRT Components 3-19
A sample service model appears as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<srtServiceModel
xmlns="http://www.metasolv.com/ServiceActivation/2004/ServiceBundle"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.metasolv.com/ServiceActivation/2004/ServiceBundle
C:\ASAP\srt\srtServiceModel.xsd">
<serviceBundle>
<serviceBundleActionName>String</serviceBundleActionName>
<serviceBundleSpawning>
<parameterName>Text</parameterName>
<parameterValue>Text</parameterValue>
</serviceBundleSpawning>
<description>String</description>
<serviceAction>
<serviceActionName>String</serviceActionName>
<serviceActionSpawningLogic>
<alwaysCondition>1</alwaysCondition>
<expression>Text</expression>
</serviceActionSpawningLogic>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>String</parameterName>
<parameterValue>String</parameterValue>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<includeOrderDataInResponse>true</includeOrderDataInResponse>
<description>String</description>
</serviceAction>
</serviceBundle>
<querySpawningLogic>
<northBoundMapping>
<parameterName>String</parameterName>
</northBoundMapping>
<returnDataOnParameter>
<regularExpression>String</regularExpression>
<evaluateCondition>true</evaluateCondition>
</returnDataOnParameter>
</querySpawningLogic>
</srtServiceModel>
Manually Deploying SRT Data
This section describes how to deploy data that includes SRT configuration
information.
The deployment manager manually creates the directory structure on a UNIX machine
and places relevant SRT configuration files within the directory structure as follows:
/META-INF/activation-model.xml // contains references to the location of
files
/SRT/srt.xml // populate core SRT tables and order translation bindings
/SRT/SQL/Deploy/ // SQL scripts for table creation and insertion of custom data
/SRT/SQL/Undeploy/ // SQL scripts for custom table/data deletion
/SRT/Scripts/ // custom scripts
/SRT/Translations/ // contains all xslt translations
/SRT/java/lib/ // custom java lookups (jar files)
/SRT/java/src/ // source code for custom java lookups
/SRT/translation.xml

External Adapters
3-20 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
The activation_model.xml file identifies the components contained in the service
activation archive to be deployed by the SADT. These components include, at a
minimum, one or more service models, and the required State Tables or JInterpreter
provisioning classes.
The SRT.xml file is an XML document that conforms to srtServiceModel.xsd.
The translation.xml file conforms to SrtTranslation.xsd.
When the directory structure has been created, the deployment manager runs the
createSAR script, providing a path to the directory structure as a command-line
argument.
The command is:
CreateSar [-help] sar_file_dir
The current directory must be the base from which the SAR file is made and it is the
parent directory of the vendor directory. sar_file_dir specifies where you want to put
the SAR file you have created. The SAR file name is generated based on the name in
activationmodel.xml.
The createSAR script first checks for the existence of the
/META-INF/activation-model.xml file to determine whether it references a specific
path. If no path is found, the /SRT directory is assumed to be in the root directory of
the specified path. A SAR file containing this optional path and directory structure are
created. The /META-INF/activation-model.xml file is always placed in the SAR file
off the root directory.
After the SAR file has been created, the deployment manager deploys the SAR file to
ASAP using the SADT by providing the path to the SAR file and the SAR file name.
The SADT extracts configuration data from the SAR file by first checking for the
existence of /META-INF/activation-model.xml inside the SAR file to see if it
references a specific path. If no path is found, the /SRT directory is assumed to be in
the root of the SAR.
The SADT takes the following subsequent actions:
■ Populates core SRT database tables and load translation bindings using the srt.xml
file
■ Runs any custom sql scripts
■ Loads custom java scripts
■ Loads translations
■ Loads custom Java lookups
The SRT cache is automatically updated when it receives a new work order and a dirty
cache is detected.
For more information on the SADT, refer to ASAP System Administrator’s Guide.
External Adapters
This section provides details on the external adapters provided with SRT.
JDBCAdapter
This adapter lets you integrate an external system with SRT to perform lookups
against the database. This adapter runs SQL and uses the results in a translation.

External Adapters
Working with SRT Components 3-21
Class Name
com.mslv.view.rule.adapter.JDBCAdapter
Parameters
jdbc:sqlStatement
■ The SQL statement to execute. Parameter placeholders can be indicated using a
question mark (?). For example: SELECT NE_ID FROM NE_LOOKUP WHERE
REGION = '?'. Each parameter can be passed with the name in:x, where x is the
position of the parameter, starting from 1.
jdbc:dataSource
■ The JNDI name of the JDBC datasource in Oracle WebLogic Server.
in:x
■ The xth input parameter. Parameter numbering starts at 1.
Example
<LookupType>
<lookupName>NE ID Lookup</lookupName>
<lookupType>SQL</lookupType>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>jdbc:sqlStatement</parameterName>
<parameterValue>SELECT NE_ID FROM NE_ID_LOOKUP WHERE REGION = ? AND NE_TYPE
= ?</parameterValue>
</inputParameter>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>jdbc:dataSource</parameterName>
<parameterValue>com/sample/jdbc/CustomDataJDBC</parameterValue>
</inputParameter>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>in:1</parameterName>
<lookupParameterName>REGION</lookupParameterName>
</inputParameter>
<inputParameter>
<parameterName>in:2</parameterName>
<lookupParameterName>HLR</lookupParameterName>
</inputParameter>
<outputParameter>
<parameterName>NE_ID</parameterName>
<xpath>NE_ID_LOOKUP/sql/row-set/row/NE_ID</xpath>
</outputParameter>
</LookupType>
BSF Adapter
This adapter lets you integrate the SRT with JavaScript to perform lookups,
calculations, or validations against information that is located in the service request.
This adapter runs an SRT server extension and uses the results as an external instance.
Class Name
com.mslv.view.rule.adapter.BSFAdapter
Parameters
bsf:scriptEngine
■ The name of script engine.
bsf:script

External Adapters
3-22 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
■ The file name of the script.
bsf:expression
■ The expression for the script (optional).
bsf:line
■ The line number of the script to start (optional).
bsf:column
■ The column number of the script to start (optional).
bsf:typeEnabled
■ The boolean value for BSF enable types.
bsf:nodeName
■ The node name to return.
bsf_return
■ The Boolean value to enable a return.
in:x
■ The xth input parameter. Parameters are for the JavaScript function and parameter
numbering starts at 1.
All other parameters are parameters for the JavaScript function.

A
Sample XML Files, Schemas, and Transformations A-1
ASample XML Files, Schemas, and
Transformations
This appendix contains the following:
■ Sample activationModel.xml
■ Sample srt.xml
■ Sample translation.xml
■ Sample translation.xslt
Sample activationModel.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<activationModel
xmlns="http://www.metasolv.com/ServiceActivation/2003/ActivationModel"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.metasolv.com/ServiceActivation/2003/ActivationModel
D:\ccm_databases\ASAP~sleung_windows\ASAP\jmx\xsd\SA_Archive.xsd" name="Nortel_
PASSPORT_3_0_ATM_FR">
<name>NORTEL,PASSPORT_3_0,PCR3.0,ATM_FR_QOS,1.0</name>
<description>Nortel ATM/FR PASSPORT_3_0 PCR3.0 Cartridges</description>
<vendor>Nortel</vendor>
<technology>PASSPORT_3_0</technology>
<softwareLoad>PCR3.0</softwareLoad>
<version>
<author>Nortel Networks</author>
<label>1.2</label>
<majorVersion>1</majorVersion>
<minorVersion>2</minorVersion>
<createDate>2001-11-30</createDate>
<validDuration>P1Y2M3DT10H30M</validDuration>
</version>
<component>
<serviceModel>Nortel/PASSPORT_3_0/common/service_model/atm_fr_
asdl.xml</serviceModel>
</component>
<component>
<serviceModel>Nortel/PASSPORT_3_0/atm_qos/service_model/atm_
csdl.xml</serviceModel>
</component>
<component>
<serviceModel>Nortel/PASSPORT_3_0/fr_qos/service_model/fr_
csdl.xml</serviceModel>
</component>

Sample srt.xml
A-2 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
<component>
<javaProvisioningFile>
<jarFile>Nortel/PASSPORT_3_0/common/java/lib/PP30Comm.jar</jarFile>
</javaProvisioningFile>
</component>
<component>
<cLibraryFile>Nortel/PASSPORT_3_
0/common/cpp/lib/libPP30Comm.so</cLibraryFile>
</component>
<role name="administrator">
<description>System Administrator</description>
</role>
</activationModel>
Sample srt.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<srtServiceModel xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="C:\Documents and
Settings\btang\Desktop\parameterMap.xsd">
<serviceBundle>
<serviceBundleActionName>POTS_BUNDLE_ADD_LINE</serviceBundleActionName>
<serviceBundleSpawning>
<parameterName>BUNDLE_ID</parameterName>
<parameterValue>POTS-1</parameterValue>
</serviceBundleSpawning>
<description>This Bundle Contains both POTS-1 and POTS-2</description>
<serviceAction>
<serviceActionName>C-ADD_POTS_LINE</serviceActionName>
<includeOrderDataInResponse>true</includeOrderDataInResponse>
<description>This is a basic Add Residential Line</description>
<serviceActionSpawningLogic>
<equalsCondition>
<parameterLabel>NE_ID</parameterLabel>
<parameterValue>TOR_REM1</parameterValue>
</equalsCondition>
</serviceActionSpawningLogic>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>NE_ID</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>NE_ID</parameterName>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>DN</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>DN</parameterName>
<defaultValue>6792727</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LATA</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LATA</parameterName>
<defaultValue>236</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LCC</parameterName>
<externalParameter>

Sample srt.xml
Sample XML Files, Schemas, and Transformations A-3
<parameterName>LTG</parameterName>
<defaultValue>1</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LTG</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LTG</parameterName>
<defaultValue>1</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LEN</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LEN</parameterName>
<defaultValue>1010101</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
</serviceAction>
<serviceAction>
<serviceActionName>C-ADD_POTS_LINE</serviceActionName>
<includeOrderDataInResponse>true</includeOrderDataInResponse>
<description>Add Line and Options Example</description>
<serviceActionSpawningLogic>
<alwaysCondition/>
<expression>NE_ID LIKE "TOR_REM2"</expression>
</serviceActionSpawningLogic>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>NE_ID</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>NE_ID</parameterName>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>DN</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>DN</parameterName>
<defaultValue>6792727</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LATA</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LATA</parameterName>
<defaultValue>236</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LCC</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LTG</parameterName>
<defaultValue>1</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LTG</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LTG</parameterName>
<defaultValue>1</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>

Sample srt.xml
A-4 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LEN</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LEN</parameterName>
<defaultValue>1010101</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>OPT1</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>option1</parameterName>
<defaultValue>CTR</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>OPT2</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>option2</parameterName>
<defaultValue>LCDR</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
</serviceAction>
</serviceBundle>
<serviceBundle>
<serviceBundleActionName>POTS_BUNDLE_ADD_LINE_
FAILED</serviceBundleActionName>
<serviceBundleSpawning>
<parameterName>BUNDLE_ID</parameterName>
<parameterValue>POTS-3</parameterValue>
</serviceBundleSpawning>
<description>POTS-3 Fail and Rollback Example</description>
<serviceAction>
<serviceActionName>C-ADD_POTS_LINE</serviceActionName>
<includeOrderDataInResponse>true</includeOrderDataInResponse>
<description>This Action will be failed and Rollback</description>
<serviceActionSpawningLogic>
<definedCondition>
<parameterName>NE_ID</parameterName>
</definedCondition>
</serviceActionSpawningLogic>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>NE_ID</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>NE_ID</parameterName>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>DN</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>DN</parameterName>
<defaultValue>6792727</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LATA</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LATA</parameterName>
<defaultValue>236</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>

Sample srt.xml
Sample XML Files, Schemas, and Transformations A-5
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LCC</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LTG</parameterName>
<defaultValue>1</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LTG</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LTG</parameterName>
<defaultValue>1</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LEN</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LEN</parameterName>
<defaultValue>1010101</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>OPT1</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>option2</parameterName>
<defaultValue>CTR</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>OPT2</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>option2</parameterName>
<defaultValue>3WC</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
</serviceAction>
</serviceBundle>
<serviceBundle>
<serviceBundleActionName>POTS_4_FAIL_AND_RETRY_
EXAMPLE</serviceBundleActionName>
<serviceBundleSpawning>
<parameterName>BUNDLE_ID</parameterName>
<parameterValue>POTS-4</parameterValue>
</serviceBundleSpawning>
<description>POTS-4 Fail and Retry Example</description>
<serviceAction>
<serviceActionName>C-ADD_POTS_LINE</serviceActionName>
<includeOrderDataInResponse>true</includeOrderDataInResponse>
<description>This Action will be failed and Retry</description>
<serviceActionSpawningLogic>
<alwaysCondition/>
<expression>DN = 6794747</expression>
</serviceActionSpawningLogic>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>NE_ID</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>NE_ID</parameterName>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>

Sample srt.xml
A-6 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>DN</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>DN</parameterName>
<defaultValue>6792727</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LATA</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LATA</parameterName>
<defaultValue>236</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LCC</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LTG</parameterName>
<defaultValue>1</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LTG</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LTG</parameterName>
<defaultValue>1</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LEN</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LEN</parameterName>
<defaultValue>1010101</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>OPT1</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>option1</parameterName>
<defaultValue>CTR</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>OPT2</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>option2</parameterName>
<defaultValue>RETRY</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
</serviceAction>
</serviceBundle>
<serviceBundle>
<serviceBundleActionName>POTS_5_EXIT_MAINTENACE_MODE_FORCE_
DISCONNECT</serviceBundleActionName>
<serviceBundleSpawning>
<parameterName>BUNDLE_ID</parameterName>
<parameterValue>POTS-5</parameterValue>
</serviceBundleSpawning>
<description>Exit Maintenace Mode - Force Disconnect</description>

Sample srt.xml
Sample XML Files, Schemas, and Transformations A-7
<serviceAction>
<serviceActionName>C-ADD_POTS_LINE</serviceActionName>
<includeOrderDataInResponse>true</includeOrderDataInResponse>
<description>Exit Maintenace Mode - Force Disconnect</description>
<serviceActionSpawningLogic>
<equalsCondition>
<parameterLabel>NE_ID</parameterLabel>
<parameterValue>BEIJING</parameterValue>
</equalsCondition>
</serviceActionSpawningLogic>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>NE_ID</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>NE_ID</parameterName>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>DN</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>DN</parameterName>
<defaultValue>6792727</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LATA</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LATA</parameterName>
<defaultValue>236</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LCC</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LTG</parameterName>
<defaultValue>1</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LTG</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LTG</parameterName>
<defaultValue>1</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>LEN</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>LEN</parameterName>
<defaultValue>1010101</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>OPT1</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>OPT1</parameterName>
<defaultValue>CTR</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>OPT2</parameterName>

Sample translation.xml
A-8 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>OPT2</parameterName>
<defaultValue>MAINT</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
</serviceAction>
</serviceBundle>
<serviceBundle>
<serviceBundleActionName>RAW-1_SEND_A RAW_
COMMAND</serviceBundleActionName>
<serviceBundleSpawning>
<parameterName>BUNDLE_ID</parameterName>
<parameterValue>RAW-1</parameterValue>
</serviceBundleSpawning>
<description>Sends a Raw Command to the SERVORD DMS Prompt</description>
<serviceAction>
<serviceActionName>C-RAW_COMMAND</serviceActionName>
<includeOrderDataInResponse>true</includeOrderDataInResponse>
<description>Query all Unassigned DNs in a Particular DN
Range</description>
<serviceActionSpawningLogic>
<notDefinedCondition>
<parameterName>OPT1</parameterName>
</notDefinedCondition>
</serviceActionSpawningLogic>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>NE_ID</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>NE_ID</parameterName>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
<serviceActionParameterMapping>
<parameterName>RAW_CMD</parameterName>
<externalParameter>
<parameterName>RAW_CMD</parameterName>
<defaultValue>QDNSU R 5551000 5552000 ANCT S</defaultValue>
</externalParameter>
</serviceActionParameterMapping>
</serviceAction>
</serviceBundle>
</srtServiceModel>
Sample translation.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<northBoundIntegration xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="C:\parameterMap.xsd">
<translation>
<translationName>POTSTranslation</translationName>
<translationScript>POTSTranslation.xslt</translationScript>
<translationDispatch>
<xpath>
<xpath>//@name</xpath>
<xpathReturn>POTS-Sample</xpathReturn>
</xpath>
</translationDispatch>
</translation>
<instance name="NCName"/>

Sample translation.xslt
Sample XML Files, Schemas, and Transformations A-9
</northBoundIntegration>
Sample translation.xslt
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/products/oss/xml/ServiceActivation"
xmlns:sa="http://java.sun.com/products/oss/xml/ServiceActivation"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mslv-sa="http://www.metasolv.com/oss/ServiceActivation/2003"
xmlns:co="http://java.sun.com/products/oss/xml/Common"
xmlns:fo="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Format">
<xsl:output method="xml" indent="yes" standalone="yes" media-type="xml"/>
<xsl:template match="/">
<createOrderByValueRequest
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/products/oss/xml/ServiceActivation"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mslv-sa="http://www.metasolv.com/oss/ServiceActivation/2003"
xmlns:co="http://java.sun.com/products/oss/xml/Common">
<orderValue xsi:type="mslv-sa:ASAPOrderValue">
<apiClientId>SRT</apiClientId>
<orderKey>
<co:applicationContext>
<co:factoryClass/>
<co:url/>
<co:systemProperties/>
</co:applicationContext>
<co:applicationDN>System/ENV_
ID/ApplicationType/ServiceActivation/Application/1-0;4-6;ASAP/Comp/</co:applicatio
nDN>
<co:type>javax.oss.order.CreateOrderValue</co:type>
<primaryKey>
<xsl:value-of select="//@serviceOrderId"/>
</primaryKey>
</orderKey>
<priority>3</priority>
<requestedCompletionDate>2003-06-11T12:00:00</requestedCompletionDate>
<services>
<parameter>
<name>NE_ID</name>
<value>TOR_REM2</value>
</parameter>
<parameter>
<name>DN</name>
<value>
<xsl:value-of select="//number"/>
</value>
</parameter>
<parameter>
<name>LDATA</name>
<value>236</value>
</parameter>
<parameter>
<name>LCC</name>
<value>1</value>
</parameter>
<parameter>
<name>LTG</name>
<value>1</value>
</parameter>

Sample Usage of XML and XPATH Parameters
A-10 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
<parameter>
<name>LEN</name>
<value>
<mslv-sa:value>
<xsl:value-of select="//len"/>
</mslv-sa:value>
</value>
</parameter>
</services>
<mslv-sa:parentKey>
<co:applicationContext>
<co:factoryClass/>
<co:url/>
<co:systemProperties/>
</co:applicationContext>
<co:applicationDN/>
<co:type/>
<primaryKey/>
</mslv-sa:parentKey>
<mslv-sa:origin>MetaSolv</mslv-sa:origin>
<mslv-sa:organizationUnit>POTS</mslv-sa:organizationUnit>
<mslv-sa:batchGroup/>
<mslv-sa:rollbackState>rollback_not_
required</mslv-sa:rollbackState>
<mslv-sa:externalSystemId>MetaSolv-Pots</mslv-sa:externalSystemId>
<mslv-sa:processType>IMMEDIATE</mslv-sa:processType>
<mslv-sa:neId/>
<mslv-sa:srqAction>REMOVE</mslv-sa:srqAction>
<mslv-sa:infoParms/>
<mslv-sa:extendedWoProperties/>
</orderValue>
</createOrderByValueRequest>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Sample Usage of XML and XPATH Parameters
The <xmlValue> and <xpathValue> tags in SRTServiceActivation.xsd support XML
and XPATH parameters.
There are three ways of passing parameters to a cartridge:
1. When parameters are passed in input work order. For example, suppose you want
to pass the following work order.
<MetaSolv>
<MetaSolvRequest name="POTS">
<NE_ID_UNICO-HIN>E_UNICO-HIN_1-0_HOST</NE_ID_UNICO-HIN>
<TIME>2008-10-13T08:45:00</TIME>
<BUNDLEID>PRODUCT_VALUE</BUNDLEID>
<MSISDN>1234567890</MSISDN>
<NUMBER>6742727</NUMBER>
<LEN>1010202</LEN>
<XMLparm>
<X>123</X>
</XMLparm>
<XPATHparm>//XYZ</XPATHparm>
<NEWINDEX>//welcome</NEWINDEX>
<SCALARINDEX>14</SCALARINDEX>

Sample Usage of XML and XPATH Parameters
Sample XML Files, Schemas, and Transformations A-11
<INPARM>HOST_CLLI</INPARM>
<RETURN_DATA_PREFIX>
<x>dummywwww</x>
</RETURN_DATA_PREFIX>
</MetaSolvRequest>
</MetaSolv>
You want to send XMLparm, RETURN_DATA_PREFIX, and XPATHparm
parameters as XML and XPATH parameters respectively. For this, the cartridge
developer has to create an XSLT that can extract the value of the XML parameter
as an XML.
Following is an example of XSLT fragment containing XPATH expression for
extracting XML parameter:
<xmlValue>
<xsl:copy-of
select="/MetaSolv/MetaSolvRequest/XMLparm/self::node()"></xsl:copy-of>
</xmlValue>
Following is an example of XSLT fragment containing XPATH expression for
extracting XPATH parameter:
<xpathValue>
<xsl:value-of select="//XPATHparm"/>
</xpathValue>
2. When the value of XML and XPATH parameter is not available in the work order,
and some default value is defined in the cartridge, then the value defined in the
cartridge will be used while processing the work order.
3. The value of a parameter can also be fetched from lookup. If a lookup returns the
XML as a result, then you need to be careful while using the XPATHs on the
lookup. Currently, the XPATH expression is used only to fetch the result of the
lookup. This applies for XML and XPATH parameters too. Do not extend the
current behavior of the XPATH expression to extract a part of the result or modify
the result.

Sample Usage of XML and XPATH Parameters
A-12 ASAP Service Request Translator User's Guide
