
DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE
HEADQUARTERS, UNITED STATES MILITARY ENTRANCE PROCESSING COMMAND
2834 GREEN BAY ROAD, NORTH CHICAGO, ILLINOIS 60064-3091
*USMEPCOM Regulation
No. 40-1
Effective date: May 23, 2018
Medical Services
Medical Qualification Program
OFFICIAL:
J. Cunningham
Deputy Commander/Chief of Staff
DISTRIBUTION:
Unlimited. This Regulation is approved for public release.
Executive Summary. This regulation prescribes policy and procedures for administration of the United
States Military Entrance Processing Command (HQUSMEPCOM) Medical Qualification Program.
Applicability. This regulation applies to all elements of USMEPCOM and to the recruiting and liaison
personnel of all military components insofar as their duties relate to all aspects of applicant medical
processing required under this and related regulations.
Supplementation. Supplementation of this regulation is prohibited without prior approval from
Headquarters, United States Military Entrance Processing Command (HQ USMEPCOM), ATTN: J-3/5/7
MD, 2834 Green Bay Road, North Chicago, IL 60064-3091.
Suggested Improvements. The proponent agency of this regulation is HQ USMEPCOM, [J-3/5/7 MD].
Users are invited to send comments and suggested improvements on Department of the Army (DA) Form
2028, Recommended Changes to Publications and Blank Forms, or memorandum, to HQ USMEPCOM,
ATTN: J-3/5/7 MD, 2834 Green Bay Road, North Chicago, IL 60064-3091.
Internal Control Process. This regulation contains internal control provisions and provides an internal
control evaluation checklist, in Appendix B,
for use in conducting internal controls.
This regulation supersedes USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1, May 23, 2018. This regulation contains a
number of major revisions and must be reviewed in its entirety to have a clear understanding of all revisions.
CUNNINGHAM.J
OANNE.THERES.
1091128434
Digitally signed by
CUNNINGHAM.JOANNE.THE
RES.1091128434
Date: 2020.12.03 12:27:11
-06'00'

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
i
Table of Contents (TOC)
Chapter 1
General
Paragraph
Page
Purpose
1-1
1
References
1-2
1
Abbreviations and Terms
1-3
1
Responsibilities
1-4
1
General Policy
1-5
8
Use of Reserve and National Guard Personnel/Practitioners
1-6
8
MEPS Communication with J-3/5/7 MD
1-7
8
Chapter 2
Pre-Processing
Dial-A-Doc/Email-A-Doc Program
2-1
10
Completion of the DD Form 2807-2 for Prescreening of Applicants
2-2
10
Prescreen Catagories
2-3
15
Prescreen Tracking
2-4
16
Provider Review and Determination of Complex Prescreens
2-5
20
Review of the Prescreen During the Quality Review Process
2-6
22
VA and Other Disability Compensation
2-7
23
Entry-Level Separation
2-8
23
Prior Service Applicants
2-9
24
Temporary Disability Retirement List
2-10
24
No Medical Required Projection
2-11
25
Chapter 3
Medical Processing Administration
General
3-1
27
Use of Non-Medical Personnel
3-2
27
Special Category Processor
3-3
28
Same Day Processor
3-4
28
The 6-hour Applicant Processing Window
3-5
28
Medical Examination Consent and Chaperone Policy
3-6
29
Uncooperative or Disruptive Applicants
3-7
30
Deferring Medical Processing Prior to Completion
3-8
30
Access to the MEPS Medical Department
3-9
31
Medical Exception to Policy
3-10
33
Undergarments/Body Piercing
3-11
33
Medical Photography
3-12
34
Medical Packet Assembly
3-13
34
Chapter 4
Medical Check-in
Applicant Medical Check-in
4-1
36
Walk-In Applicants
4-2
36
Front Loading
4-3
37
Chapter 5
Medical Brief
Medical Brief
5-1
38

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
ii
Paragraph
Page
Chapter 6
Hearing Testing and Cerumen Removal
Hearing Testing Procedures
6-1
40
Conducting Repeat Audiograms
6-2
40
Profiling Hearing
6-3
41
Cerumen Removal
6-4
41
Chapter 7
Vision
Vision Screening Guidance
7-1
43
Screening for Undisclosed Contact Lenses
7-2
43
Color Vision Testing
7-3
44
Depth Perception Testing
7-4
46
Visual Acuity Testing
7-5
46
Non-Contact Tonometer
7-6
48
Refractive Eye Surgery Guidance
7-7
48
Vision Consults
7-8
48
Chapter 8
Measurement of Height/Weight/Body Fat Percentage/BMI/Vital Signs
Height/Weight Measurement
8-1
50
Body Fat Percentage Calculation
8-2
50
Body Mass Index Calculation
8-3
52
Courtsey Height/Weight/Body Fat Percentage Measurements
8-4
52
Special Considerations
8-5
52
Blood Pressure Measurement
8-6
53
Heart Rate Measurement
8-7
54
Temperature Measurement
8-8
55
Chapter 9
Clinical Laboratory Improvement Program
Clinical Laboratory Improvement Program
9-1
56
Chapter 10
Obtaining the Applicant Medical History
Completion of the DD Form 2807-2 During the Medical History Interview
10-1
58
Behavioral Health Screening
10-2
59
The Closing Review
10-3
61
Applicant Disclosure After Medical Processing
10-4
62
Chapter 11
Accession Medical Evaluation
Completing the Medical Examination on the DD Form 2808
11-1
64
Profiling and Qualification Determination
11-2
74
Medical Waivers
11-3
77
Medical Read
11-4
78
Notification of Disqualified Applicants
11-5
81
Air Force X-Factor Testing
11-6
82

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
iii
Paragraph
Page
Chapter 12
Orthopedic/Neurologic
Orthopedic/Neurologic Screening Examination
12-1
83
Chapter 13
Consultations
Consultants
13-1
93
Consultation Process
13-2
94
Payment of Consultants
13-3
96
Payment of Ancillary and Laboratory Services
13-4
96
Consultation Timeframes
13-5
96
Consultation MOC Ticket Procedures
13-6
97
Transportation
13-7
97
Chapter 14
Medical Check-Out
Shipping Applicant Check Out
14-1
99
Inspection Check Out
14-2
99
Accession Medical Examination Check Out
14-3
99
Temporary Check Out
14-4
100
Reconciliation
14-5
100
Common USMIRS Entries
14-6
100
Chapter 15
Inspections
Inspection of an Applicant Medically Qualified for Service
15-1
101
Inspection of an Applicant Not Medically Qualified for Service
15-2
102
When a Medical Inspection is NOT Required
15-3
102
Chapter 16
Special Medical Examinations
Released From Active Duty
16-1
104
Service Members Processing for Commission and Warrant Officer
16-2
104
Dis-enrolled Reserve Officers’ Training Corps
16-3
104
Army Airborne Screening
16-4
105
Army Blue to Green
16-5
106
Military Accessions Vital to National Interest Recruitment Program
16-6
106
General Officer
16-7
106
Overseas Applicants
16-8
107
Non-MEPS Medical Applicants (Other than Overseas Processors)
16-9
108
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Applicants
16-10
108
Public Health Service Applicants
16-11
108
Reserve Officer Training Corps and Service Academy Cadets/Midshipmen
16-12
109
Individual Ready Reserve
16-13
109

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
iv
Paragraph
Page
Chapter 17
Quality Review Program
Quality Review Program
17-1
110
Chapter 18
Fee Basis Providers
Fee Basis Provider Responsibilities
18-1
111
Requesting FBPs
18-2
112
Placing Daily FBP Requests in the FBP Application
18-3
112
FBP Provider Work Record
18-4
114
FBP Provider Work Record Verification
18-5
115
Chapter 19
Medical Training Program
General
19-1
118
Initial Lead/Medical Technician Training
19-2
118
Initial Medical NCOIC/Supervisory Medical Technician Training
19-3
118
Confirmed Training Orders
19-4
119
Required Medical Training of All Medical Technicians
19-5
120
Chief Medical Officer Quarterly Review
19-6
121
Mandatory USMEPCOM Provider Medical Training and Documentation
19-7
121
MEPS Medical Provider Six Part Folder Requirements
19-8
124
Chapter 20
Medical Equipment, Supplies, and Cleaning
Audiometric Equipment Calibration and Audio Booth Maintenance
20-1
127
Height/Weight Measurement Equipment
20-2
128
Gulick II Tape
20-3
129
Proteinuria Qualitative Test
20-4
129
Glycosuria Qualitative Test
20-5
129
Pregnancy Test
20-6
129
Safety Data Sheets
20-7
130
Virtual Medical Library
20-8
130
Cleaning of the Medical Department
20-9
130
Chapter 21
Shipping Disruptions
Medical Qualification Status Change of a Shipping Applicant
21-1
132
Differences of Interpretations of Accession Medical Standards for Shipping
Applicants
21-2
133
No Shipping on (Working) Copies
21-3
134
Chapter 22
Medical Emergencies in the MEPS
Medical Emergencies in the MEPS
22-1
135

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
v
Paragraph
Page
Table
F-1. USMEPCOM Prescreen and Med Read Review Timeline Table
156
Figures
2-1. Example of Open PULHES
17
2-2. Example of Temporary Disqualified PULHES
18
2-3. Example of Medical Failure Code Box
18
2-4. Example of RBJ Date Box
18
2-5. Example of Disqualified PULHES
19
2-6. Example of ICD Code Box
19
2-7. DD Form 2807-2 Section VIII Prescreen Determination Box
20
2-8. DD Form 2807-2 Section VIII Item 2 For MEPS Use Only
21
3-1. MEPS Examination Consent Stamp
29
3-2. Medical Packet Assembly
35
10-1. SF 507 Overprint of Alcohol & Other Drug/Substance Abuse Block
60
10-2. SF 507 with Overprint of the Closing Review Block
61
10-3. Example of SF 507 with Overprints
63
11-1. Example of Applicant Profile
76
11-2. Example of Applicant Profile Continued
76
20-1. Background Noise Levels
128
20-2. Height Device
128
E-1. USMEPCOM Authorized Serious Medical Condition Letter
153
E-2. USMEPCOM Authorized Medical Disqualification Letter
154
Appendices
A. References
136
B. Internal Control Evaluation Checklist
140
C. Glossary
142
D. Proteinuria/Glycosuria
152
E. Letters
153
F. Supporting Medical Documentation Review Timelines
155
G. USMEPCOM Supporting Medical Documentation Cover Sheets
157
H. “N” Status Code
162
I. Encrypted E-mail or Direct Exchange of Cover Sheets
164

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
1
Chapter 1
General
1-1. Purpose
The purpose of this regulation is to establish policies and procedural guidance for the USMEPCOM Medical
Qualification Program (UMQP). This program is executed at USMEPCOM locations such as Military
Entrance Processing Stations (MEPS) and Remote Processing Stations (RPS), and is applicable to all
applicants medically processing for accession into the Military Services and other federal organizations as
approved by higher authority. The UMQP includes the following: medical prescreening, accession medical
examination, and rendering a medical qualification determination. The purpose of the UMQP is to
determine if an applicant meets both the Department of Defense (DoD) accession medical and applicable
Service specific standards. USMEPCOM designated and trained providers are the DoD medical authorities
for medical evaluations. These providers are considered the subject matter experts for determining whether
an applicant meets the medical requirements of Title 10 and is qualified, effective, and able-bodied for
appointment, enlistment, or induction into the Military Services. USMEPCOM provides medical testing
support to other federal agencies including special category non-applicants such as the National Civilian
Community Corps, and the Federal Bureau of Investigation when approved by the Deputy Assistant
Secretary of Defense for Military Personnel Policy.
1-2. References
References are listed in Appendix A.
1-3. Abbreviations and Terms
Abbreviations and terms used in this regulation are explained in Appendix C, Glossary.
1-4. Responsibilities
a. J-3/5/7 Director will:
(1) Exercise primary staff responsibility and develop policies and procedures for applicant medical
processing and related matters for the UMQP.
(2) Publish USMEPCOM policies, procedures and guidance for the DoD enlistment medical
qualification program.
(3) Manage United States Military Entrance Processing Command Integrated Resource System
(USMIRS) medical changes, and manage user acceptance of these changes.
b. USMEPCOM Command Surgeon will:
(1) Assist J-3/5/7 Director in developing and managing policies and procedures related to the
UMQP.
(2) Assist J-3/5/7 Medical Division (MD) in formulating medical policies and procedures for
medical quality/performance improvement and contract management aspects of the UMPQ.
(3) Ensure Command wide compliance with the policies set forth in this regulation.
(4) Manage systematic feedback and support to Sector and Battalion Commanders on the UMQP.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
2
(5) Provide responses to special inquiries (congressional, inspector general, special action, etc.).
(6) Assist USMEPCOM Acquisitions and Contracting Special Staff Office (A&C SSO) as needed
and provide special and technical expertise in managing USMEPCOM medical contracts associated with
UMQP.
(7) Manage USMEPCOM special programs as assigned.
(8) Coordinate with the J-3/5/7 MD staff on the medical aspects of future initiatives including
definition of requirements and studies.
(9) Provide technical expertise in support of future technical initiatives impacting the UMQP.
c. J-3/5/7 Medical Division Chief (MDC) will:
(1) Ensure Command wide compliance with the policies and guidance set forth in this regulation.
(2) Ensure the execution and quality of the UMQP in accordance with (IAW) the policies of the
DoD and the Commander, USMEPCOM.
(3) Centrally manage and administer the DoD enlistment medical qualification program and
facilitate standardized applicant medical processing, services and decisions.
(4) Be responsible for daily applicant medical processing mission and manage J-3/5/7 MD daily
medical support for MEPS medical processing issues through the Operations Center (MOC) ticket system
and Accession Medicine Branch Customer Service Phone Line.
(5) Manage USMEPCOM Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) testing program and the drug
and alcohol testing (DAT) programs.
(6) Formulate medical policies and procedures for applicant HIV testing program, DAT testing
program, and medical operational aspects of the UMQP.
(7) Provide supervision of the HIV/DAT Program Office and Accession Medicine Branches
(8) Manage the training program for USMEPCOM on medical policies and procedures for HIV
testing program, DAT testing program, and medical operational aspects of the UMQP.
(9) Assist USMEPCOM A&C SSO as needed, and provide support in managing USMEPCOM
medical contracts associated with UMQP.
(10) Assist J-3/5/7 Director in managing USMIRS medical changes, and user acceptance of these
changes.
(11) Ensure collaboration with Command Surgeon Office personnel as required and participate in
Quality Medical Assessment Teams, when assigned.
(12) Provide oversight of Medical Division performance improvement program which includes

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
3
trend analysis, metrics planning and execution.
(13) Develop the curriculum for the USMEPCOM Grand Rounds and the annual Medical
Leadership Training Seminar (MLTS).
d. J-3/5/7 Medical Division, Accession Medicine Branch Chiefs (AMBCs) will:
(1) Formulate medical policies and procedures for medical operational aspects of the UMPQ.
Advise the Command Surgeon, J-3/5/7 Director and the MDC on all medical issues in support of daily
applicant medical processing mission.
(2) Execute the J-3/5/7 MD operational aspects of the UMQP and ensure adherence to the DoD
medical standards and applicable USMEPCOM policies and guidelines.
(3) Ensure collaboration for quality aspects of the UMQP with the Command Surgeon.
(4) Ensure the MEPS comply with the policies and guidance set forth in this regulation.
(5) Respond to MOC tickets and assist the Command Surgeon in reviewing responses to special
inquiries as needed.
(6) Engage Service Medical Waiver Review Authorities (SMWRAs) as necessary to facilitate
applicant medical processing while authorizing use of medical funds effectively.
(7) Conduct evaluation visits of MEPS medical providers, as needed, and support quality medical
assessment team visits to the MEPS. This includes evaluation and assessment of MEPS’ adherence to
USMEPCOM Regulations (UMRs) 40-1, 40-2, 40-8, and 40-9.
(8) Provide clinical support for business process reengineering efforts, assigned medical projects
and continuous performance improvement efforts for the UMQP trend analysis, and metrics planning and
execution.
(9) Assist J-3/5/7 Director and MDC in managing USMIRS medical changes, and manage user
acceptance of these changes.
(10) Serve as the lead physician on assigned policy development projects. Develop and provide
training for USMEPCOM on current and pending medical processes to facilitate consistent implementation
of medical policies and procedures.
(11) Perform applicant medical processing when required.
(12) Provide Command Surgeon ongoing clinical support, as needed, to execute USMEPCOM
Existed Prior to Service (EPTS) and other special programs.
(13) Serve as a supervisor for the assigned MD personnel.
e. J-3/5/7 MD, Accession Medicine Branch Medical Management Analysts (MMAs) will:
(1) Provide support to the medical paraprofessional staff of the UMQP.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
4
(2) Provide field support to all processing locations and external agencies on all accession
medicine processing issues, questions and concerns.
(3) As needed, provide staff assistance visits (SAVs), individual training visits (ITVs), and medical
reassessment visits (MRVs) to MEPS including evaluation and assessment of USMEPCOM regulatory
medical policy in USMEPCOM regulations and policies. Provide support to the Inspector General program
as required.
(4) Ensure completion of MOC tickets applicable to the UMQP.
(5) Review and recommend updates to USMEPCOM regulations and policies.
(6) Provide medical technical support for business process reengineering efforts, assigned medical
projects and continuous performance improvement efforts for the UMQP trend analysis, and metrics
planning and execution.
(7) Provide Command Surgeon medical technical coding support, as needed, for the USMEPCOM
EPTS program.
(8) Manage the Command wide Clinical Laboratory Improvement Program (CLIP).
(9) Manage the Command wide special programs such as NOAA applicants processing.
(10) Provide management analyst support to the human immunodeficiency virus/drug and alcohol
testing (HIV/DAT) programs.
(11) Manage the medical logistics/supply program and provide first line support.
f. J-3/5/7 MD, HIV/DAT Program Officer will:
(1) Manage the USMEPCOM Applicant Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Drug and
Alcohol Programs in accordance with USMEPCOM Regulation (UMR) 40-8
(Department of Defense
(DoD) Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Testing Program and Drug and Alcohol Testing (DAT)
Program.
(2) Respond to HIV/DAT MOC tickets in support of daily applicant medical processing.
(3) Collaborate with the USMEPCOM Contracting Officer Representative (COR) for the HIV
contract to ensure USMEPCOM compliance with contract requirements.
g. USMEPCOM Acquisitions and Contracting Special Staff Office will:
(1) Manage USMEPCOM medical contracts associated with the UMQP. Provide the COR and
alternate contracting officer representative (ACOR) personnel for managing completion of workload
associated with medical contracts.
(2) Provide medical logistics contract support and manage business needs of the UMQP.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
5
(3) Provide acquisition support for medical contracts associated with the UMQP.
h. MEPS Commanders will:
(1) Ensure MEPS personnel comply with this regulation.
(2) Ensure adherence to USMEPCOM medical policies. Any deviation from current medical
processing policies must be authorized by an exception to policy (ETP). ETP must be approved by
submitting it through J-3/5/7 MD and signed by the Command Surgeon (or their designee).
(3) Ensure Fee Basis Provider (FBP) training and administrative requirements are met IAW
UMR
40-2.
i. MEPS Operations Officers (OPSOs) will:
(1) Be responsible for monitoring applicant flow through the MEPS Medical Department.
(2) Keep the MEPS Commander informed of applicant flow and current processing concerns.
(3) Oversee the MEPS Quality Review Program (QRP).
(4) Ensure medical data is updated in USMIRS in a timely and accurate manner.
j. MEPS Chief Medical Officers (CMOs) will:
(1) Manage the MEPS Medical Department, and execute the UMQP at the local MEPS level.
(2) Supervise assigned personnel including the Assistant Chief Medical Officer(s) (ACMOs),
Medical Officers (MOs) and the MEPS Medical Non-Commissioned Officer in Charge (Medical
NCOIC)/Supervisory Medical Technician (SUP MT).
(3) Serve as the local DoD medical authority and subject matter expert for accession medical
evaluations.
(4) Serve as the final authority for medical qualification determinations at the local level.
(5) Establish a professional working relationship with the Medical NCOIC/SUP MT and provide
them the support to execute the UMQP.
(6) Ensure medical staff is fully trained in conducting all aspects of the UMQP.
(7) Manage assigned ACMOs, MOs and FBPs, ensuring that they are processing applicants IAW
DoD and USMEPCOM standards, including documentation of performance issues.
(8) Ensure each applicant’s medical documents are appropriately reviewed for completeness and
accuracy.
(9) Prepare and conduct quarterly reviews and inspections of the Medical Department.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
6
(10) Ensure all other MEPS medical personnel training requirements are met.
(11) Ensure all medical personnel comply with Occupational Safety and Health Administration
(OSHA) requirements.
(12) Respond promptly to Dial-A-Doc/Email-A-Doc questions.
(13) Act as the appointed Laboratory Director.
k. MEPS Assistant Chief Medical Officers (ACMOs) will:
(1) Establish a professional working relationship with the CMO as well as the rest of the Medical
Department.
(2) Support and assist the CMO with the execution of the UMQP as indicated by the CMO and as
outlined in this regulation.
(3) In the absence of the CMO, be administratively in charge of the MEPS Medical Department,
execute the Medical Qualification Program at the local MEPS level, as outlined above, and perform any
required CMO duties as designated by the MEPS Commander.
l. MEPS Medical Officers (MOs) will:
(1) Establish a professional working relationship with the CMO and ACMO(s), as well as the rest
of the Medical Department.
(2) Support and assist the CMO with the execution of the UMQP as indicated by the CMO and as
outlined in this regulation.
m. MEPS Medical Non-Commissioned Officers in Charge/Supervisory Medical Technicians
will:
(1) Establish a professional working relationship with the CMO as well as the rest of the Medical
Department.
(2) Support and execute CMO-directed medical decisions and policies.
(3) Supervise and provide written evaluations for all medical technicians.
(4) Ensure each medical station is properly supplied and staffed for an efficient applicant flow
through the Medical Department processes.
(5) Serve as the government point of contact (GPOC) for USMEPCOM medical contracts, and
ensure compliance with COR assigned responsibilities.
(6) Ensure quality control (QC) of medical packets with complete and legible entries.
(7) Act as the primary trainer for the Medical Department technicians, ensuring they are thoroughly
trained in all aspects of the Medical Program.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
7
(8) Be responsible for the daily checks, calibration, periodic maintenance, and timely repairs of
medical equipment to optimize functionality.
(9) Coordinate scheduling of annual biomedical equipment maintenance.
(10) Ensure daily organization, professional appearance, and cleanliness of the MEPS Medical
Department.
(11) Coordinate with the other MEPS departments and Service Liaisons (SLs) on medical matters
impacting applicant flow.
(12) Ensure disruptive applicants are managed appropriately.
(13) Assist the Commander and the CMO in the requirements of UMR 40-1, 40-2, 40-8, and
40-9
to include ensuring contract providers perform medical evaluation services appropriate to their Defined
Provider Category (DPC) level.
(14) Ensure QRP is completed prior to applicant processing IAW UMM 680-3-1
.
(15) Ensure weekly and quarterly departmental and CMO-directed training is accomplished.
(16) Ensure all medical personnel comply with OSHA requirements.
(17) Establish verification and validation procedures for invoice reconciliation.
(18) Complete all required tasks within the established time period.
(19) Ensure the accuracy of USMIRS data entry.
n. MEPS Lead Medical Technicians will:
(1) Establish a professional working relationship with the CMO, Medical NCOIC/SUP MT and
the medical staff.
(2) Support and execute CMO and Medical NCOIC/SUP MT-directed medical decisions and
policies.
(3) Ensure the quality of the UMQP in the absence of a Medical NCOIC/SUP MT.
(4) Assist the Medical NCOIC/SUP MT with the duties outlined in the preceding section.
(5) Ensure accuracy of USMIRS data entry.
o. MEPS Medical Technicians will:
(1) Establish a professional working relationship with the CMO and NCOIC/SUP MT.
(2) Support and execute CMO and NCOIC/SUP MT/Lead Medical Technician- directed medical

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
8
decisions and policies.
(3) Perform QC checks accurately and daily.
(4) Execute applicant vision and hearing testing, specimen collections, and other assigned medical
services.
(5) Perform accurate and daily USMIRS, FBP, and consultation reconciliation.
(6) Complete the Medical Department TSJTS
within 90 working days after arrival.
(7) Ensure that each prescreen is completed accurately and timely, and the process tracked
accordingly in USMIRS.
(8) Ensure QRP is completed prior to applicant processing IAW UMR 680-3
.
(9) Comply with all initial and refresher training requirements for the UMQP as well as additional
USMEPCOM training as established by NCOIC/SUP MT.
(10) Ensure accuracy of USMIRS data entry.
p. Fee Basis Provider (FBP) responsibilities. FBPs are contracted providers who will conduct
accession medical processing IAW all applicable USMEPCOM regulations.
1-5. General Policy
a. Performance of Medical Evaluation Services. All personnel performing medical evaluation
services for USMEPCOM will adhere to the current version of the DoD Instruction (DoDI) 6130.03
Volume 1 (Medical Standards for Miltiary Service: Appointment, Enlistment, or Induction), UMR 40-1,
UMR 40-2, UMR 40-8, and UMR 40-9.
b. Applicant Medical Qualification Determination. Rendering a medical qualification
determination is a critical part of applicant processing. A qualification determination will be rendered by
USMEPCOM medical providers with a Defined Provider Category (DPC) Level of 3 or higher. The CMO
is ultimately responsible for the accuracy of the final applicant qualification determination at the local level.
1-6. Use of Reserve and National Guard Personnel/Practitioners
Reserve and National Guard (NG) personnel/practitioners in drill status or on active duty for training (ADT)
will not be used for applicant processing at the MEPS. Commanders with questions will contact J-3/5/7
for further clarification.
1-7. MEPS Communication with J-3/5/7 MD
a. The USMEPCOM MOC ticket system will be used for applicant medical processing issues. If
immediate help is needed after submitting a MOC ticket, the Accession Medicine Branch Customer Service
Phone Line should be utilized.
Note: Do not submit personal and medical information (PHI/PII) via MOC ticket.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
9
b. Use the following address for mailing information to J-3/5/7 MD
HQ USMEPCOM
ATTN: J-3/5/7 MD (position or person who should receive the mail)
2834 Green Bay Road
North Chicago, IL 60064-3091
c. Use the following number for faxing information to J-3/5/7 MD. If faxing personal or medical
information, call J-3/5/7 MD first and verify someone is available to immediately retrieve the fax from the
machine.
FAX: (847) 688-2453
Note: Emails containing PII/PHI must be encrypted.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
10
Chapter 2
Pre-Processing
2-1. Dial-A-Doc/Email-A-Doc Program
a. This program provides recruiters with direct communication to the MEPS Medical Department,
enabling them to obtain answers to questions concerning an applicant’s medical condition(s) or issue(s)
prior to submission of a prescreen and scheduling a MEPS medical examination. This communication will
allow the recruiter to understand DoD and USMEPCOM medical standards as applied to individuals they
are currently interviewing and/or clarification about supporting medical information/documents required
for medical processing. The Email-A-Doc program must comply with Privacy Act and encryption
requirements of USMEPCOM.
b. Each MEPS will have a local Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) governing the program. The
MEPS may have one or both programs.
c. Any inquiry that cannot be answered by local Medical Department personnel will be referred to J-
3/5/7 MD via MOC ticket for resolution.
d. An example of both the Dial-A-Doc SOP and Email-A-Doc SOP can be found on SPEAR
under
general information.
2-2. Completion of the DD Form 2807-2 for Prescreening of Applicants
a. The DD Form 2807-2
Accessions Medical History Report is the official form used to document
applicant medical history data. Completion of the DD Form 2807-2 by the applicant initiates the prescreen
process. The purpose of the prescreen is to facilitate the efficient and timely processing of applicants for
Military Service by providing a mechanism by which the applicant may do the following (per the
DoDI
6130.03-V1):
(1) Fully disclose all medical history.
(2) Submit all supporting medical documentation.
(3) Provide authorization for the DoD Components to request and obtain their medical records.
(4) Acknowledge that information provided constitutes an official statement.
(5) Provide authorization for medical examination as part of the accession evaluation.
b. All MEPS Medical Departments will conduct a medical prescreen program. The USMEPCOM
Medical Prescreen Program Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) is located on SPEAR
. It will be
implemented by the CMO with support from the MEPS Commander and the Interservice Recruitment
Committee (IRC) (reference
UMR 601-23). Effective management of the prescreen process by the MEPS
Medical Department will enable the Recruiting partners to remain updated on the status of their applicants.
If there are workload issues, the MEPS Commander and CMO should work with the Service Liaison (SL),
and IRC if needed, so that the quality of medical prescreening is not compromised.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
11
c. The DD Form 2807-2 will be completed by every applicant prior to a medical examination at the
MEPS. This form must be completed and signed by the applicant. An accurate and complete prescreen is
critical to the medical evaluation process. The MEPS will not accept any applicant prescreens that are
missing required signatures and/or supporting medical documentation. Special attention must be given to
pages 2 and 7, ensuring that all required signatures are present. If a prescreen is incomplete upon
administrative review, then the MEPS will return the incomplete prescreen to the appropriate SL for
correction. The MEPS Medical Department will not review a
DD Form 2807-2 with incomplete/missing
information. The MEPS Medical Department will return incomplete prescreens to the MEPS Files Room.
d. The DD Form 2807-2
may be completed digitally, hand-written, or a combination of both. MEPS
will accept forms with computer-generated and/or hand-written check marks, X’s or initials in the “YES”
or “NO” boxes. Digital or wet signatures are authorized. If the form is completed manually, it must be
completed with black ink.
e. All applicants must provide their SSN on the DD Form 2807-2.
The DoD ID number (item 4b of
DD Form 2807-2) is not required at time of prescreen submission. A prescreen must not be rejected due to
a missing DoD ID number.
f. A DD Form 2807-2
is valid for 180 days from the date of the applicant signature in Section II.
After 180 days or if the applicant changes the Service Processed For (SPF) during the prescreen process,
an updated prescreen will be required.
g. Specific instructions on completing the DD Form 2807-2
can be found in the Prescreen Program
TSJTS found on SPEAR. The DD Form 2807-2 is divided into the following eight sections:
(1) SECTION I – APPLICANT: Contains applicant information.
(a) This information is to be filled out by the applicant.
(b) The MEPS Medical Department will ensure that this portion is completed.
(c) It is the Recruiting Service’s responsibility, not the MEPS Medical Department’s, to
validate the accuracy of this information (e.g., address, sex (at birth)/gender information).
(2) SECTION II – AUTHORIZATION STATEMENT: Must be completed and signed by the
applicant and Recruiting representative.
(a) If the applicant’s age is < 18 years, but ≥ 16 years, 11 months, then items 2a, b, and c must
be completed by the applicant’s parent or guardian.
(b) The date of the applicant’s signature must be prior to or on the same date as the
parental/guardian and Recruiting representative’s signature dates. Names, dates, and signatures may be
completed by hand or digitally.
(c) Medical Department personnel may not review an applicant’s medical documentation
without this authorization. This authorization must be signed by all required parties prior to any review of
an applicant’s medical history.
(d) The date the applicant signs this section starts the 180 day prescreen period.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
12
(3) SECTION III – MEDICAL HISTORY: The applicant must complete ALL medical history
“YES” or “NO” questions 1-164 regardless of gender or birth sex.
(a) If the specific questions are not applicable, the applicant will mark “NO”.
(b) For items 51 (date of last PAP smear) and 55 (first day of last menstrual period) the
applicant will either enter a date or leave the item blank if the question is not applicable.
(c) For item 162 if the answer is “NO” then parts a-d of that question will be left blank.
(4) SECTION IV – APPLICANT COMMENTS: Applicants must explain all "YES" answers to
items 1 - 164 that were answered in SECTION III.
(a) Explanations will begin with the item number. The applicant will then describe each
answer to the best of their ability.
(b) The applicant should provide as much information as possible, such as date(s) of
problem(s)/condition(s); provide names of Health Care Providers (HCPs), clinic(s) and/or hospital(s) along
with the city and state; explain what was done (e.g., evaluation and/or treatment); and describe the current
medical status, if applicable.
(c) Below are examples of explanations of “YES” answers; all are acceptable. Explanations
may be brief, if the attached supporting medical documentation provides enough pertinent detail for the
provider to render a prescreen processing determination.
• 9 – I have been wearing glasses since age 8 (or grade 2).
• 27 – I was told by my mother that when I was a child I needed an inhaler. I don’t
remember why, but have never used an inhaler since. I think I was around 2 years old
but not real sure.
• 84 – I had a football injury that required an ACL repair to my left knee in October of
2018. The surgery was performed by Dr. Smith, at Jones Regional Medical Center in
Wichita, Kansas. The repair was successful and I was able to continue playing football
two years later.
• 136 – I was suspended from high school in 2018 for fighting with a classmate. I served
a 5 day suspension. I did not get into any further fights and graduated from Taft High
School in 2019.
(5) SECTION V – HEALTH CARE PROVIDER/INSURANCE CARRIER CONTACT
INFORMATION: Applicants enter current/previous primary care physicians(s)/practitioner(s) and/or
clinic(s) where care is received and current/previous insurance carrier(s) information.
(a) The applicant will complete this information to the best of their ability.
(b) The prescreen review should not be discontinued if this information is left blank or is
incomplete.
(6) SECTION VI – MEDICAL RECORDS RELEASE: For USMEPCOM medical processing,
the applicant must mark “All records” in item 1. MEPS providers require access to all pertinent medical

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
13
records in order to conduct comprehensive reviews.
(a) The Recruiter will provide the MEPS location information where the applicant will be
processed. The Fax number entry is not required to be filled out.
(b) The authorization statement must be read by the applicant before signing. The signature
can be digital or wet signed. The date can be printed or typed.
(c) The parent or guardian of a minor applicant will enter their full name in last, first, middle
initial format, signature (CAC or wet) and date signed.
Note: The DD Form 2807-2
requires a parent/guardian of minor applicant to sign in two places. These
signatures are for any or all parents/guardians that have legal custody of a minor applicant. There may be
instances where one parent will sign in item 2 of SECTION II and another parent will sign in item 8 of
SECTION VI. It is not a requirement for medical personnel to determine legal custody. This is the
responsibility of the Recruiter who signs the
DD Form 2807-2 acknowledging that the information is
complete and true. If the signature blocks are incomplete/inconsistent in anyway, the issue will be presented
to the SL for reconciliation.
(7) SECTION VII – MEDICAL PROVIDER’S SUMMARY AND DESCRIPTION OF
PERTINENT INFORMATION: During the prescreen process a provider will review and comment on
identified conditions in SECTION III/IV and on supporting medical documents that might impact the
medical qualification determination.
(a) The provider will do the following:
1. Write a concise summary of the essential points for each condition and the date each
occurred.
2. If the condition is disqualifying, write “CD” (considered disqualifying) along with the
corresponding DoDI 6130.03-V1 citation and the Accession Policy (AP) approved ICD code, if applicable.
3. If the condition is qualifying, write “NCD” (not considered disqualifying).
4. If a determination cannot be made due to insufficient supporting documentation, then
list the outstanding requirements needed to make a determination.
(b) Draw a line across the block under the last line of comments, and sign and date the line so
future reviewing providers will know where the last provider left off.
(c) Make additional entries under the last line drawn in order to summarize the results of
subsequent documentation reviews until a determination is made. Attach a SF 507
(Standard Form) if more
space is required.
(d) If the original DD Form 2807-2
expires, then the newly submitted current valid prescreen
is the only form to be written upon by the reviewing provider. The reviewing provider will transcribe from
the expired prescreen to the current prescreen all listed CD conditions and any significant NCD conditions,
and will include the corresponding AP approved ICD codes and DoDI citations. The provider may annotate
“See prior PS” for extensive details previously documented on the expired prescreen.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
14
(e) On rare occasions, a Service may submit a new DD Form 2807-2
prior to the expiration
date of the original one, e.g., in order to correct a pre-screen discrepancy. In such a case, a reviewing
provider will follow procedures in paragraph (d) above, and will annotate in Section VII of the original
DD
Form 2807-2 – “form expired due to submission of a new DD Form 2807-2”, and will continue annotation
on the new DD Form 2807-2. The expired form must be retained as part of the medical record.
(f) Upon review of the medical records the provider may discover additional significant
medical history that will be recorded in this section of the prescreen. The provider will decide if additional
records are needed for any newly discovered medical conditions.
(8) SECTION VIII – MEDICAL PROVIDER’S PRESCREEN DETERMINATION BASED ON
AVAILABLE INFORMATION: (See Paragraph 2-3
for prescreen category definitions)
(a) For a simple prescreen:
1. If the administrative review finds that the prescreen is complete, then the medical
technician will: Record the date in block 1a, mark “PA” for “processing authorized” in block 1b, and record
their initials in block 1d of SECTION VIII of
DD Form 2807-2. The medical technician’s initials indicate
they have reviewed the simple prescreen and processing is authorized.
2. No further review of a complete prescreen by a provider is required prior to medical
examination.
3. If the administrative review finds that the prescreen is incomplete, the medical
technician will: Record the date in block 1a, mark “PH” for “processing hold” in block 1b, and record their
initials in block 1d of SECTION VIII of the
DD Form 2807-2. The medical technician’s initials indicate
they have reviewed the simple prescreen and processing is in a hold status until the Service corrects the
administrative errors.
(b) For a complex prescreen:
1. The authorizing provider will: record the date in item 1a, mark the appropriate
processing status in item 1b, complete item 1c if applicable and record their initials in item 1d of SECTION
VIII of
DD Form 2807-2.
2. The authorizing medical provider will then record/stamp their name in item 3a, sign in
item 3b, and date in item 3c of SECTION VIII of DD Form 2807-2 indicating that they have authorized
medical processing at the MEPS.
h. If an administrative review by the medical technician, prior to the provider review, reveals an
incomplete DD Form 2807-2
prescreen packet (e.g., missing previously requested supporting medical
documentation), it will not be processed but will be returned to the files room. The medical technician will
record the date in block 1a, mark “PH” for “processing hold” in block 1b, and record their initials in block
1d of SECTION VIII of the
DD Form 2807-2. The prescreen coversheet will be updated and given to the
appropriate SL with the reason why the prescreen was incomplete. The SL will have to sign the medical
record out of the files room in order to make corrections to the prescreen.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
15
2-3. Prescreen Categories
a. A simple prescreen is defined as a DD Form 2807-2
with “NO” responses to all questions except
for the items below.
(1)
A DD Form 2807-2 with “YES” answers to any of the following items only, is also categorized
as simple prescreen. All “YES” responses must have explanations in Section IV of the DD Form 2807-2.
No supporting medical documentation is required for the following (except for item 20):
• Item #7: Lazy eye correction
• Item #9: Contact lenses or glasses
• Item #11: Color vision deficiency or color blindness
• Item #12: Tubes in ear drums before 4 years of age
• Item #16: Tonsillectomy more than 30 days ago
• Item #20: Dental braces or plan to wear braces. Note: To meet accession standards, a
letter must be included from their orthodontist stating that active orthodontic treatment
will be completed prior to being sworn into or beginning Active Duty (AD).
• Item #43: Pyloric stenosis surgery during the first year of life
• Item #49: Pregnancy ending in vaginal delivery or C-section greater than six (6)
months ago, miscarriage or voluntary interruption of pregnancy more than six (6)
months ago, ectopic pregnancy more than six (6) months ago, breastfeeding ending
more than one (1) month ago
• Item #97: Simple laceration closure without subsequent loss of function
• Item #138: Based on the corresponding description that does not raise concerns of a
behavioral health condition IAW DoDI 6130.03
-V1.
• Item #145: Marijuana use only
• Item #153: Birth control pills, IUDs, Depo-Provera shot, or contraceptive implants,
patches, or rings; over the counter multi-vitamins
• Item #159: Wisdom teeth surgery more than 30 days ago
• Item #161: Prior Service, honorable discharge without complex medical conditions
indicated on the prescreen. Submit DD-214, NGB 22 or REDD Report (long form)
with DD Form 2807-2
(2)
A simple prescreen will be submitted on a projected applicant to the files room NLT 1100 for
review by the medical technician conducting QRP at 1300.
(3)
A Prescreen Cover Sheet is not required for simple prescreens.
(4)
If any one of the medical conditions listed above is considered to be part of a more complex
medical history, or the applicant’s written explanation indicates additional conditions not listed above, then
the simple prescreen will be returned to the SL for corrections. It should be re-submitted for review as a
complex prescreen.
b. A complex prescreen is defined as a DD Form 2807-2
with “YES” answers on any items other than
those listed in the paragraph above.
(1)
A complex prescreen will be submitted to the files room NLT 1100. An applicant with a
complex prescreen will not be projected for a medical examination prior to authorization for processing,
i.e., “PA”.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
16
(2)
A complex prescreen must have a Prescreen Cover Sheet properly filled out by the SL/GC IAW
the USMEPCOM Medical Prescreen Program.
(3)
A complex prescreen will be reviewed by the Medical Department IAW the USMEPCOM
Medical Prescreen Program.
(4)
The complex prescreen review timeline will be completed IAW the USMEPCOM Medical
Prescreen Program (see also Table F-1
. in Appendix F).
Note: If a prescreen is returned to the Service for additional supporting medical documentation, a new
prescreen cover sheet will be submitted to the files room with the additional documentation and will be
combined with the original prescreen packet. When the resubmitted prescreen is received by MEPS, the
prescreen review timeline will be calculated based on the number of new pages only.
(5)
MEPS will remove any PII/PHI or other unnecessary documentation not required for official
MEPS processing functions (e.g., projections, reservations, unnecessary supporting medical
documentation, etc.).
(6)
PII/PHI violation will be processed IAW UMR 25-53.
2-4. Prescreen Tracking
a. In order to standardize the tracking of a prescreen and give the most current status, a system has
been put in place to capture this information in USMIRS:
(1) The USMEPCOM Prescreen Coversheet is the only authorized form to be used when
submitting supporting medical documentation during the prescreen process. After the provider completes
the complex prescreen review, a completed prescreen cover sheet will be returned to the SL via scanned
copy through an encrypted Microsoft outlook email into a MEPS public folder; or it may picked up by the
SL from a specific location in the medical department that is a secure area where PII/PHI of the applicant(s)
will be protected. Guidance on setting up encrypted e-mail or direct exchange of coversheets is provided
in Appendix I
.
(a) Standardized prescreen “N” status’s have been added to USMIRS in order to give any
USMIRS user instant status on an applicant who is in the prescreen process. Each “N” status that pertains
to the prescreen is broken down as a “V code” in USMIRS.
1. MEPS prescreen tracking, participation and timeliness rates are measured by the
following codes:
• VA Prescreen Received, No Med Records – Simple prescreens only
• VB Prescreen Received, Med Records 5 Pages or Less
• VC Prescreen Received, Med Records 6-32 Pages
• VD Prescreen Received, Med Records 33-62 Pages
• VE Prescreen Received, Med Records 63-92 Pages
• VF Prescreen Received, Med Records 93 or More Pages
• VG Prescreen Incomplete/Not Reviewed by Med Provider

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
17
• VH Prescreen In-Review
• VI PR Complete; Processing Authorized, Time Line Met
• VJ PR Complete; Processing Authorized, Time Line Not Met
• VK PR Complete; Processing Not Justified, Time Line Met
• VL PR Complete; Processing Not Justified, Time Line Not Met
• VM PR Complete; PNJ, SMWRA Requested Exam, Time Line Met
• VN PR Complete; PNJ, SMWRA Requested Exam, Time Line Not Met
2. USMIRS Work ID (WKID) codes used for prescreen tracking:
• UMRMIS WKID – B030L
• USMIRS WKID – B030R
• USMIRS WKID – B030J
(b) See Appendix H
for USMIRS “N” status codes.
(c) USMIRS WKIDs automatically populate when entering the data that indicates an open
status (O) for additional Medical Evaluation Treatment Records (METR), a Temporary Disqualification
(TDQ), or a Disqualification (DQ) into the PULHES of the USMIRS Medical Data screen.
1. When entering an open profile (for METR) in USMIRS: There is no specific prescreen
“N” status completion code for any prescreen in a METR determination status. For all METR prescreens,
the “N” status code of VH should be removed and the open profile entered in the Medical Data screen of
USMIRS (
Figure 2-1). No other prescreen “N” status code should be entered after the B030L is committed.
The information on what needs to be re-submitted to the Medical Department will be annotated on the
Prescreen Coversheet that is given to the SL.
Figure 2-1. Example of Open PULHES
Figure 2-1. Example of Open PULHES
2. When entering a Temporary Disqualification: There is no prescreen “N” status
completion code for any prescreen with a TDQ determination status. For all TDQ prescreens the “N” status
code of VH should be removed and the “3T” should be inputted in the appropriate PULHES serial (
Figure
2-2). A medical failure box will then require the failure date and the fail code based on the DD Form 2807-
2 item number (Figure 2-3). An International Classification of Diseases (ICD) code box will then require
the fail code, date ICD code was entered, the ICD code/version, and PULHES code (Figure 2-3).
3. Once the “3T” is entered into the PULHES serial and medical failure and ICD codes
are entered, USMIRS will then require a Reevaluation Believed Justified (RBJ) date be inputted (Figure 2-
4). In most cases the DoDI 6130.03-V1 will specify timeframes (i.e., 6 months) on medical conditions that
will eventually resolve and allow medical processing at a later date. When calculating an RBJ date, it will
be done based on calendar day. The RBJ date starts the day of assignment of the “3T”. Only when the RBJ
date is reached will the applicant prescreen be re-evaluated. Once a “3T” is entered all further MEPS

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
18
processing is unauthorized. No other prescreen “N” status code should be entered when the B030J (for
TDQ) is committed. The TDQ information will be annotated on the Prescreen Cover Sheet that is given to
the SL
.
Figure 2-2. Example of Temporarily Disqualified PULHES
Figure 2-2. Example of Temporarily Disqualified PULHES
Figure 2-3. Example of Medical Failure Code Box
Figure 2-3. Example of Medical Failure Code Box
Figure 2-4. Example of RBJ Date Box
Figure 2-4. Example of RBJ Date Box
4. When entering a Disqualification: For all DQ prescreens the “N” status code of VH is
removed and the “3P” is be inputted in the appropriate PULHES serial (Figure 2-5). A medical failure box
will then require the failure date and the fail code based on the DD Form 2808 item number (Figure 2-3).
An ICD code box will then require the fail code, date ICD code was entered, the ICD code/version, and
PULHES code (
Figure 2-6).
5. Once the “3P” is entered into the PULHES serial and medical failure and ICD codes
are entered, you must then enter appropriate prescreen “N” status code. An applicant can be authorized to
process with a prescreen “3P” so the prescreen completion “N” status code must be put in USMIRS in
conjunction with the “3P” (either a VG, VI, VJ, VK, VL, VM, VN). All records with a “3P” will have a
B030R (for DQ) AND a prescreen completion “N” status code. The DQ information will be annotated on
the Prescreen Cover Sheet that is given to the SL.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
19
Figure 2-5. Example of Disqualified PULHES
Figure 2-5. Example of Disqualified PULHES
Figure 2-6. Example of ICD Code Box
Figure 2-6. Example of ICD Code Box
6. After the MEPS provider completes a prescreen review, the prescreen cover sheet used
upon initial submission will be completed by the Medical Department (technicians and providers). Once
the prescreen coversheet has been completed with a prescreen determination, a copy of the prescreen
coversheet will be given to the SL via any of the following methods (see
Appendix I, for guidance on
establishing an encrypted e-mail or direct prescreen coversheet exchange):
a. Digitally transmitted via an encrypted outlook email
b. Digitally sent to a secure electronic folder set up by the MEPS Information
Technology Specialist (ITS) to which both the Medical Department and SL have access. The original
prescreen coversheet(s) will be maintained in the applicant medical packet.
c. Manually picked up by the SL- In this case the Medical Department will establish
a specified location in a secure area to which the SL may be given access. Copies of prescreen coversheets
will be separated by Service (i.e., in a stackable/hanging paper tray) and covered with a
DD Form 2923,
Privacy Act Cover Sheet. The Medical Department will be overall responsible for the time(s), place, and
the way SL picks up prescreen coversheets as long as PII and PHI is protected and it does not interfere with
applicant medical processing. The original prescreen coversheet(s) will be maintained in the applicant
medical packet.
7. The prescreen coversheet is used in conjunction with the prescreen “N” status V codes,
and prescreen WKID’s to give the SL the most up to date information on their particular applicant. The
“N” status codes and WKID’s give a prescreen processing status. The prescreen coversheet goes into step
by step detail of the prescreen through the entire submission and review process. It includes processing
status and any additional instructions (i.e., as with the case for any METR processing decisions where a
resubmission of the prescreen with additional medical documents is determined).

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
20
8. MEPS Medical Department personnel will enter in USMIRS Medical Data screen
(MD01) only prescreens that reflect a disqualification status (B030J or B030R) or are incomplete (B030L)
as indicated by the CMO/ACMO/MO/FBP on
DD Form 2807-2. The date the reviewing provider annotates
the DQ, TDQ, and/or METR in section VII, item 1a is the date used to enter the transaction in USMIRS. If
the prescreen reveals no disqualifying and/or open condition(s), the Medical Data screen in USMIRS will
not be updated and only the prescreen “N” status codes will be used to track prescreens through USMIRS.
2-5. Provider Review and Determination of Complex Prescreens.
a.
All complex prescreens will be reviewed by providers who have achieved at least a DPC-2 level.
b.
Reviewing providers will list by item number in Section VII all conditions reported by the applicant
in Sections III and IV, and each condition will be annotated with “CD” or “NCD”. For “CD” conditions,
the corresponding section of the DoDI 6130.03
-V1 will be cited, and AP approved ICD 10 code will be
listed. If more space is required the MEPS will utilize a SF 507 and attach to the DD Form 2807-2.
c.
Only the original DD Form 2807-2 submitted by the SL will be used. However, if the original DD
Form 2807-2 expires, then the newly submitted current valid prescreen is the only form to be written upon
by the reviewing provider. If a Service submits a new DD Form 2807-2 prior to the expiration date of the
original one, then a reviewing provider will annotate in Section VII of the original DD Form 2807-2 –
“form expired due to submission of a new DD Form 2807-2”. The provider will transcribe from the expired
prescreen all CD conditions and any significant NCD conditions to the current prescreen, including the
corresponding ICD-10 code and DoDI citation. The provider may annotate “See prior PS” for extensive
details previously documented on the expired prescreen.
d.
Current valid prescreen will be in the packet on top of expired prescreens.
e.
The reviewing provider will then make a processing determination, which will be recorded in
Section VIII on DD Form 2807-2 (see Figure 2-7
) as follows:
Figure 2-7. DD Form 2807-2 Section VIII Prescreen Determination Box
Figure 2-7. DD Form 2807-2 Section VIII Prescreen Determination Box
(1) Processing Authorized (PA): This authorizes the Recruiting Service to project the applicant for
a medical examination at the MEPS. The reviewing provider will check the “PA” box, and date and initial
the appropriate row in Section VIII, items 1.a. and 1.d. The provider will document in item 1.c. any
disqualifying conditions from Section VII, and include the AP approved ICD code, condition (diagnosis),
and PULHES. Complete items 3.a., b., and c. with printed or stamped name of reviewing provider,
signature, and date of signing (if not already signed).
(2) Processing Requested by SMWRA (PRW):

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
21
(a) If a SMWRA submits a request to the MEPS to authorize processing for an applicant, and
the CMO concurs, then the reviewing provider will enter the date in item 1.a., mark “PRW” in item 1.b.,
and initial in item 1.d.
(b) If the CMO does not concur with the SMWRA request to authorize processing for an
applicant, then the CMO will request assistance from J-3/5/7 MD for resolution.
(3) Processing Hold (PH): This item defers processing of the prescreen pending administrative
corrections prior to a MEPS provider review. The reviewing medical technician will enter the date in item
1.a., mark “PH” in item 1.b. and initial in item 1.d.
(4) Return Justified (RJ): This allows an applicant (with a temporarily disqualifying condition that
is expected to resolve) to continue medical processing at a later date. Processing is not authorized prior to
this date. The reviewing provider will enter the date in item 1.a., annotate the RJ date in item 1.b. “RJ”
box, and initial in item 1.d.
(5) Medical Evaluation and/or Treatment Records (METR): This defers processing of the applicant
pending submission of required additional supporting medical documentation, prior to making a processing
determination. The reviewing provider will mark the “METR” box, and date and initial items 1a and 1d.and
date. The provider will complete a prescreen cover sheet, listing the requirements, and return it to the
submitting Service for action.
(6) Processing Not Justified (PNJ): This discontinues processing of the applicant due to safety
concerns for the applicant, for the MEPS personnel, or for other applicants. Examples of safety concerns
include active contagious disease (e.g., active tuberculosis), active behavioral health issues (e.g., psychosis,
homicidal/suicidal ideation or gesture), etc. Any decision to “PNJ” an applicant requires authorization by
J-3/5/7 MD via MOC ticket.
f. Item 2.a-i of Section VIII will be left blank. (See Figure 2-8.)
Figure 2-8. DD Form 2807-2 Section VIII Item 2 For MEPS Use Only
Figure 2-8. DD Form 2807-2 Section VIII Item 2 For MEPS Use Only
g. Item 4d, Section VIII will not be completed until a final processing determination is made. The
provider who makes the determination will annotate the total number of pages of supporting medical
documentation submitted with the DD Form 2807-2
throughout the prescreen process.
h. No specialty consultations/ancillary services will be ordered for applicants until the applicant
undergoes the medical examination.
i. The reviewed, completed, and signed DD Form 2807-2
is an “original” document and is maintained
in the applicant’s medical packet. If a packet does not exist for the applicant, one must be created. After
review of the
DD Form 2807-2 the applicant’s packet will be returned to the files room.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
22
j. The MEPS Medical Department is not obligated to review a DD Form 2807-2 prescreen with
incomplete administrative information. In these instances, the MEPS Medical Department will annotate in
Section VII the date in item 1.a., mark “PH” in item 1.b. and initial in item 1.d. The administratively
incomplete prescreen will be returned to the files room. The SL will be informed of the required corrections
with a prescreen coversheet and the VG “N” status code in USMIRS. In this case the SL will not reprint
or resubmit duplicate supporting medical documentation, nor remove pages from the packet. The medical
record must be signed out, corrected, and returned to the files room with a new prescreen coversheet.
2-6. Review of the Prescreen During the Quality Review Process
a. The MEPS Quality Review Process (QRP) is done IAW UMM 680-3-2.
b. The medical technician will ensure there is a DD Form 2807-2 with every medical record for every
projected applicant that is processing through the Medical Department either as a full medical examination,
inspection (shipping or medical), or consultation.
c. QRP of simple prescreens requiring a review:
(1)
Prescreens without discrepancies: If the applicant has a prescreen that meets the requirements
for projection, the applicant is scheduled for a MEPS medical examination within 2 business days. For
example, a simple prescreen that is submitted to the Files Room NLT 1100 on Monday and is without
discrepancies when reviewed during QRP, is scheduled for medical examination at the MEPS on
Wednesday.
(2)
Prescreens with discrepancies that were corrected: If the applicant’s prescreen had
deficiencies or errors that were rectified by 1100 the day before scheduled processing, and the prescreen
now meets the requirements for projection, the “N” status code VA “Prescreen Received, No Med Records”
will be removed and the projected medical examination will continue.
(3)
Prescreens with discrepancies that have not been corrected: If the applicant’s prescreen has
deficiencies or errors that have not been rectified by 1100 the day before scheduled processing, the
projection will be deleted in accordance with
UMR 601-23, and the “N” status code VA “Prescreen
Received, No Med Records” will remain as an indicator that the prescreen did not clear QRP.
Note: If a complex prescreen is submitted for QRP as a simple prescreen, the projection will be deleted
and the prescreen will be returned to the SL with the UMF 680-3-2-E
, which will have the comment
“Resubmit as a complex prescreen” annotated on it.
d. QRP of complex prescreens which have been reviewed, authorized processing, and included in a
medical packet:
(1)
Applicant packet without discrepancies: If the applicant’s packet meets the requirements for
further medical processing, the applicant can be brought to the MEPS for a MEPS medical examination in
2 business days.
(2)
Applicant packet with discrepancies: If the applicant’s packet has administrative deficiencies
or errors, the Service will have until 1100 the next business day to correct the deficiencies/errors. If the
deficiencies or errors are not rectified by 1100 the day before scheduled processing, the projection will be
deleted IAW
UMR 601-23.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
23
Note: All other medical “N” status codes must be cleared by the medical technician for MEPS processing
to continue.
e. All prescreen deficiencies or errors will be annotated on a UMF 680-3-2-E
Quality Review Program
(QRP) Discrepancy List (DL) based on input provided by the medical technician during QRP.
f. The UMF 680-3-2-E
Quality Review Program (QRP) Discrepancy List (DL) will be provided to the
sponsoring SLs/GCs immediately following QRP, to allow for timely correction of identified discrepancies
NLT 1100 the following day.
g. QRP reconciliation will occur the day before scheduled processing. If the identified discrepancies
are not corrected, the projections will be deleted.
2-7. VA and Other Disability Compensation
a. All Prior Service applicants who have a Veterans Affairs (VA) disability compensation or who
have been referred to their Service disability evaluation system for determination of fitness will have a
standard VA compensation and pension physical in addition to any other examinations required by Service
specific regulations prior to receiving any compensation/benefits. The applicant will have records of the
medical examination that document the physical condition(s) (for disability) at the time of
separation/retirement from Military Service.
b. An applicant with a Service-connected disability, as determined by the VA, that has requested
MEPS processing will provide appropriate medical documentation to the MEPS as a part of the prescreen
process. A disability rating has no correlation to re-accession or fitness for duty standards. MEPS medical
providers will assess the medical conditions related to the disability rating to determine if the applicant
meets DoDI standards.
c. In-Service personnel who did not meet medical retention standards for their specific Service may
have been referred to a Medical Evaluation Board (MEB) or Physical Evaluation Board (PEB) for a fitness
for duty determination. Personnel found not fit for duty may have been separated from Service. The
applicant’s medical diagnoses and physical limitations for which they were separated will be listed on the
MEB and PEB records.
d. An applicant who was medically separated from Military Service will submit the Medical
Evaluation Board (MEB) and Physical Evaluation Board (PEB) records as part of the prescreen process.
e. The medical qualification determination will be rendered based upon the DoDI 6130.03
-V1
standards and not the disability ratings or percentages.
2-8. Entry Level Separation
a. An Entry Level Separation (ELS) is an administrative discharge, and is given to individuals who
separate prior to completing 180 days of Military Service, or when discharge action was initiated prior to
180 days of Service. However, this type of discharge often indicates a "reason" such as pregnancy,
performance in training or medical issues. An individual with an ELS may, under certain conditions, be
allowed to re-enter in the military.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
24
b. An ELS applicant will have a DD Form 214 and will have a “Y” (Yes) status in the Defense
Manpower Data Center entry in USMIRS. In most cases an ELS applicant will have the annotation
“uncharacterized” in item 24 (usually this item is where you see Honorable, Dishonorable, General etc. for
the type of discharge). All ELS applicants require a new medical examination and are processed according
to accession standards, to include height/weight Service standards.
c. The ELS applicant will submit the prescreen with all relevant supporting medical documentation
(i.e., discharge paperwork).
Note: In many cases an ELS applicant will still have medical data in USMIRS and may have a copy
of their initial MEPS medical evaluation that is still within two year expiration date. In these cases the
medical examination is considered expired because that applicant has reported to initial entry training
and/or advanced individual training. A new accession medical evaluation (including the prescreen) is
required for MEPS processing.
2-9. Prior Service Applicants
The Recruiter/SL is responsible for identifying if the RE Code is related to a medical condition or not, and
include the reason for discharge (Medically Related Discharge or Administrative Only Discharge). If the
recruiting Service determines that the RE code is medically related, then the Service is responsible for
ensuring that the applicant submits the required supporting medical documentation, e.g., reason for
discharge, counseling notes, military medical records related to medical condition discharge, discharge
physical examination, and MEB/PEB documents if an MEB and/or PEB were held. If the recruiting Service
determines that the RE code is NOT medically related, then no further documentation is required for
medical processing.
2-10. Temporary Disability Retirement List
a. Military SMs on the Temporary Disability Retirement List (TDRL) have physical disabilities that
deem them unfit for military duty, but the disability has not sufficiently stabilized to accurately assess its
permanent degree of disability.
b. TDRL placement is determined by the PEB. The SM may remain on the TDRL for up to five years,
providing the condition does not change during that time.
c. Within the five year period, TDRL military members are periodically reexamined for fitness (at
least once every 18 months) in order to determine if the disability stabilizes. If at any time the SM is found
fit for duty they will be removed from the TDRL and returned to military duty. When an SM is rated with
a disability of 30% or greater, they will be transferred to the Permanent Disability Retirement List (PDRL)
and are essentially retired. SMs rated with a disability of less than 30% (and less than 20 years of service)
will be discharged from the TDRL with severance pay. Any applicant that was on the TDRL is authorized
a MEPS physical for re-entry into Military Service.
d. The applicant will submit all medical evaluations and medical board documents during their TDRL
status as part of the prescreen. The TDRL applicant will submit all relevant medical documentation (i.e.,
TDRL periodic assessment physical(s), PEB documents). The Medical Department will process the TDRL
applicant as an accession medical examination using prior Service standards.
e. PDRL retirees will not be processed.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
25
2-11. “No Medical Required” Projection
a. An applicant with a B0M0 work ID in USMIRS, which indicates “no medical required”, may be
projected to skip MEPS medical processing. SLs are prohibited from projecting a B0M0 applicant when
any valid medical data (including prescreen data) exists in the applicant’s medical record and/or USMIRS.
b. The following types of applicants can be processed in a “no medical required” (B0M0) status:
(1) Any Prior Service applicant that has a medical examination, annual periodic health assessment
(PHA), or separation health assessment (SHA) accomplished prior to retirement, discharge, or release from
AD that is within 15 months of the date of MEPS processing.
(2) Any In-Service applicant that has a current periodic medical examination within 5 years, or a
current annual PHA within 15 months of the date of MEPS processing.
c. It is the responsibility of the recruiting Service to determine prior to requesting an examination if
the applicant is eligible for B0M0 processing based upon a valid medical examination, PHA, or SHA.
MEPS medical processing starts with the submission of a prescreen and will not be discontinued once
initiated for these applicants. No ETP for a B0M0 will be granted.
d. Overseas applicants are authorized to be placed in a “no medical required” (B0M0) status in order
to process their enlistment information through the processing section for accession into the military. This
can only be done after the overseas physical examination is entered into USMIRS.
(1) The MEPS will enter any information missing on the overseas examination into USMIRS
medical data screen as follows:
(a) Trans (Transaction Code) enter a B040
(b) Physical (date) enter the date of examination found in item 1 of the DD Form 2808
(c) HTP (Home Town Physical) entered as NO (default)
(d) Special (physical) entered as N (default)
(e) Hgt (Height) entered as 88.00
(f) Wgt (Weight) entered as 333
(g) Fat (Body Fat Percentage) left blank
(h) Hair (color) entered as black (default)
(i) Eyes (color) entered as blue (default)
(j) BP (Blood Pressure) entered as 999/999
(k) PiP entered as P14

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
26
(l) RG (Red/Green Test) automatically skipped
(m) FLNT (FALANT) automatically skipped
(n) VA (Visual Acuities) entered as 099 for all entries (i.e., 20/099)
(o) AFVT (Depth Perception Test) entered as an X (not given)
(p) Refrac (Auto-Refraction) entered as an X (not given)
(q) Audio (Hearing Test) entered as 90 for all entries (i.e., 500-90, 1000-90, 2000-90 etc.)
(r) PULHES entered as a 1 for any category not profiled (this is so the accession data can be
easily entered by the processing section)
(s) Wvr (Waiver) entered as N (default)
(t) Consult entered as a N (default)
(u) Pys Rvw (Private Physical Paperwork Review) entered as N (default)
(v) Phys Type (Type of Physical) entered as 2 (default)
(w) HCG (Pregnancy Test) enter M for males, and P for females (default based on birth sex)
(x) HIV Tests entered as followed; Specimen Number – enter 99999999, Test Date – will
automatically populate with physical date entered, Test Status entered as a 5Z
(y) Drug Tests entered as followed; Specimen Number – enter 99999999, Test Date – will
automatically populate with the physical date entered, Results – enter as a Z Z
(z) Breath Alcohol Test – Test Date – will automatically populate with the physical date
entered, Code – entered as a Z (not given), Result – entered as 000 (default)
(2) Once the above steps are accomplished, an overseas applicant may be processed in a B0M0
status for the purposes of processing their accession data through the MEPS processing section.
e. Medical data in USMIRS may still exist for an applicant who had shipped out to initial entry
training and/or had an expired medical evaluation with a disqualification. This is considered invalid medical
data (even if within 2 years) for the purposes of MEPS processing, and is used only as a reference until it
is purged from USMIRS. In these cases a new MEPS medical evaluation is required for accession unless
the applicant has a valid In-Service physical examination, PHA, or SHA as outlined above. An applicant
with invalid medical data, but a valid examination may be processed as a B0M0.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
27
Chapter 3
Medical Processing Administration
3-1. General
a. All forms will be completed in black ink. If corrections must be made, entries will be corrected by
lining through once and entering the corrected entry above, below, or adjacent to the original entry.
Corrections and changes must be initialed and dated by the person making the correction. Use of white out
or correction tape on any applicant medical documents is not authorized.
b. “Night” testing is for aptitude testing and not medical testing. The MEPS are not authorized to
perform any medical services or medical processing during “night” testing.
c. In the case of MEPS-to-MEPS packet transfers, the original medical documentation must be
received by the gaining MEPS before applicant can be medically processed. Medical processing on copies
is not authorized. These packets are considered mission critical and can be shipped overnight IAW UMR
25-50.
d. Medical treatment of applicants by MEPS medical staff (government and contract) is not authorized
except for providing Basic Life Support (BLS) in the event of a cardiopulmonary arrest.
e. The MEPS may perform other examinations as listed in Chapter 16.
Additional federal applicant
medical examinations may be performed when authorized by the DoD on a space and resources available
basis, with prior approval given by USMEPCOM Command Surgeon with concurrence by USMEPCOM
Chief of Staff (CoS).
f. Medical treatment of MEPS or contract employees is prohibited except for providing BLS in the
event of a cardiopulmonary arrest.
g. A medical examination for accession is valid for 2 years or until the applicant has reported to initial
entry training. If the medical examination is going to expire before the applicant reports for initial entry
training, the CMO, Medical NCOIC/SUP MT, or MEPS Commander is authorized to approve a new, full
medical examination. The expired examination will be attached as supporting medical documentation to the
new examination. A new prescreen is not required under these circumstances.
h. If any portion of the original medical examination is lost, the applicant will receive a new
examination to include a new drug and HIV test.
i. An individual who reported to initial entry training, was separated and returns to the MEPS within
two years to apply for re-accession into a military Service, will require a new prescreen and full medical
examination (to include new drug and HIV tests). The previous examination will be attached as supporting
medical documentation to the new examination, if available. Separation documentation and related medical
records will be provided to the MEPS in accordance with Chapter 2
in this regulation.
3-2. Use of Non-Medical Personnel
a. MEPS-assigned non-medical personnel may be authorized to perform functions in the Medical
Department at the discretion of the CMO. Non-medical personnel with proper training and documentation
in their training folder may perform the following:

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
28
(1) Chaperone applicants
(2) Measure height, weight, and body fat percentage
(3) Demonstrate ortho/neuro maneuvers
(4) Observe urine specimen collection
(5) Verify drug results
(6) Verify HIV results
(7) Check applicants into the Medical Department
(8) Present the medical briefing
(9) Enter medical data into USMIRS
b. All other medical tests and examinations may not be performed by non-medical personnel.
Note: Additional administrative functions as determined by the Medical Department (making copies, etc.)
may also be performed.
c. Any personnel not assigned to the MEPS (Reservists, students, externs, interns, Recruiters, Service
Liaisons, etc.) are not authorized to work in the Medical Department.
3-3. Special Category Processor
Special-category processing should be done IAW UMR 601-23.
When in doubt as to the eligibility of an
applicant for special-category processing, seek guidance from HQ USMEPCOM, J-3/5/7 MD through the
MOC.
3-4. Same Day Processor
The MEPS Medical Department is authorized to conduct the medical brief before the ASVAB for same-day
processors. Upon completion of the ASVAB, all applicants will return to the Medical Department for
continued medical processing as applicable. If the medical processing is discontinued, but front-loading
has occurred, then the medical data must be entered into USMIRS and the PULHES will be annotated as
an open profile. The reason for the open PULHES must be documented on the DD Form 2808
.
3-5. The 6-hour Applicant Processing Window
During normal MEPS operations, the goal is to allot the Recruiting Services a 6-hour applicant processing
window to work new contracts. For each Service, the 6-hour window begins when the first scheduled
applicant completes their medical evaluation and is released from the MEPS Medical Department to the
appropriate Recruiting SL/GC office. The first group of applicants through the Medical Department should
be a mix of all Services. The quality of the medical examination/inspection will not be compromised
to meet compliance with the 6-hour window goal. Refer to UMR 601-23
for additional guidance.
Note: If processing a limited number of applicants per Service, then it may not be possible for the first group
to be a mix of all services.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
29
3-6. Medical Examination Consent and Chaperone Policy
a. Commanders may appoint any MEPS employee (on the recommendation of the CMO/Medical
NCOIC/SUP MT) to serve as a chaperone, as long as that person has successfully completed the chaperone
training as verified by the CMO/Medical NCOIC/SUP MT. Appointment orders (see Confirmed Training
Orders) remain in effect throughout the period of employment at the MEPS unless otherwise revoked by the
MEPS Commander. When the MEPS Commander is replaced, the Chaperone appointment remains in
effect. Re-training is not required when a change of command occurs. Once appointed by the MEPS
Commander, the chaperone policy will be reviewed annually and documented in the employee’s training
folder.
b. All applicants will read the MEPS Examination Information Sheet prior to the medical
examination. After reading, applicants will date, print, and sign their name on the top three lines of the
Consent Stamp in block 73 of DD Form 2808
. The Consent Stamp will be signed once by the applicant to
cover the medical examination and any subsequent medical inspections.
c. The chaperone will be the same biological sex as the applicant. When the examining provider is of
the opposite biological sex of the applicant, a chaperone must be provided while the applicant is in a state of
undress. When the examining provider is of the same biological sex as the applicant, a chaperone will be
provided on request of either the applicant or the examining provider. The applicant or provider may request
a chaperone at any time, and one must be provided. At no time will a Recruiter or SL be authorized to
function as a chaperone.
d. The examining provider must confirm that the applicant does or does not want a chaperone before
beginning the medical examination (whenever the applicant will be in a state of undress).
(1) If no chaperone is required/requested, then the last two lines of the Consent Stamp will be left
blank.
(2) During the initial medical examination, if a chaperone is required/requested, then the last two
lines of the Consent Stamp will be completed.
Figure 3-1. MEPS Examination Consent Stamp
Figure 3-1. MEPS Examination Consent Stamp
Note: The MEPS are authorized to use mailing labels in lieu of a stamp.
(3) When an applicant returns for an inspection and a chaperone is required/requested, the
chaperone will print their name, the word “chaperone”, the word “inspect”, the chaperone’s initials, and the
date the entry in block 73 of DD Form 2808 or SF 507
.
e. If the chaperone observes impropriety during the applicant’s medical examination, the examination

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
30
must be immediately stopped. Refer to TSJTS for additional guidance. A detailed explanation of observed
irregularities during a chaperoned examination will be provided after the examination has been stopped and
the applicant is fully clothed.
f. Chaperones are not required during interviews conducted while the applicant is fully dressed;
however, the provider and/or applicant may have a chaperone upon request.
Note: Chaperones are required for every medical provider who interacts with applicants until satisfactory
completion of the provider’s security clearances.
3-7. Uncooperative or Disruptive Applicants
If an applicant is uncooperative or disruptive, the Medical NCOIC/SUP MT or CMO will counsel the
applicant on their inappropriate behavior, and a decision will be made by the CMO whether or not the
applicant may continue processing. If the applicant’s processing is discontinued, the applicant will be
placed in an ‘N’ status and escorted to the MEPS Operations Officer. The Medical NCOIC/SUP MT or
CMO will ensure that the PULHES reflects an open profile and that the incident is documented on the
DD
Form 2808 item 79 (e.g., uncooperative or disruptive) with further explanation/information in item 89.
Refer to UMR 601-23 for additional guidance.
Note: Discontinuation of processing of these applicants is not considered a BAT/DAT/HIV refusal. Also,
a psychiatric consultation should be considered for a possible underlying behavioral health condition.
3-8. Deferring Medical Processing Prior to Completion
a. The MEPS medical examination begins once the applicant has been properly checked into the
Medical Department. The MEPS medical examination, once started, should be followed through to
completion unless the applicant wishes to discontinue processing of their own accord. The CMO, ACMO,
MO, or FB-CMO is authorized to defer an applicant’s processing if:
(1) The applicant appears to be a threat to self, MEPS or other applicants, e.g., active contagious
disease, homicidality, or suicidality.
(2) Additional medical records must be submitted in order to determine whether an applicant can
safely continue medical processing.
(3) The applicant has had a medical examination at another MEPS and the original records are not
present.
(4) The applicant does not comprehend English well enough to complete processing requirements.
(5) The applicant is attempting to process under false pretenses (e.g., special contact lenses to pass
color vision testing, etc.).
(6) The applicant appears to be under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
(7) The applicant has a positive HCG test result.
The MEPS medical provider will contact J-3/5/7 MD concerning any unique situations.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
31
Note: In all instances of an applicant being deferred, the applicant will be placed in an “N” status in
USMIRS with a code of “P2” along with an explanation of the medical discrepancy. The applicant’s profile
will be left in an “open” status. Any medical tests that have been completed by the applicant will have the
results entered into USMIRS, and any required fields that have not been completed must be filled in with
the following: 333 for weight, 88.00 for height, 90 for hearing. Medical documents will be kept in the
medical packet and maintained in the files room.
b. Once the exam is deferred, the CMO/ACMO/MO/FB-CMO will determine which parts of the exam
may still be completed.
c. Any discontinuation of processing will be documented on the DD Form 2808
item 89, and the
MEPS Commanding Officer will be informed.
3-9. Access to the MEPS Medical Department
a. Recruiters or Service Liaisons- These non-MEPS personnel will not be allowed under any
circumstances in the Medical Department during processing time when applicants are present. Each MEPS
will develop a local policy regarding entrance of Recruiters and SLs into the Medical Department when
applicants are not present (i.e., to submit medical reviews, applicant waiver issues, address MEPS
administrative issues, etc.).
b. Other Non-MEPS Personnel- Other non-MEPS personnel are defined as those individuals who
are not assigned (or tasked to work) in the Medical Department of the MEPS they wish to access (e.g.,
family members, non-MEPS military leadership, or MEPS personnel who work at a different MEPS). These
non-MEPS personnel will not be allowed under any circumstances in the Medical Department during
processing time when applicants are present. Each MEPS will develop a local policy regarding entrance of
other non-MEPS personnel into the Medical Department when applicants are not present.
Note: For VIP visitors, MEPS will coordinate with HQ USMEPCOM in advance.
c. MEPS Non-Medical Personnel- Each MEPS will develop a local policy regarding entrance of
MEPS non-medical personnel, who are not functioning as chaperones, into the Medical Department.
d. MEPS leadership- For the purposes of this policy, MEPS leadership is defined as the MEPS
Commander and other respective members of higher command (Battalion, Sector, HQ USMEPCOM).
MEPS leadership may visit and observe operations within the Medical Department, to include examination
areas where both public activities (e.g., hearing, vision, laboratory, etc.) and private aspects of the
examination are conducted. In order to maintain appropriate consideration for applicant privacy and
consent, the following guidance is required:
(1) Applicant consent is required for MEPS leadership to enter and observe activities in any area
within the Medical Department where medical information is discussed and/or elements of an examination
are performed (whether in a state of undress or not).
(2) MEPS leadership will be allowed to observe applicants of any biological sex during private
aspects of the medical examination only when applicants are fully dressed, such as during the medical
history interview.
(3) MEPS leadership will be allowed to observe applicants of the same biological sex when

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
32
applicants are partially undressed, specifically the ortho/neuro examination. They may also observe
applicants of the opposite biological sex with the explicit approval, in writing (e.g., email), from the J-3/5/7
Director each time observation of applicants of the opposite biological sex occurs.
(4) MEPS leadership will not be allowed to observe applicants during private aspects of the
medical examination when applicants are in a state of undress, specifically the general medical examination
(except as a chaperone).
(5) In order for MEPS leadership to observe the private aspects of the medical examination, the
following training is required:
(a) Chaperone Training- This TSJTS
must be completed prior to observing the private aspects
of the medical examination and be annotated on a UMR 40-1 CTO that is kept in the Medical Department.
The purpose of this is to ensure a minimum basic understanding of the roles and responsibilities of personnel
serving as chaperones in this environment.
(b) Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Training-The HIPAA and
Privacy Act Training (DHA—US001) available through Joint Knowledge Online (JKO) is required and
must be completed prior to observing the private aspects of the medical examination.
(6) MEPS leadership may only observe the private aspects of the medical exam of applicants of
the same biological sex. Observation is permissible when all of the following conditions are met:
(a) The applicant has provided their consent to allow MEPS leadership to be present in the
exam area to observe that aspect of the examination being conducted. Verbal consent is permissible;
however, written documentation of this consent is encouraged. If written consent is obtained, then MEPS
personnel should enter "Applicant consents to MEPS Leadership observing history and/or examination" in
Block 89 of DD Form 2808
. Acquiring an applicant’s consent will include the following, as a minimum:
1. Identification to the applicant of the MEPS Leader (by name, rank, and position) who
wishes to observe the medical activity;
2. Explanation of the reason for the observation, e.g., quality control, process
improvement, etc.. and that this observer will not be participating or assisting in any manner with their
medical examination (except if as a chaperone);
3. Disclosure that the MEPS Leader observing the medical activity has completed, and
maintains current, required training regarding the protection of sensitive and personal health information;
4. Description of the aspects of the examination to be observed, e.g., the ortho/neuro
exam, medical history, etc.;
5. Assurance of the requirement for confidentiality by the MEPS Leader regarding
anything that may be seen or heard during the observation period by the MEPS Leader, except for mission-
required reasons as part of their official duties;
6. Understanding by the applicant that whether or not the applicant consents to the
MEPS Leader being allowed to observe their examination, their decision will have no bearing on the final
medical qualification determination;

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
33
7. Acknowledgement from the applicant that they may withdraw their consent at any
time during their examination without any repercussion, by indicating to their examining provider that they
no longer consent to observation of their examination;
(b) MEPS leaders observing private aspects of the medical examination may not ask questions
or engage with the applicant in a state of undress (except when serving in the capacity of a chaperone), and
then only as required to perform the duty. Observers may move freely within the exam areas, as space and
circumstances allow, with care to not interfere with the performance of the examination.
Note: Talking to the applicants and asking questions afterwards is permissible within the Medical
Department, but must be done outside the exam areas and only when the applicant is dressed, preferably in
the common waiting area. Care should be taken to ensure that any discussions are not overheard by other
applicants.
(7) If the MEPS medical provider has specific concerns regarding the inappropriateness of
observation of private aspects of the examination by MEPS Leadership, they may raise these concerns to
the chain of command. While it is understood that MEPS leadership does not need the CMO's permission
to observe activities as described in this regulation, careful consideration of the risks and benefits with
respect to a specific applicant’s situation should be made before proceeding.
e. Further Guidance- The above guidance promotes collaboration between the Medical Department
and MEPS leadership and improves situational awareness of medical operations among the entire team.
Any deviation from this guidance requires an exception to policy (ETP) request which must be submitted
via MOC ticket for J-3/5/7 MD review and approval by the USMEPCOM Commander or authorized
representative.
Note: Command Surgeon Office medical staff, J-3/5/7 MD staff and USMEPCOM Inspector General Medical
Inspectors are all considered medical personnel who may be tasked to access the MEPS Medical
Departments. The general intent is to allow the Medical Department to complete medical processing
uninterrupted. This policy should not preclude reasonable access to the MEPS Medical Department by
MEPS non-medical personnel, e.g., the MEPS Operations Officer ensuring effective applicant processing
flow or working e-Security program areas, MEPS ITS resolving a network issue, etc.
3-10. Medical Exception to Policy
Any deviation from medical processing and procedures outlined in this USMEPCOM regulatory guidance
requires an approved ETP. Obtaining a medical ETP requires the MEPS Commander to submit a request
to J-3/5/7 MD through the appropriate Chain of Command. All Medical ETPs will be reviewed by the J-
3/5/7 MDC and must be approved by the Command Surgeon or their designee. Approved medical ETPs
will be maintained at the MEPS, and a copy will be retained at USMEPCOM J-3/5/7 MD. A template for
requesting medical ETPs can be found on SPEAR.
3-11. Undergarments/Body Piercing
a. Applicants undergoing a medical evaluation will be required to wear undergarments authorized by
USMEPCOM.
b. An applicant’s sponsoring Service is responsible for informing the applicant of authorized
undergarments. Applicants are required to remove all piercings and gauges of any type prior to medical

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
34
processing. If the applicant has a piercing that cannot be removed, the SL will be informed by the MEPS
Medical Department that processing of this applicant is on hold until removal of the piercing.
c. If the applicant does not have the authorized undergarments, the SL will be informed by the MEPS
Medical Department. The MEPS Medical Department may complete all portions of the medical
examination with the exception of the height/weight and the ortho/neuro exam. The provider will annotate
the applicant's PULHES accordingly, and the applicant’s medical data will be entered into USMIRS.
3-12. Medical Photography
Photography of applicants is not permitted in the MEPS Medical Department.
3-13. Medical Packet Assembly
Applicant medical packet will be assembled IAW Figure 3-2. There is a Medical Record Quality Check
TSJTS that accompanies this packet assembly that can be found on SPEAR.
USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
36
Chapter 4
Medical Check-in
4-1. Applicant Medical Check-in
a. The medical staff is required to biometrically check applicants in and out of the MEPS Medical
Department using USMIRS and e-Security IAW UMR 601-23.
In the event that e-Security is not available,
the MEPS Medical Department will still be required to check applicants in and out by verifying that a signed
UMF 680-3A-E
(Request for Examination) is present. If manual processing is required, the MEPS will take
action to replace the forms used on a daily basis IAW UMR 601-23. All applicants must have and wear
name tags.
b. The applicant packet will be reviewed for the following documentation upon check-in:
(1) UMF 680-3A-E
.
(2) Completed and reviewed DD Form 2807-2
.
(3) The parental consent in Sections II and VI must be signed if the applicant is a minor.
Note: Date of parental signature must be the same date or after the applicant’s date of signature.
(4) DD Form 1966/5 (if applicable). The parental consent in Section VIII must be signed if the
applicant is a minor in accordance with UMR 601-23
.
Note: Date of parental signature must be the same date or after the applicant’s date of signature.
(5) Prior Service Documentation (when applicable).
c. The Medical Department will verify the applicant’s social security number in USMIRS, and will
confirm that all “N” statuses are cleared.
d. To ensure the efficiency of the medical check-in process, the applicant must be sent to the
Operations control desk for evaluation and resolution of any non-medical “N” statuses other than “N”
statuses in USMIRS caused by e-Security partial enrollments.
4-2. Walk-In Applicants
A walk-in is defined as an individual who has been previously determined to be processing authorized
(“PA”), arrived at the MEPS early enough to attend the medical brief in order to receive accession medical
examination and/or processing, but was not scheduled by name with the MEPS prior to close of business
on the preceding workday.
a. Only an applicant with a simple or approved complex prescreen (as indicated by a “PA” medical
processing status) is eligible to be processed as a walk-in.
b. An applicant with a complex prescreen due to a medical condition which is considered
disqualifying (“CD”), who has been authorized processing (i.e., “PA”) is eligible to be processed as a walk-
in.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
37
c. An applicant with a medical processing status other than “PA” is not eligible to process as a walk-
in.
d. The medical check-in process for walk-in applicants with simple prescreens is as follows:
(1) A medical technician will review the prescreen for completeness and will record the date in
item 1a, mark “PA” in item 1b, and record their initials in item 1d of Section VIII of DD Form 2807-2
.
(2) The “N” status code of VA will be entered and removed from USMIRS in order to properly
record the MEPS prescreen participation rate (after the applicant is properly projected as a walk-in).
e. The medical check-in process for walk-in applicants with complex prescreens who are
authorized processing is as follows:
(1) A medical technician will review the prescreen for the authorizing processing code of “PA”,
date and provider initials in items 1a, 1b, and 1d, AND the authorizing provider name, signature, and date
signed in items 3a, 3b, and 3c.
(2) The current “N” status code (most likely codes VI, VJ, VM, VN) will be removed. (See
Appendix F
for all of the USMIRS “N” status codes available.)
f. For a simple walk-in prescreen, the provider conducting the history interview will: record/stamp
their name in items 3a/4a, sign in items 3b/4b, and date in items 3c/4c of Section VIII of DD Form 2807-2
(the authorizing and examining provider blocks).
g. For a complex walk-in prescreen, the provider conducting the history interview will: record/stamp
their name in item 4a, sign in item 4b, and date in item 4c of Section VIII of DD Form 2807-2
indicating
they are the examining provider that conducted the history interview during the medical examination.
4-3. Front Loading
a. Front loading refers to medical tests that are authorized to be performed before the Medical Brief.
Front loading is not authorized during “night” aptitude testing timeframes.
b. The following tests may be done prior to the Medical Brief:
(1) Blood Pressure/Heart Rate
(2) Vision Screening
(3) Hearing Screening
(4) Preliminary check for cerumen (ear wax)
Note: HIV or Drug specimen collection is not allowed prior to or during the medical brief.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
38
Chapter 5
Medical Brief
5-1. Medical Brief
a. The medical brief is used to inform and instruct the applicant, and to assist them in the review and
completion of the following required medical documentation: DD Form 2005, DD Form 2807-2,
DD Form
2808, USMEPCOM Forms (UMF) 40-8-1-E, UMF 40-1-15-E, UMF 40-1-18, and Standard Form (SF) 507
Medical Record. A copy of the most current standardized medical brief is available on SPEAR under
medical brief.
b. The provider, medical technician, or non-medical MEPS personnel with documented training will
give the brief in English only. If a non-medical MEPS staff member gives the medical brief, a Medical
Department staff member must be available to answer applicant questions. The briefer must follow the
standardized medical brief verbatim, and may use the medical brief script document on SPEAR
under
medical brief to assist with this. The MEPS Medical Department will print the medical brief slides and the
audio script document, and have it on hand in a binder for use in case the MEPS must brief the applicants
without IT equipment.
c. The medical brief has been automated and has a voiceover for all slides that may be used by the
medical briefer. When using the voiceover, the medical briefer will only have to ensure that the voice plays
with each slide by clicking the horn icon in the top right corner of each slide. The briefer is authorized to
adjust the audio settings so the voiceover plays automatically with each slide change. The medical briefer
may brief the applicants verbally, use the voiceover, or use a combination of both. No other alteration to
the medical brief is authorized.
d. The medical brief is an audio and visual presentation with examples and important information on
each slide. It is important for the medical briefer to display each slide to the applicant in order for them
visualize and read what is needed to be done as the briefer is telling them. The briefer should only be
talking about the slide displayed. The combination of visualization of the slides, a clear concise
briefer/voiceover, a controlled environment and an opportunity for the applicant to ask questions will help
to ensure that all required medical information and instructions were presented in a standardized fashion.
e. The medical briefer will be responsible for conducting the brief and ensuring that the applicants
have a clear understanding of the content of the forms they are reviewing and filling out. The briefer may
further verbally clarify slides, and may also have other medical personnel present to circulate and assist.
Applicants must remain in the medical briefing room until all forms are completed.
f. The medical staff is responsible for identifying the forms, for instructing the applicants how to
complete each form, for explaining how to sign/date each form, as applicable, and for ensuring all applicant
questions have been answered. The following forms, provided by the MEPS Medical Department, may be
completed by the applicant while waiting for the medical brief to begin:
(1) DD Form 2005
Privacy Act Statement.
(2) MEPS Examination Information Sheet.
(3) UMF 40-1-15
-E, Supplemental Health Screening Questionnaire (SHSQ).

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
39
(4) UMF 40-8-1-E Drug/Alcohol and HIV Acknowledgement.
(5) UMF 40-1-18
Tattoos/Brands/Piercing/Ear Gauging/Scars/Birthmarks.
g. The Breath Alcohol Test (BAT) is performed immediately after the medical briefing. The BAT will
be accomplished using the prescribed procedures in UMR 40-8
.
h. MEPS personnel will not discuss an applicant’s medical history in the public medical briefing
setting. If an applicant has questions that are not of a general nature for all applicants, MEPS personnel will
discuss the applicant’s personal medical history in a private setting where other applicants will not overhear
the discussion.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
40
Chapter 6
Hearing Testing and Cerumen Removal
6-1. Hearing Testing Procedures
a. Hearing tests will be conducted in an environment that is as quiet as possible. Procedures on how
to accomplish the audiogram program can be found in the TSJTS
on SPEAR (J-1 Workforce Development
Training and Conference Division under Job Task Sheets).
b. The information that will be entered into the audiometer will include:
(1) Applicant name (last then first).
(2) Last four digits of applicant SSN.
c. Eyeglasses, ear piercings, and hearing aids will be removed before testing. Ensure the applicant
understands the test and required responses. Advise applicants that job selection may depend on the results
of this test. Only audiograms performed by the MEPS will be used for rendering the medical qualification
determination.
d. Audiograms must be reviewed by trained technicians to ensure the validity of the results and proper
recordkeeping.
e. The results at 500, 1000, 2000, 3000, 4000, and 6000 cycles per second will be recorded on the
DD
Form 2808, item 71a (and 71b, if the initial hearing test is failed). The entire unit serial number and date
the unit was calibrated must also be recorded in item 71a (and 71b, if the initial hearing test is failed).
f. A repeat audiogram, if indicated IAW Paragraph 6-2
, will be performed on a different audiometer.
Repeat hearing tests for additional job opportunities are not authorized.
g. Hearing testing at the MEPS adheres to strict military accession standards and, once complete, is
the hearing test of record for accession. Applicant-provided hearing testing conducted outside the MEPS,
after initial MEPS hearing testing, will not be used to refute any MEPS hearing testing results.
Note: A medical technician will observe the applicant during repeat audiograms to ensure applicant with
unilateral hearing loss does not switch the audiometer headphones or the left and right headphone jacks.
6-2. Conducting Repeat Audiograms
a. If the applicant fails the initial hearing test, the ears should be examined by authorized MEPS
medical staff for the presence of cerumen obstruction.
(1) If the applicant fails the initial hearing test and there is no cerumen obstruction, the MEPS
hearing test may be repeated only once, either on the same day or after at least 48 hours of hearing rest, at
the provider’s discretion. The applicant must be advised to avoid exposure to loud noise during the 48 hour
rest period. Document this advice on the DD Form 2808
in items 78 or 89.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
41
(2) If the applicant fails the initial hearing test, and there is cerumen obstruction, the MEPS hearing
test may be repeated once the same day, after cerumen removal. If the applicant fails the second test, it may
be repeated one final time in 48 hours. The applicant must be advised to avoid exposure to loud noise during
the 48 hour rest period. Document this advice on the DD Form 2808
in items 78 or 89.
b. If the applicant is returning on a different date from the initial MEPS exam for hearing testing, enter
a “3T” under the H-factor of the “PULHES” in USMIRS, and enter an RBJ date corresponding to the advised
rest period and/or ear trauma. If the DD Form 2808
items 71a and 71b are full, any subsequent audiometry
results will be recorded in item 73 or on the SF 507.
c. After the audiogram has been repeated, use the best hearing test result to profile the applicant’s
hearing.
6-3. Profiling Hearing
a. When properly calibrated, the audiometer used at the MEPS will automatically determine and print
out a hearing profile.
b. Medical standards provided in the DoDI 6130.03
-V1 will be used to profile the applicant’s hearing.
6-4. Cerumen Removal
a. Each MEPS shall develop and maintain a protocol for cerumen removal for those applicants with
cerumen obstruction that prevents adequate visualization of the external auditory canal and the tympanic
membrane (TM). Adequate examination of the TM consists of visualizing the reflective cone (triangle), the
pars flaccida of the TM, and the handle of the malleolus behind the TM. If one or more of these structures
cannot be seen because of cerumen, then cerumen removal is required. Cerumen removal will be performed
at the discretion of the CMO. Before cerumen removal is attempted, the provider must ensure that the
USMEPCOM SF 600 Ear Wax Removal Consent Form ha
s been completed by the applicant and signed by
the provider. The original SF 600 is to be kept with the DD Form 2808. A copy of the SF 600 will be
maintained in a medical administrative file for two years.
b. Only the following methods (at the discretion of the CMO) are approved for cerumen removal at
the MEPS:
(1) Manual lavage (“elephant/rhino ear”).
(2) Direct external canal curettage, by provider only.
(3) Debrox or hydrogen peroxide/water solution (50/50).
c. The MEPS medical staff may only perform cerumen removal when a certified (trained in cerumen
removal) medical provider is present at the MEPS. The CMO and Medical NCOIC/SUP MT shall oversee
the cerumen removal program and ensure that all personnel who perform cerumen removal comply with all
training and guidance found on SPEAR
under cerumen removal. If cerumen removal is unsuccessful, the
MEPS provider may refer the applicant for a consultation for cerumen removal.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
42
d. If the applicant does not tolerate the cerumen removal, or there is a contraindication that precludes
performance/continuation of the procedure, then the applicant should be referred for ENT consultation.
e. If the cerumen removal is discontinued due to a medical complication, the applicant should
immediately be evaluated by the MEPS medical provider to determine if they should be transferred to a
local emergency department for further treatment IAW the MEPS Post-procedure Evaluation Plan (example
may be found on SPEAR
).

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
43
Chapter 7
Vision
7-1. Vision Screening Guidance
Vision screening will be performed by trained MEPS Medical Department personnel on all applicants
undergoing an accession medical examination at the MEPS. The vision screening consists of several
mandatory, Service specific, and job specific vision tests. MEPS Medical Departments must be familiar
with all vision tests and how they apply to the applicants based on the Service for which they are processing.
The medical staff must be familiar with all equipment associated with vision screening, its use, proper
preventive maintenance and cleaning procedures per the guidelines in this regulation and the manufacturers’
instructions.
a. On the DD Form 2807-2
applicants must indicate if they wear corrective lenses (glasses or
contacts).
b. During the medical examination:
(1) All vision screenings will be performed with the room lights on.
(2) Applicants that wear corrective lenses must bring them for their examination (glasses are
preferred due to ease of removal during the vision screening).
(3) The medical staff will annotate the applicant’s eye color in item 60b, and if they wear corrective
lenses will annotate “with RX” in item 72c.
(4) Medical staff will annotate if the applicant normally wears corrective lenses but did not bring
them, along with any follow on instructions if applicable (e.g., applicant could not complete heterophoria
testing due to not having corrective lenses) in item 73, 89 or on the SF 507
.
c. The vision screening at the MEPS adheres to strict military accession standards and, once complete,
is the vision screening of record.
d. Results received from MEPS-directed vision consults may be utilized to render a qualification
determination.
e. Non-MEPS directed vision testing provided by the applicant will not be used to refute any MEPS
directed vision testing.
7-2. Screening for Undisclosed Contact Lenses
a. Before medical technicians conduct any vision testing, they must ask each applicant if they wear
corrective lenses.
b. The medical technician will then screen all applicants for the presence of contact lenses by shining
a pen light into the applicant’s eyes prior to vision testing.
c. In all cases, the medical technician must examine the applicant’s contact lenses for tint. The
following tinted types may be found:

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
44
(1) Designer tinted contacts give the wearer the eye color of their choosing. These lenses have a
colored outer area that aligns with the iris and a central colorless area to align with the pupil. These types
of contact lenses will not alter color vision testing results. Processing may continue with these designer
lenses in place, but medical technicians will ensure the eye color recorded for the applicant matches the
actual color of the iris and not the designer color of the lens.
(2) Color correcting lenses are used as an aid to “passing” color vision tests and have a central area
of tint that aligns with the pupil. These lenses filter colors so that the applicant can see the dot patterns of the
Pseudoisochromatic Plates (PiP), and are NOT authorized to be worn during MEPS medical processing.
An example of these lenses can be found on SPEAR.
d. If a medical technician identifies an applicant attempting to “pass” vision tests with un-disclosed
contact lenses or by using color corrective lenses, medical processing will be stopped, and the medical
examination will be discontinued by the CMO, and the applicant’s profile will be placed in an “open” status.
The applicant will be placed in an “N” status and MEPS processing will be deferred for six months. The
MEPS Commander or their designee will submit a STARNET report for medical irregularity.
7-3. Color Vision Testing
a. Color vision testing is not used for medical qualification determination for Service, but is performed
on all applicants for MOS/NEC, i.e., job selection. Color vision testing at the MEPS consists of
administration of the Pseudoisochromatic Plates (PiP) test and the Red/Green test, if necessary. All
applicants testing for color vision are given the PiP color vision test. All Army applicants from ALL
components, who FAIL the PiP test are then given the Red/Green test. If the applicant passes one color
vision test, then the subsequent test will not be conducted (e.g., if an Army applicant passes the PiP, do not
test them with the Red/Green test).
b. When conducting the PiP color vision test, the applicant will be tested at a distance of 24 to 30
inches from the PiP book with the room lights on and the book placed on a Richmond Light Color Perception
stand. The applicant will be tested with corrective lenses in place, if applicable.
c. If the applicant normally wears corrective lenses but does not have them, the PiP test may still be
administered. If the applicant cannot identify the PiP plates, do not fail the applicant. Annotate in item 73
that the applicant did not have corrective lenses and must bring them in to complete the PiP test. Discontinue
color vision testing until the applicant returns with corrective lenses
d. The applicant will be instructed to read the number aloud. The applicant is not allowed to touch the
test plates during the test. Each of the 14 plates will be displayed for a maximum of THREE seconds before
the plate is turned. The applicant will be shown the demonstration plate number “35” first. The
demonstration plate does not count towards the actual test score. If an incorrect response is given DO NOT
provide the correct answer. Continue the PiP test by showing the remaining 14 plates. If the applicant
answers with a number, whether incorrect or correct, the plate can be turned. If the applicant does not answer
before three seconds has expired, the plate will be turned.
e. The results will be recorded as the number correct over the total number of test plates displayed in
item 66 “PIP” of the
DD Form 2808 (EXAMPLE: “12/14 Corr”). Also, P (pass) or F (fail), and 2 digits
(representing the correct number of plates) will be entered into USMIRS (example P12 or F11).
f. Writing instruments will not be used to turn the plates in order to avoid stray marks that may draw

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
45
attention to the number that needs to be read by the applicant. White space or color dots will not be touched
in order to avoid oil smudges on the book. The PiP book(s) must remain closed, unless an applicant is
being tested, in order to prevent fading of the plates and to extend the service life of the books. When the
plates/books become unserviceable, they must be replaced.
g. Upon completion of daily color vision testing, the MEPS will reshuffle the PiP test plates at least
once. The test plates may be shuffled at any time after color vision processing has ended. If the MEPS
suspects that an applicant has memorized the order of the plates, the plates may be reshuffled at any time
during color vision testing. When the MEPS reshuffle the PiP test plates, the demonstration plate of “35”
(first plate) and the unused plate of “75” (last plate) should not be reshuffled.
h. All Army, Army Reserve and Army Guard, who fail the PiP test will then be given the Red/Green
test. This test consists of twelve plates that are broken down as 6 black plates, 3 red plates, and 3 green
plates. The Red/Green plates will be placed in the same book as the PiP plates.
(1) The applicant will be tested 30 inches from the Army Red/Green plates with the room lights
on and the book placed on a Richmond Light Color Perception stand. The applicant will be tested with
corrective lenses in place, if applicable.
(2) Each of the twelve plates will be shown for a maximum of THREE seconds. The applicant will
be instructed “Please read the colors aloud.” The applicant is not allowed to touch the test plates.
(a) The applicant will first be shown the two demonstration plates, one black then one colored.
The first demonstration plate must be a black plate. The next demonstration plate must be a colored plate
(either red or green). These two plates do not count towards the test score. If an incorrect response is given
by the applicant, DO NOT provide the correct answer.
(b) After completion of the demonstration plates, begin the actual Red/Green test. The
applicant must be shown the remaining 10 plates (5 black and 5 colored). The applicant must respond with
the color shown (black, red, or green) within the THREE second time limit.
(c) The applicant must respond correctly to all 5 of the red and green plates to pass the test. One
miss equals failure.
(d) The MEPS staff member may reshuffle the order of the six color plates when the PiP plates
are reshuffled. There must always be a black plate as the first plate and then between each of the red or
green plates.
(3) The Red/Green test results will be recorded as “PASS” or “FAIL” in item 66 “RED/GREEN”
on the DD Form 2808
and in USMIRS.
i. Repeat color vision testing is not authorized, except as described in Paragraph 7-3c
. above.
j. The MEPS are not authorized to request consults for further color vision testing.
k. Non-MEPS directed color vision testing provided by the applicant will not be used to refute any
MEPS directed color vision testing.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
46
7-4. Depth Perception Testing
a. Depth Perception testing will be conducted for MOS/NEC, i.e., job classification only. The MEPS
Medical Department will administer Depth Perception testing according to the following:
(1) All Air Force applicants from all components will be tested for depth perception using the
Armed Forces Vision Tester (AFVT) using the OPTEC 2300.
(2) All Marine Corps and Navy applicants will be tested for depth perception using the MCST.
(3) Select Army and Coast Guard applicants will be tested for depth perception using the MCST
after a job classification (MOS/NEC) has been selected which requires depth perception capability.
b. MCST: The Depth Perception test conducted with the MCST consists of one booklet containing
two vectographic pages and one pair of adult polarized glasses. Technicians will follow the guidance in
the TSJTS
for conducting the MCST.
c. AFVT/OPTEC 2300: The AFVT Depth Perception test is conducted with the OPTEC 2300 device.
The examiner should not rush through the demonstration and practice period which precede the actual test.
Technicians will follow the guidance prescribed in the TSJTS
for administering the Depth Perception
Testing with the OPTEC 2300 Vision Tester.
d. If the applicant wears corrective lenses and does not have them, the depth perception test may still
be administered. If the applicant cannot pass the depth perception test without their corrective lenses, do
not fail the applicant. Annotate in item 73 that the applicant did not have their corrective lenses and must
bring them in to complete the depth perception test. Discontinue depth perception testing until the applicant
returns with corrective lenses.
e. Repeat depth perception testing is not authorized, except as described in Paragraph 7-4d
above.
f. The MEPS are not authorized to request consults for further depth perception testing.
g. Non-MEPS directed depth perception testing provided by the applicant will not be used to refute
any MEPS directed depth perception testing.
7-5. Visual Acuity Testing
a. All applicants will have their uncorrected distance and near visual acuities tested in a room with
the lights on.
b. If indicated, specific refraction will be determined using the auto-refractor. The auto-refractor will
be connected to an Uninterrupted Power Supply with surge protection on the battery backup and surge side.
c. Uncorrected visual acuities will be measured with the OPTEC 2300 and with the applicant’s
corrective lenses removed.
(1) For both distance and near visual acuities, the applicant must be able to read the largest letters
in the OPTEC 2300 (20/400 line). An applicant may miss no more than one on the first line of the OPTEC
2300 (20/400) and no more than three per line for all other lines in order to pass that line. If the applicant

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
47
cannot pass the first line of the OPTEC 2300, test the applicant for finger count by holding up fingers 1
meter from the applicant’s eyes. If the applicant can correctly answer the number of fingers held up, record
the vision as 20/FC (finger count). If the applicant fails the finger count but perceives light, the result will
be recorded as 20/LP (light perception).
(2) Annotate vision testing results in terms of English Snellen Linear System (20/20, 20/40 etc.).
Use only full numbers for vision testing results. Do not use (+) or (-) signs in connection with visual acuity.
(3) If uncorrected vision is 20/50 or worse in either eye and/or the applicant wears glasses or
contact lenses, then the applicant must be tested using the auto-refractor to determine corrected vision.
Note: If the applicant wears glasses, they WILL NOT be tested with glasses to determine corrected vision.
The applicant must be tested by the MEPS auto-refractor in order to determine the most current corrected
vision.
(4) When using the auto-refractor, applicants cannot miss more than one of the letters/numbers
displayed on the lines indicating visual acuities of 20/40 or better. The smallest line of letters/numbers that
the applicant can read with not more than one error will be recorded as the best visual acuity. If the visual
acuities are worse than 20/40, no errors are permitted.
d. Corrected visual acuities will be determined using the auto-refractor or the pinhole method
without the applicant wearing corrective lenses.
(1) The auto-refractor is used when the applicant wears corrective lenses and/or is 20/50 or worse
in the worse eye, and for all Officer candidates with visual acuity worse than 20/20:
(a) Use subjective refractive error for entries on DD Form 2808
, item 62, check “AUTO”. The
"confidence index" (CI) or “reliability number” is the number to the right of the print out from the auto-
refractor. The higher the value, the more accurate the reading with a max value being 9. A CI of "E"
indicates an error. For CI <8 or “E”, repeat auto-refraction. Two tests with a CI <8 or “E” may indicate
pathology of the cornea or lens (e.g., keratoconus, cataracts, extreme dry eye, corneal scarring, etc.).
(b) The auto-refractor printout slip will be attached to the SF 507
.
(c) When a spherical equivalent (SE) of the refractive error needs to be manually calculated,
add the sphere algebraically to one-half of the cylinder, as in the following example:
Refraction: +7.00 -2.50 x 90
Spherical equivalent = (+7.00) + 1/2(-2.50) = +5.75
(2) Though the auto-refractor is preferred when operationally feasible, the Pinhole method may be
used when the applicant’s distance and near uncorrected visual acuity is worse than 20/20 but better than
20/50 in either eye. The Pinhole method should not be used for Officer Candidates. If the applicant’s
uncorrected visual acuity is 20/50 or worse, the auto-refractor must be used to obtain corrected visual
acuities.
(a) The pinhole method is administered by having the applicant hold the black pinhole device
up to the eye that is being tested.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
48
(b) Instruct the applicant to identify and read the smallest line that can be read through any
hole on the device.
(c) Allow the applicant time to get used to the pinhole device and adjust it as necessary.
(d) Record the results and annotate “PINHOLE” in item 61 next to Distance Vision and in item
63 next to Near Vision. Note there will be no Cylinder (Cyl) or SE result.
(e) When the pinhole method is the same or worse than the unaided vision, results will be
entered 20/NC (NC=no correction) in items 61 and 63.
7-6. Non-Contact Tonometer
Abnormally high intraocular pressure can be indicative of glaucoma, a disqualifying condition. This test is
performed only on NOAA physical applicants. Intraocular pressure measurement is conducted at the MEPS
using the MEPS Non-Contact Tonometer and will be performed on each eye. (See TSJTS
for vision on how
to use the Non-Contact Tonometer.)
7-7. Refractive Eye Surgery Guidance
a. The UMF 40-1-4 Refractive Eye Surgery Worksheet
will be utilized during the prescreen to obtain
information required to render a qualification determination.
b. If the applicant with a history of refractive eye surgery cannot provide documentation of the second
post-operative refraction, an auto-refraction may be performed at the MEPS. If the results of the MEPS
performed auto-refraction demonstrate a difference of > +/- 0.5 diopters from the initial post-operative
refraction for spherical or cylinder vision, then a MEPS directed manifest refraction must be obtained prior
to rendering a qualification determination.
7-8. Vision Consults
a. Optometry consultation, if available, is preferred for the evaluation of refraction errors, cornea or
lens pathology, and should be requested for the following:
(1) A Cyl reading in excess of 3.00 diopters in order to rule out keratoconus.
(2) An auto-refractive error of +/-8.00 to +/- 10.5 SE requiring manifest refraction for
confirmation.
Note: If the auto-refractive error is in excess of +/-10.50 SE, then the applicant is disqualified (DQ) and a
MEPS directed vision consult should not be requested.
(3) The applicant’s visual acuity does not correct to 20/40 or better in one or both eyes (either
distance or near vision). For example, the provider should consider a consult for 20/50 or worse.
Note: The optometry consult request to rule out keratoconus should include a complete eye exam with
dilated slit lamp exam, manifest refraction, topography or pentacam with interpretation, and intraocular
pressures (IOPs). The consultation request should specify that color copies of topography or pentacam must
be included in the report. The optometry consult request to confirm auto-refractive error should include
manifest refraction only.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
49
b. Ophthalmology consultation, if available, is preferred for the evaluation of the following:
(1) Suspected pathology of the following structures: retina, vascularity, optic nerve, vitrea, ocular
mobility/m otility, etc.
(2) Unilateral vision loss defined as a difference of 50 or more in the denominator of the corrected
distance visual acuities.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
50
Chapter 8
Measurement of Height/Weight/Body Fat Percentage/Body Mass Index/Vital Signs
8-1. Height/Weight Measurement
a. All Service-specific height, weight and body fat standards are established by the respective Service
recruiting commands. They are provided to USMEPCOM for implementation to meet the guidelines of the
DoDI 1308.3, and may be found on the SPEAR J-3/5/7 Medical Division
page under Service Height and
Weight. The height, weight, and body fat measurement of the applicant performed by the medical staff are
considered the official measurements for accession. If at any point during their DEP time, a previously
qualified applicant has a height, weight or body fat measurement performed by the MEPS Medical
Department which is now outside of Service-specific standards, the applicant is then temporarily
disqualified and their profile will be changed accordingly.
b. The Medical Department will ensure that, on the day of processing, the medical packets of all applicants
being processed that day are readily available for documentation of measurements. The measurements will be
documented on the DD Form 2808
and entered into USMIRS.
c. The applicant’s height (rounded up to the nearest half-inch) without shoes or socks will be
annotated in item 53 on the DD Form 2808
in decimal format. The applicant will stand upright with heels
together on a flat surface with the head held horizontally, looking directly forward with the line of vision
horizontal and the chin parallel to the floor. Any hairstyles that may interfere with an accurate height
measurement or scalp examination will be addressed by the applicant and their recruiting Service prior to
arrival at the MEPS for examination. Heights not listed on Service-specific height/weight charts are
disqualifying and will be profiled accordingly. The ICD codes of UDR.HT (under-height) or OVR.HT
(over-height) will be used.
d. The applicant’s weight (lbs.) will be measured in their undergarments only, and will be annotated
in item 54 on the DD Form 2808
. Weight will be measured and recorded to the nearest pound within the
following guidelines: if the weight fraction is less than 1/2 pound, round down to the nearest pound; if the
weight fraction is 1/2 pound or greater, round up to the next highest pound (.1-.4 round down, .5-.9 round
up).
e. Once the medical examination is complete, the applicant will not return for repeat height and weight
measurements until the RBJ date.
f. Any RBJ date adjustments requested by the Services will be directed to J-3/5/7 MD via a MOC
ticket. J-3/5/7 MD physicians retain the authority to adjust an RBJ date for an applicant not meeting
Service-specific height and weight standards.
g. Upon SPF change, the RBJ date will be removed, and the applicant will be re-evaluated using new
Service-specific height and weight standards.
8-2. Body Fat Percentage Calculation
a. The applicant who exceeds the Service-specific maximum allowable weight is considered
overweight. An applicant who is overweight will undergo a body fat measurement and calculation (except
for the Marine Corps, unless requested).

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
51
b. The body fat measurement and calculation will be completed by trained MEPS personnel. Body
fat measurement and calculation of overweight applicants will be performed using a Gulick II Tape. (See
Paragraph 20-3 for a description of the authorized tape, and the TSJTS
for specific guidance.) To assist
with calculating body fat percentage, the Automated Body Fat Worksheet which can be found on SPEAR
will be used. This worksheet is an official form to document all MEPS measurements. The MEPS are to
use the male/female body fat percentage charts from the
DoDI 1308.3 for all Services. The charts can be
found on SPEAR J-3/5/7 Medical Division page under Service Height and Weight.
c. The RBJ date for an overweight applicant exceeding the allowable body fat percentage will be
calculated based upon both the applicant’s weight and body fat percentage. The RBJ date starts on the day
of measurement.
(1) Weight RBJ date will be calculated based on the number of pounds that must be lost in order to
meet the maximum allowable weight. The RBJ date will reflect a waiting period of 4 calendar days for every
1-pound to be lost.
(2) Body fat percentage RBJ date will be calculated based on the number of percentage points that
must be lost in order to meet the maximum allowable body fat percentage. The RBJ date will reflect a
waiting period of 16 calendar days for every 1-percentage point to be lost.
(3) Both RBJ dates will be compared, and the applicant will be assigned the lesser of the two
(weight vs. body fat) RBJ date calculations.
(4) If Service’s standards do not require body fat percentage calculations, then the MEPS will use
the calculated RBJ date based on weight.
(5) There is an RBJ date calculator (Microsoft Excel File) on SPEAR
to determine the calendar date
the applicant can return to the MEPS.
(6) Only J-3/5/7 MD retains the authority to adjust RBJ date (upon Service request) which will be
submitted via a MOC ticket. The official height and weight standards are Service-specific; therefore,
USMEPCOM is not authorized to issue an ETP for height and/or weight standards.
d. Applicants who exceed weight and body fat percentage standards will be profiled as “P-3T” in item
76 on the DD Form 2808
, unless disqualification (“P-3P”) is requested by the Service. In item 77, the
profiling provider will use the following:
(1) For item no. use 54 and/or 55b.
(2) For Medical Diagnosis use “overweight” or “over body fat”
(3) For ICD code use OVR.XX
(4) For profile serial use “P-3T”
(5) For RBJ Date use the lesser of the two calculated RBJ dates
(6) Mark disqualified

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
52
(7) Annotate examiner initials
(8) Item 74 will not be changed. (See Chapter 11
for further guidance.)
Note: If disqualification for an overweight applicant is requested by a Service in order to apply for a waiver,
then the profile may be changed accordingly by the MEPS provider. For applicants disqualified for being
overweight, item 74 will be marked as “IS NOT MEDICALLY QUALIFIED”, and item 77 will be
completed accordingly.
8-3. Body Mass Index Calculation
a. Applicants who are underweight according to their Service-specific standards will have their Body
Mass Index (BMI) calculated, will be temporarily disqualified, and will have an RBJ date assigned, if
indicated. A BMI calculator may be found on the Automated Body Fat Worksheet or the following website:
http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/educational/lose_wt/BMI/bmicalc.htm
The BMI result will be rounded to
the nearest tenth when recording it on the DD Form 2808.
b. The minimum acceptable BMI for Military Service is 17.5 (except for the Marine Corps, see below
in Paragraph 8-5
). If an applicant’s BMI is between 17.5 and 19.0, then the provider will determine if a
referral to their Primary Care Provider (PCP) or behavioral health (BH) is indicated in order to determine
if there is any underlying disqualifying medical condition. A chart is available on
SPEAR that provides the
weight corresponding to the 17.5 and 19.0 BMI measurements.
c. Applicants with a BMI less than 17.5 will be temporarily disqualified and an RBJ date provided in
order to allow the applicant time to meet the minimum BMI of 17.5. The RBJ date will reflect a waiting
period of 4 calendar days for every 1-pound increment to gain weight.
d. If a disqualification for underweight BMI is requested by a Service in order to apply for a waiver,
then the profile may be changed accordingly by the MEPS provider. For applicants disqualified for
underweight BMI, item 74 will be marked as “IS NOT MEDICALLY QUALIFIED”, and item 77 will be
completed accordingly.
8-4. Courtesy Height/Weight/Body Fat Percentage Measurements
Courtesy measurements are defined as any height, weight or body fat measurement and calculation
performed outside of the accession medical examination or inspection. MEPS medical personnel are not
authorized to perform courtesy measurements on any applicant.
8-5. Special Considerations
a. Non-Prior Service Marine Corps applicants with a BMI less than 19.0, will have their BMI recorded
on the DD Form 2808
item 73 (or 89 depending on who documents the BMI). These applicants will be
disqualified, profiled with “P=3P” for being underweight, and not given an RBJ date. (See Marine Corps
Information Sheet on
SPEAR).
b. Navy Regular and Reserve applicants with a BMI less than 17.5, will have their BMI recorded on
the DD Form 2808
item 73 (or 89 depending on who documents the BMI). These applicants will be
disqualified, profiled with “P=3P” for being underweight and not given an RBJ date.
c. Air Force Reserve applicants who exceed the weight or body fat percentage Service-specific
standard will be disqualified, profiled with “P=3P” and not given an RBJ date. Any Air Force Reserve

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
53
applicant disqualified for exceeding the height/weight/body fat percentage Service-specific standard will
do one of the following:
(1) Return to the MEPS to undergo an inspection. If the returning applicant meets the
height/weight/body fat percentage standard, then the profile will be changed to “P=1”. If the applicant still
does not meet the height/weight/body fat percentage Service-specific standard, then the “P=3P” will remain
unchanged.
(2) Alternatively, obtain an approved waiver from the Air Force Surgeon General (SG) for
exceeding the weight or body fat percentage Service-specific standard, and submit the waiver to the MEPS.
The MEPS Medical Department will record the waiver information in item 87 of the DD Form 2808
and in
USMIRS. The MEPS Operations section will use the waiver code HBB to complete the enlistment process
in USMIRS.
8-6. Blood Pressure Measurement
a. A blood pressure (BP) measurement will be obtained with the applicant seated with feet flat on the
floor and legs uncrossed for a minimum of one minute prior to the initial BP measurement. Instruct the
applicant not to talk while taking BP. For proper BP measurement, ensure that the BP cuff is at the heart
level and that the BP cuff is placed over the brachial artery on bare skin.
b. Abnormal readings are either one of the following:
(1) Systolic measurements greater than 140mmHg.
(2) Diastolic measurements greater than 90mmHg.
c. If the initial BP obtained by the automatic BP machine is abnormal, one manual BP measurement
will be performed by the provider after the applicant has been seated for a minimum of five minutes. The
results will be annotated in item 58.b. A manual BP measurement of 140/90 or lower is not disqualifying.
The manual BP measurement will be entered into USMIRS.
d. If an applicant has a manual BP measurement with a systolic blood pressure > 180 and/or diastolic
> 120, and is symptomatic (i.e., headache, vision changes, chest pain, dyspnea, etc.), this is considered a
hypertensive emergency and processing will be stopped. The MEPS will contact emergency services to
transport the applicant to the nearest emergency department. The applicant’s profile will be left in an
“open” status and the remainder of the medical examination will be deferred.
e. If an applicant has a manual BP that exceeds 140/90, but is less than 180/120, and the applicant is
symptomatic then processing will be stopped, the profile left in an “open” status, and the applicant will be
referred to their PCP or an ER as appropriate for further evaluation and treatment. The applicant should be
provided with the UMF 40-1-11, USMEPCOM Blood Pressure Measurement Worksheet
.
f. If an applicant has a manual BP that exceeds 140/90, but is less than 180/120, and the applicant is
asymptomatic then processing will continue, and the profile left in an “open” status. The applicant will
be provided with the UMF 40-1-11, and the provider will instruct the applicant to do one of the following
at the discretion of the Service:
(1) MEPS BP average- The Service may hold the applicant over until the next processing day or

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
54
project them for inspection within 5 calendar days from the initial medical examination for one repeat
manual blood pressure measurement at the MEPS. The two manual BP measurements will be averaged,
and qualification determination rendered in accordance with the DoDI 6130.03
-V1.
(2) Non-MEPS BP average- The applicant will be directed to obtain 2 manual BP measurements
on two separate days within 5 calendar days from a licensed healthcare practitioner (MD, DO, NP, or PA).
The applicant must provide the clinical documentation of the BP evaluation and a completed
UMF 40-1-
11 to be submitted as a med read for further review. The BPs obtained outside the MEPS will be averaged.
The average of those 2 BPs will be documented in item 89 and qualification determination rendered in
accordance with the
DoDI 6130.03-V1. Note that BP measurements from Fire Stations, EMS, or other non-
health care facilities do not satisfy this requirement.
8-7. Heart Rate Measurement
a. During the automated BP measurement, a Heart Rate (HR) measurement will be obtained with the
applicant seated with feet flat on the floor and legs uncrossed for a minimum of one minute prior to the initial
HR reading. Instruct the applicant not to talk while measuring the HR.
b. Abnormal readings are either one of the following:
(1) HR measurement < 60 BPM (bradycardia).
(2) HR measurement >100 BPM (tachycardia).
c. If the applicant has bradycardia or tachycardia, a provider will evaluate them to determine if they
are symptomatic (e.g., dyspnea, chest pain, dizziness, diaphoresis, nausea, etc.). Evaluation should include
a manual HR measurement. If the applicant is symptomatic, the MEPS will contact emergency services
to transport them to the nearest emergency department. The applicant is disqualified for symptomatic
arrhythmia and will be profiled accordingly. A MEPS directed EKG is not indicated for an applicant
disqualified for symptomatic bradycardia or tachycardia.
d. If an asymptomatic applicant has bradycardia, then an EKG should be performed in order to
determine if a disqualifying conduction disorder is present.
(1) If a disqualifying conduction disorder IS NOT identified with EKG, then the profile will be left
in an “open” status and the applicant will be referred for MEPS directed cardiology consultation.
(2) If a disqualifying conduction disorder IS identified with EKG, then the asymptomatic applicant
will be profiled accordingly. No further MEPS directed evaluation is required. The applicant should be
referred to their PCP for follow up and treatment.
e. If an asymptomatic applicant has tachycardia, the MEPS is authorized to do up to two automated
HR measurements by a medical technician, and a third (manual) measurement by a provider, if necessary.
The HR measurements must be obtained at least 15 minutes apart. The first result is recorded in item 57. If
the first result is abnormal, all subsequent results will be recorded in item 73. The last HR measured is the
result entered into USMIRS. An asymptomatic applicant with a HR of >100 BPM on three measurements
at the MEPS is disqualified for persistent tachycardia. The applicant should be referred to their PCP for
further evaluation and treatment. A MEPS directed EKG is not indicated for an applicant disqualified for
persistent asymptomatic tachycardia.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
55
8-8. Temperature Measurement
a. A single temperature measurement will be taken on each shipping applicant and recorded in item
56 on the DD Form 2808
. A shipping applicant with a temperature ≥100.4
o
F (38
o
C) will be evaluated by
a MEPS medical provider. The shipping applicant will be temporarily medically disqualified for 72 hours.
The “P” in the PULHES of the physical profile, item 76, will be updated to “3T” and the shipping applicant
will be given an RBJ date in USMIRS 72 hours out. Item 77 should be updated accordingly, and item 74
should NOT be changed for a temporary disqualification.
b. A single temperature measurement should be taken on any applicant that appears to be ill during
MEPS processing. If the temperature is ≥100.4
o
F (38
o
C), then processing will be stopped and examination
deferred IAW Paragraph 3-8
.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
56
Chapter 9
Clinical Laboratory Improvement Program
9-1. Clinical Laboratory Improvement Program
The CLIP is a quality improvement program for all MEPS laboratories to maintain certification. Clinical
Laboratory Improvement Program (CLIP) recertification occurs in odd numbered years for all MEPS
laboratories. CLIP standards may be found in DoDM 6440.02
. The program includes laboratory
inspections, implementation of various quality control measures, and completion of mandatory College of
American Pathologists (CAP) proficiency testing twice yearly (February and September).
a. CLIP SOP – The CLIP SOP will be updated and posted each calendar year on
SPEAR J-3/5/7
Medical Division page under the CAP/CLIP. Each MEPS must download a copy of the SOP from SPEAR.
Once downloaded, the MEPS will print a copy of the SOP and place it in the CAP/CLIP (or medical section
SOP) binder.
b. Renewing CLIP Certificates – When recertification is required, a Tasking Message will be sent
to the each MEPS with instructions on how to complete this requirement. There are several items that must
be submitted in order to receive CLIP recertification. The CLMS Waived Testing Survey Checklist and
Waived Complexity Form 1D v1.1 must be completed and sent with a copy of the current MEPS Lab
Certificate to the CLMS/DHA email address identified in the Tasking Message.
c. CAP Testing – All MEPS laboratories must maintain current CLIP certification. In order to comply
with CLIP requirements, all MEPS must review and update their Lab SOP annually and complete biannual
proficiency testing. This proficiency testing is a component of the quality control procedures required to
maintain certification and is funded by the Department of the Army. Proficiency testing is administered by
the CAP and monitored for USMEPCOM by the US Army Program Manager Center for Clinical
Laboratory Medicine.
d. CAP Kits –
(1) Messages will release twice a year to the MEPS with required timelines for CAP kit
submission. CAP kits must be refrigerated, therefore MEPS mailrooms will ensure the kits are delivered
ASAP to the Medical NCOIC/ SUP MT. Once received, the kits must be stored at 2-8 degrees Celsius
(35.6-46.4 degrees Fahrenheit) until testing can be performed.
(2) Failure to complete CAP proficiency testing may result in cessation of all laboratory activities
at the MEPS by the CLIP regulatory officer.
e. Laboratory Director Appointment –
(1) The DoD Center for Clinical Laboratory Medicine OASD (HA)/TMA requires that each MEPS
lab be appointed a Laboratory Director.
(2) Each MEPS Laboratory Director must be a government physician who oversees the laboratory
locally (e.g., CMO/ACMO).
(3) An interim Laboratory Director will be appointed when there is a CMO/ACMO vacancy. A
Sector Medical Officer (SMO) will be appointed in the interim. Government non-providers, contract
providers, and any other non-government personnel may not be appointed. J-3/5/7 MD will be notified of

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
57
an interim director appointment.
(4) When a MEPS requires an Interim Laboratory Director, the following will be submitted to
Sector Medical for review for completeness and accuracy:
(a) Six months of UMF 40-1-8 and UMF 40-1-6
logs.
(b) A copy of the two most recent CAP proficiency testing results.
(c) A completed Clinical Laboratory Improvement Program Change Request Form
(CLMS
Form 2), which is available on SPEAR.
(5) Once the review is completed, a change of director memorandum will be forwarded to the US
Army Program Manager Center for Clinical Laboratory Medicine for processing.
(6) The MEPS Medical Department will coordinate via email with their respective Sector Medical
and submit quarterly subsequent UMF 40-1-8 logs, UMF 40-1-6
logs, as well as CAP testing results (if
applicable) for review. The MEPS will continue to follow the above guidance until a CMO/ACMO can be
appointed as Laboratory Director.
f. MEPS Change of Address – If a MEPS changes physical location, a change of address request is
required. The MEPS will complete the CLIP - Change Request Form (CLMS Form 2)
and forward it to the
J-3/5/7 MD to request an official change of address. The attachment will then be forwarded to the US Army
Program Manager at the Center for Clinical Laboratory Medicine for processing.
g. Procedure for Requesting CAP Web Access:
(1) Each MEPS laboratory must have at least two site administrators (Medical NCOIC/SUP MT
and Lead Medical Technician).
(2) In situations where one or both of the site administrators no longer work at the MEPS, the
Laboratory Director must submit a letter to CAP requesting the current site administrator be changed. The
letter will include the MEPS CAP number, name of the departing site administrator as well as the name of
the new site administrator. The letter should be sent via email to contactcenter@cap.org.
(3) The new MEPS site administrator must create a CAP account by going to the CAP website
(http://www.cap.org/
). The MEPS administrator will click log in (in the upper right corner on CAP website),
then click on my profile, then register with CAP and request access to the MEPS laboratory contents on the
CAP website. The new site administrator will receive an email confirmation once registration is completed.
h. Annual CAP Survey Renewal Forms - All MEPS Medical Departments must reorder CAP
proficiency test kits by accessing the online store on the CAP website.
i. In addition, each MEPS must download the Excel spreadsheet located on the CAP website by
November 1, annually. Once the order has been completed, a copy of the order form will be sent to J-3/5/7
MD and to the Center for Clinical Laboratory Medicine. The MEPS will be notified by CAP or J-3/5/7 MD
when to complete the on-line reorder process. The reorder form is required in order for the MEPS Medical
Departments to receive the CAP proficiency test kits.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
58
Chapter 10
Obtaining the Applicant Medical History
10-1. Completion of the DD Form 2807-2 During the Medical History Interview
a. The medical history interview will be conducted by the MEPS interviewing provider in a
professional manner and with appropriate introductions. The interview will be conducted prior to the
medical and the ortho/neuro examinations. The applicant’s medical history as documented on the
DD Form
2807-2 will be reviewed by the interviewing provider with each applicant in a confidential setting. All
forms will be completed in black ink.
b. At the beginning of the interview, the provider will verify the applicant’s identity and review the
applicant’s medical packet in order to:
(1) Determine if the applicant is a minor and if so, ensure the DD Form 1966/5 is present.
(2) Determine if the applicant provided updates to SECTION IV.
(3) Transfer the following relevant information from SECTION VII of the DD Form 2807-2
to the
DD Form 2808 IAW Chapter 11:
(a) Each condition considered disqualifying (“CD”), if any, including Accession Policy (AP)
approved ICD-10 code and DoDI 6130.03
-V1 citation.
(b) Any significant condition(s) not considered disqualifying (“NCD”), based upon the
provider’s clinical judgment.
(4) Determine if any focused examination may be indicated.
c. During the interview, the provider will document in SECTION IX of the DD Form 2807-2
:
(1) If the applicant provided comments, including any updates from SECTION IV, the provider
will summarize the applicant’s medical history as discussed during the interview.
(a) For every updated item reported by the applicant, the provider will comment beginning
with the corresponding item number (1-164). The provider will ask the applicant for pertinent information,
and document with sufficient detail to determine whether the condition is “CD” or “NCD” according to the
current version of the DoDI 6130.03
-V1.
(b) For “CD” conditions, the provider will also annotate the corresponding AP approved ICD-
10 code and the DoDI 6130.03
-V1 citation.
(c) Decide whether any updated conditions will require further supporting medical
documentation, i.e., a med read, in order to render a qualification determination.
(d) The interviewing provider is not required to transpose the prescreen provider’s comments
from SECTION VII to SECTION IX.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
59
(2) If the applicant denies any significant medical history (i.e., all “no” answers), provides no
updates during the medical brief, and discloses no additional information during the medical interview, then
the provider will document in section IX that the applicant has no significant medical history and “No
updates”.
d. At the completion of the interview, the provider will transfer the following relevant information
from SECTION IX of the DD Form 2807-2 to the DD Form 2808 IAW Chapter 11
:
(1) Every “CD” condition, if any, including the corresponding Accession Policy (AP) approved
ICD-10 code and the DoDI 6130.03
-V1 citation.
(2) Any significant condition(s) not considered disqualifying (“NCD”), based upon the provider’s
clinical judgment
(3) Every condition which will require further supporting medical documentation for a med read.
e. After the medical history interview is concluded the provider will:
(1) For applicants with simple prescreens, document in Section VIII of the DD Form 2807-2
(in
the authorizing and examining provider sections) the following:
(a) Leave item 2 blank.
(b) Record/stamp their name in items 3a/4a.
(c) Sign in items 3b/4b.
(d) Date in items 3c/4c.
(2) For applicants with complex prescreens, the interviewing provider will do the following in
Section VIII of the DD Form 2807-2
(in the examining provider sections):
(a) Leave item 2 blank.
(b) Record/stamp their name in item 4a.
(c) Sign in item 4b.
(d) Date in item 4c.
10-2. Behavioral Health Screening
All USMEPCOM medical providers will assess applicant behavioral health during the medical examination
process utilizing the following tools: Alcohol & Other Drug/Substance Abuse History; the Supplemental
Health Screening Questionnaire (SHSQ – UMF 40-1-15
-E); and the Applicant Behavioral Health
Assessment (ABHA).
a. Alcohol & Other Drug/Substance Abuse History

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
60
(1) The provider will complete the Alcohol & Other Drug/Substance Abuse History, found on the
overprint on the Standard Form (SF) 507, and record any medically relevant details. This tool has been
provided specifically to assist the provider in the determination of an applicant’s current condition or history
of alcohol dependence, drug dependence, alcohol abuse, or other drug abuse.
Figure 10-1. SF 507 overprint of the Alcohol & Other Drug/Substance Abuse Block
Figure 10-1. SF 507 overprint of the Alcohol & Other Drug/Substance Abuse Block
(2) The provider will complete the block by asking the applicant if they have ever used alcohol,
marijuana, other illegal drugs, or other substances (e.g., inhalants, injectables). The applicant will answer
“Yes” or “No” to these questions.
(a) A “No” answer requires the provider to place a mark in the “No” column for each substance
in the “Ever Used” box and no other annotation needs to be made.
(b) A “Yes” answer requires the provider to place a mark in the “Yes” column for each
substance used. The provider will then also complete the “Use Disorder” box for any "Yes" answer to the
“Ever Used” box. The provider will utilize items 145, 146, and 147 of the DD Form 2807-2
; the
Supplemental Health Screening Questionnaire (SHSQ) per Paragraph 10-2b.; and behavioral health
consultation, if necessary, in order to determine if the use of the substance should be classified as a disorder.
1. The provider will mark "No" if they determine that the use is not considered a disorder.
2. The provider will mark "Yes" if they determine that the use is considered a disorder,
and profile accordingly.
3. The provider will mark "Deferred" if they determine that more information is needed
to make a determination. The applicant’s profile will be left in an “open” status until the provider has the
information needed (consult, counseling records, etc.) to render a qualification determination.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
61
b. Supplemental Health Screening Questionnaire (UMF 40-1-15-E)
(1) Items 1-7. These demographic items are completed by the applicant during the Medical Brief.
(2) Item 8. The applicant will answer all parts of item 8 (letters a through l) during the Medical
Brief. Any “Yes” answer in item 8 must have an explanation in item 14. The provider will review item 8
(Screening Questions Part 1) and address each “Yes” answer explained in item 14 by documenting on the
overprinted SF 507.
(3) Item 9. The applicant will answer all parts of item 9 (letters a through c) during the Medical
Brief. The provider will review item 9 (Screening Questions Part 2) to determine if the applicant meets the
diagnostic criteria for alcohol use disorder.
c. Applicant Behavioral Health Assessment (ABHA). The ABHA questions are a framework for
discussion of behavioral health areas of concern. The interviewing provider will ask the required questions
in these areas and will record the results on the overprinted SF 507. The ABHA questions may be found on
SPEAR. (See Figure 10-3
for an example of documentation of the behavioral health interview.)
10-3. The Closing Review
The Closing Review (CR) checklist on the overprinted SF 507 will be completed by the interviewing
provider. If the medical history interview must be postponed, the CR will be completed upon return of the
applicant to the MEPS. If an 'Admits' box is checked for any area, the appropriate condition must be circled
in the ‘Conditions’ box and details will be provided on the SF 507. After the CR is completed, the provider
will initial and date.
Figure 10-2. SF 507 with Overprint of the Closing Review Block
Figure 10-2. SF 507 with Overprint of the Closing Review Block

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
62
10-4. Applicant Disclosure After Medical Processing
If an applicant discloses additional significant medical information at any time after completion of medical
processing, then a UMF 601-23-E must be completed in the presence of the applicant. (See UMR 601-23
for guidance.)

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
64
Chapter 11
Accession Medical Evaluation
The Accession Medical Evaluation is a review of an applicant’s medical history, a head-to-toe examination
of an applicant to the Armed Forces, and a qualification determination IAW the DoDI 6130.03-V1
in order
to ensure that individuals considered for appointment, enlistment, or induction into the Military Services
are:
a. Free of contagious diseases that may endanger the health of other personnel.
b. Free of medical conditions or physical defects that may reasonably be expected to require excessive
time lost from duty for necessary treatment or hospitalization, or may result in separation from the Military
Service for medical unfitness.
c. Medically capable of satisfactorily completing required training and initial period of contracted
service.
d. Medically adaptable to the military environment without geographical area limitations.
e. Medically capable of performing duties without aggravating existing physical defects or medical
conditions.
The accession medical evaluation includes a review and completion of the DD Form 2807-2
(see Chapters
2 and 10) and the DD Form 2808, and may include review of non-MEPS generated supporting medical
documentation which consists of the following: 1) Prescreen medical documents, 2) consult/ancillary
service result, 3) waiver determination, and 4) medical read (med read) medical documents.
The qualification determination is the process by which a medical provider who is trained in accession
medical evaluations interprets and applies the medical standards for appointment, enlistment or induction
into the Military Services to each applicant IAW the DoDI 6130.03
-V1.
11-1. Completing the Medical Examination on the DD Form 2808
a. Each applicant must undergo a medical examination by a licensed medical provider at the MEPS
as part of the accession medical evaluation. The results of this examination will be recorded on the
DD
Form 2808.
b. Consultations will not be used in lieu of a MEPS examination.
c. Gloves will be worn by the provider any time that they may come into contact with bodily fluids
or mucous membranes while examining applicants. A new pair of gloves will be used with each applicant.
The examiner will adhere to current Standard Precautions, Chaperone Policies and standard medical
practices during examinations.
d. The applicant will complete items 1 through 16 during the medical briefing. The applicant will
review and verify (or correct if necessary) their demographic information during the medical briefing.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
65
e. Items 17 through 43 below are the specific areas of clinical evaluation performed by the provider.
The provider annotates each item by marking Normal, Abnormal, or NE (not examined). Each item must
have one box marked.
f. In the Notes box, item 44 and/or 89, the examining provider will annotate each abnormality by
entering the pertinent item number and provide comments. The provider will then mark each entry as “CD”
or “NCD”.
(1) Item 17: Head, face, neck, and scalp. The skull will be observed for defects and deformities
that may potentially interfere with the use of head gear. The skull should be closely examined, including
palpation, in applicants with a history of neurosurgery or head injury. Facial, scalp lesions, and cervical
lymphadenopathy should be noted.
(2) Items 18-20: Nose; Sinuses; Mouth and throat. Observe for diseases and disorders of the
nasal and oral cavities. For dental examination, see item 43 below.
(3) Items 21 and 22: Ears-General; Tympanic membranes.
(a) The external auditory canals and tympanic membranes (TM) will be examined. Adequate
examination consists of visualizing the reflective cone (triangle), the pars flaccida of the TM, and the handle
of the malleolus behind the TM. If all three are visualized, then adequate examination of the TM has
occurred. If one or more of these structures cannot be seen because of cerumen, then cerumen removal is
required.
(b) Cerumen removal will be provided for applicants whose TM cannot be properly visualized,
if determined necessary by the provider per Paragraph 6-4
.
(c) The mastoid processes must be examined for a mastoidectomy scar(s).
(4) Items 23-26: Eyes-General; Ophthalmoscopic; Pupils; Ocular motility.
(a) Routine examination will include a survey of the globe (pterygium), lids, and pupils; testing
of ocular motility in the six cardinal directions; and observation for nystagmus.
(b) An examination with an ophthalmoscope will be performed to evaluate the pupils,
refracting media, and the optic fundus.
(c) Inability to visualize the retinal vessels must be evaluated with specialty consultation IAW
Chapter 7.
(5) Item 27: Heart. Auscultation for heart sounds will include auscultation at the mitral, tricuspid,
aortic and pulmonic valve areas. Any heart murmur on exam without previously documented workup
should be evaluated with an echocardiogram, unless the examining provider is confident that the murmur
is benign.
(6) Item 28: Lungs and chest. Lungs will be auscultated anteriorly and posteriorly. The chest wall
will be visually examined for deformity. Female breasts will be visually examined for disqualifying skin
conditions, scars, nipple deformity and discharge. If necessary, in order to visualize the inframammary

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
66
crease for scars or lesions, the applicant will be asked to lift the breasts. No breast palpation/clinical
breast examination will be performed at the MEPS.
(7) Item 29: Vascular system. The extremities will be examined for varicosities, peripheral
vascular impairment, and other vascular pathology.
(8) Item 30: Anus and rectum. The male applicant will be asked to manually separate the buttocks
while standing and bending at the waist. The female applicant will be examined during the external
genitalia exam (see Paragraph 10b
below). The perianal area will be visualized for hemorrhoids, pilonidal
cysts/sinuses, anal fissures, fistulas, and warts. Digital rectal examination will NOT be performed at the
MEPS.
(9) Item 31: Abdomen and viscera. The abdomen will be palpated for organomegaly and
abdominal hernia with the applicant in the supine position.
(10) Item 32: External genitalia.
(a) Male examination. Applicants will be examined in the standing or supine position. If the
applicant is standing, then the provider should be standing or seated, but not kneeling. The testicles, penis,
scrotum and inguinal region will be examined both by visual inspection and palpation with gloves for
developmental or acquired abnormalities such as hernia and lymphadenopathy. All skin of the penis must
be checked with the foreskin retracted (if possible) by the applicant.
(b) Female examination. Applicants will be examined on the exam table in the dorsal
lithotomy position with stirrups or without stirrups (i.e., feet apart and flat on the examining table) or frog
leg position (i.e., feet together and knees apart). External examination of the vulva, perineum, and perianal
regions will be performed by visual examination for developmental or acquired abnormalities. The
examiner will palpate the inguinal region for developmental or acquired abnormalities such as hernia and
lymphadenopathy. The examiner will separate the labia manually to visually examine the epithelial and
mucosal surfaces of the vulva for lesions to include ulcerations, condyloma, open wounds, or other findings
consistent with a current genital infection. The perianal area will be examined for hemorrhoids, sinuses,
anal fissures, fistulas, and warts. The intergluteal area will be examined for pilonidal cysts/sinuses by either
having the female seated on the exam table leaning forward, or by having the female stand and lean forward.
In both approaches the applicant will manually separate the buttocks for adequate visualization of the
intergluteal cleft.
(11) Items 33 and 34: Upper extremities; Lower extremities. The upper and lower extremities
will be assessed during the orthopedic/neurologic (ortho/neuro) examination (see Chapter 12
). A focused
examination may be indicated based upon the history interview and/or review of medical documentation.
A history of instability/dislocation of any joint requires documentation of the focused examination of that
joint.
(12) Item 35 (a-c): Feet. The feet will be assessed during the ortho/neuro examination (see Chapter
12). Note that there are three blocks that must be addressed for item 35. Examination of the feet includes
but is not limited to evaluation for hammer and claw toes, pes planus, pes cavus, clubfoot, hallux valgus,
significant scars, calluses, corns, and plantar warts. Check the appropriate categories, including a. arch-
type, b. severity, and c. presence or absence of symptoms. To evaluate pes planus for rigidity, the Hubscher
maneuver may be performed. The maneuver is performed with the applicant weight bearing and the feet
flat on the floor, while the examiner dorsiflexes the hallux and observes whether the foot remains flat or

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
67
whether an arch forms. Formation of the arch with the maneuver indicates flexibility. Lack of arch
formation indicates rigidity which is, by definition, symptomatic and disqualifying. Abnormal findings,
even when not disqualifying, must be noted.
(13) Item 36: Spine, other musculoskeletal.
(a) The spine will be assessed during the ortho/neuro examination (see Chapter 12
). For female
applicants wearing sports bras during the ortho/neuro exam, the covered area may be evaluated during the
applicant’s medical examination.
(b) Complaints of lower spine discomfort are particularly difficult to evaluate. Special
emphasis must be placed on the history. Palpate the spinous processes and assess range of motion. Straight
leg raises may be used for assessing radiculopathy.
(c) Examination of the spine will include an evaluation for lumbar scoliosis, thoracic scoliosis,
and kyphosis. Chest wall and scapulae should be observed for symmetry. A scoliometer may be used for
screening, and if radiological evaluation is warranted due to apparent severity, then specify in the
consultation request the condition for which the radiologist must evaluate, and ensure that Cobb angle
measurements are requested.
(d) Any history of an orthopedic condition requires a focused examination of the involved
area. Annotate pertinent positive and negative findings of the focused exam (e.g., “non-tender” or “normal
range of motion”). Special attention should be given to a history of fractures involving joints, misalignment
of bone at the site of a healed fracture and/or compound fractures.
1. If a joint is unstable or symptomatic post-surgery, the applicant is medically
disqualified and no further consultation is required.
2. If the applicant is asymptomatic, but has a history of orthopedic surgery of a major
joint, a MEPS directed orthopedic consultation may be requested at the examiner’s discretion.
3. If surgical scars are discovered which were not reported during the prescreen process,
processing should continue and the applicant must submit the appropriate supporting medical
documentation as a med read.
4. MEPS directed X-rays may be utilized to evaluate for retained hardware, and to
determine adequacy of healing and alignment.
5. Palpable and/or symptomatic retained hardware which may interfere with the wear of
military equipment should be documented.
(14) Item 37: Identifying body marks, scars, tattoos.
(a) The provider will assess for medically significant body markings and scars.
(b) Body markings suspicious for self-harm must be documented and explained in item 89.
Detailed documentation should include illustrations, location, number, history of how scars were acquired,
age of event, hand dominance (right vs. left-handed), orientation, alignment, size, etc. A statement by the

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
68
applicant may be included in the record. The provider should determine if the applicant requires a MEPS
directed BH consult in order to render a qualification determination.
(c) The UMF 40-1-18
, Tattoos/Brands/Piercing/Ear Gauging/Scars/Birthmarks will be used to
annotate any identifying body marks according to the following guidance:
1. The CMO may authorize applicants to complete this form during the medical brief.
This can be done before the medical brief begins, during the brief, or any time prior to the administration
of the breathalyzer test. If the applicant completes the form during the brief, it will be reviewed and signed
by the provider during the medical history interview.
2. If not completed during the medical brief, the form may be filled out by the provider
or the applicant during the medical history interview. If only one side is filled out, the provider will sign
and date the bottom of that page. If both sides of the form are needed, the provider will sign the bottom of
the second page.
3. Item 44 will be annotated with “37. See UMF 40-1-18
”. Upon completion, the form
becomes a part of the medical packet and will be filed in the medical record as “other medical documents”.
(15) Item 38: Skin, lymphatics. Any rash, skin eruptions or other abnormalities, including acne
if extensive, should be documented. All skin surfaces of the applicant should be evaluated. The skin of the
arms, abdomen, and thighs must be examined using a flash light to detect scars which may be indicative of
self-harm. Woods lamp may be used for identifying hidden tattoos or scars hidden underneath tattoos.
(16) Item 39: Neurologic. If indicated by history, or by performance on the ortho/neuro exam
(e.g., severe balance or coordination deficiencies), a focused neurological evaluation must be performed
and documented in order to render a qualification determination.
(17) Item 40: Psychiatric. Specific BH evaluation may be necessary whenever a BH condition is
suspected. The provider should determine if the applicant requires a MEPS directed BH consult in order to
render a qualification determination. MEPS may provide copies of appropriate supporting medical
documentation to a consultant in a sealed envelope in order to assist them with completing the consultation.
(18) Item 41: Pelvic. Not conducted at MEPS. Check “NE”.
(19) Item 42: Endocrine. The thyroid will be palpated and consideration given to any physical
finding indicative of an endocrine dysfunction.
(20) Item 43: Dental Defects and Disease.
(a) Observe for diseases of the gingiva, presence of any orthodontic appliances, conditions
(caries), number of teeth, malocclusion, and other abnormalities. The lips should be retracted by the
applicant in order for the provider to adequately visualize the gum line and evaluate for caries. Record
“Acceptable” or “Not Acceptable” in item 43. “Not Acceptable” should be annotated for any disqualifying
dental condition. Significant dental abnormalities and defects will be annotated in item 44 and/or 89 if
necessary, even if not disqualifying.
(b) If the applicant is currently wearing orthodontic appliances and provides a signed letter
from their orthodontist stating that treatment will be completed before being sworn in or before beginning

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
69
AD, then they are not disqualified. Early completion/discontinuation of orthodontic treatment is not
disqualifying and requires no further orthodontist documentation if treatment was initiated for cosmetic
purposes or if malocclusion is confirmed to be corrected on the MEPS exam. During the shipping
inspection, the provider will ensure that the appliance has been removed.
(c) Permanent or removable retainers are not disqualifying if the applicant is in the retention
phase of treatment.
(21) Item 44: NOTES. Use item 44 to describe pertinent positive and negative findings on medical
examination. Enter the appropriate item number before each comment. Utilize item 89 for additional space
for documentation.
(SECTION - LABORATORY FINDINGS)
(22) Item 45: URINALYSIS
(a) Item 45a: Albumin. Enter the value for urine samples that show proteinuria on initial
testing; enter results as “NEG,” “Trace,” “+1,” “+2,” “+3,” or “+4”.
(b) Item 45b: Sugar. Enter the value for urine samples that show glycosuria on initial testing;
enter results as “NEG,” “100,” “250,” “500,” “1000,” or “>2000”.
Note: See Appendix D
for guidance on positive results for albumin and sugar.
(23) Item 46: URINE HCG.
(a) Enter the test result as “NEG” or “POS”.
(b) If the test is positive, the applicant will be escorted to the provider and informed by the
provider that the test indicates that she might be pregnant. The medical examination will be discontinued
and the provider will advise the applicant to see her PCP for further evaluation.
(24) Item 47: H/H. Hemoglobin/hematocrit is not conducted at the MEPS.
(25) Item 48: BLOOD TYPE. Blood type is not conducted at the MEPS.
(26) Item 49: HIV RESULTS. Record according to UMR 40-8
.
(a) HIV Specimen ID Label – Drug Test Specimen Label boxes.
(b) Because the MEPS use the same specimen labels for HIV and drug testing, the MEPS
WILL NOT place two labels in these two boxes. USMEPCOM will utilize these two boxes for HIV and
Drug testing only. The first time an applicant provides a HIV blood sample, a specimen label will be applied
to the space marked “HIV Specimen ID Label”. The Drug Test Specimen ID Label box WILL NOT be
used at that time. If an HIV re-draw is required, the second specimen label will be applied to the space
marked “Drug Test Specimen ID Label”. Any newly assigned specimen label for additional test(s) for HIV
or Drug testing must be placed in the "Drug Test Specimen ID Label" box. If there is no space in the "Drug
Test Specimen ID Label" box, use item 73 or item 89.
(27) Items 50 and 51: DRUGS; and ALCOHOL. Record according to UMR 40-8
.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
70
(28) Item 52: OTHER. Clearly annotate the test name and result of any additional testing required.
(SECTION - MEASUREMENTS AND OTHER FINDINGS)
Note: Items 53 through 72 are the specific areas of the medical process performed by the medical
technicians or trained MEPS staff.
(29) Item 53: HEIGHT. Record height (rounding up to the nearest half inch) in decimal format
(e.g., 65.25 to 65.50).
(30) Item 54: WEIGHT. Record weight to the nearest pound (e.g., 150).
(31) Item 55:
(a) 55a MIN WGT. Enter minimum weight standard per Service-specific standards. (See
Service Height and Weight on SPEAR
)
(b) 55b MAX WGT. Enter maximum weight standard per Service-specific standards. (See
Service Height and Weight on SPEAR
)
(c) 55c MAX BF %. Maximum body-fat percentage allowed (use if the screening weight is
not within the Service-specific standards).
(d) 55d BMI. The body mass index of an underweight applicant will be documented in this
box.
(32) Item 56: TEMPERATURE. Record temperature in degrees Fahrenheit to the nearest 1/10
of a degree (e.g., 99.7). (See Paragraph 8-8
for guidance.)
(33) Item 57: HEART RATE. Record HR in beats per minute (e.g., 76). (See Paragraph 8-7
for
guidance.)
(34) Item 58: BLOOD PRESSURE. Record BP in mmHg (e.g., 135 in SYS and 75 in DIAS).
(See Paragraph 8-6
for guidance.
(35) Item 59: RED/GREEN. Leave blank. Red/Green testing results are recorded in item 66.
(36) Item 60: OTHER VISION TESTS. In item 60.a. record hair color, and in item 60.b. record
right and left eye color. For any DD Form 2808
that is not printed from USMIRS this item number is labeled
OTHER VISION TESTS, and not have the hair color and eye color overprints
(37) Items 61 and 62: DISTANCE VISION; REFRACTION BY AUTO, MANIFEST or
CYCLO. (See Paragraph 7-5
for guidance.)
(38) Item 63: NEAR VISION. (See Paragraph 7-5
for guidance.)

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
71
(39) Item 64: HETEROPHORIA. Performed only on selected applicants based upon Service
requirements or clinical indication. (For instructions on how to conduct these tests refer to the TSJTS
for
vision). Results will be annotated in the individual boxes.
(40) Item 65: ACCOMMODATION. Leave blank.
(41) Item 66: COLOR VISION.
(a) The PiP test results will be recorded as the NUMBER CORRECT over total number of test
plates displayed (e.g., “13/14 Corr”).
(b) The Red/Green test will be recorded as Pass/Fail.
(c) The Color DX box is not used for MEPS medical processing. Leave blank.
(42) Item 67: DEPTH PERCEPTION. For recording the results of testing with the AFVT and
MCST, see vision TSJTS
for guidance.
(43) Items 68 and 69: FIELD OF VISION; NIGHT VISION. Leave blank. Not tested at the
MEPS.
(44) Item 70: INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE. For recording IOP results see vision TSJTS
for
guidance.
(45) Items 71a and b: AUDIOMETER. For recording audiometry results see Paragraph 6-1
for
guidance.
(46) Item 72a: READING ALOUD TEST. The reading aloud test (RAT) will be performed when
required (only on selected applicants). Use of the RAT for the purpose of evaluation of English language
proficiency is not authorized. The RAT may be administered by a trained Medical Department technician
(see TSJTS
for administering the RAT). If the medical technician determines that the applicant has
difficulty performing the RAT, they will refer the applicant to the provider to repeat the test. The provider
will make the determination of “SAT” or “UNSAT” in item 72a. and record their observations in item 89.
A copy of the reading aloud paragraph may be found on
SPEAR.
(47) Item 72b: VALSALVA. The Valsalva maneuver will be performed and annotated, when
required, to check mobility of tympanic membranes. Check “SAT” box if movement is observed in both
tympanic membranes; if not, check “UNSAT”.
(48) Item 72c: OTHER TESTING. (See Paragraph 7-1
for guidance.)
(49) Item 73: NOTES AND/OR INTERVAL HISTORY. The medical technicians will use this
item to record medical information as follows. The Drug Result Label MUST be stamped/affixed in item
73 in order to comply with drug result recording standards IAW UMR 40-8
. The Drug Result Label will be
placed in item 73 at medical check-in before any other annotations are made in item 73. If additional space
is needed then item 89 and the
SF 507 will be used. Prioritization of entries in item 73 should be the Drug
Results Label, the MEPS Examination Consent and Chaperone Stamp, additional heart rates, missing
corrected lenses information. Additional testing such as a third hearing test which may occupy a lot of space
should be documented in item 89 or on the
SF 507.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
72
(50) Item 74: MEDICAL QUALIFICATION/DISQUALIFICATION. Rendering a medical
qualification determination is the primary mission of USMEPCOM as defined in the DoDI 6130.03-
V1. The profiling examiner will check the appropriate box “IS MEDICALLY QUALIFIED” or “IS NOT
MEDICALLY QUALIFIED” only after they have rendered the final medical qualification
determination. In addition to checking item 74, the approving provider must sign item 85 (i.e., bottom-
line the profile). If the applicant is not medically qualified for accession, and the applicant is available,
have the applicant sign and date items 75a and b. If the applicant is not available when the medical
disqualification determination is rendered, then the applicant will be notified via a Disqualification (DQ)
Letter. See Appendix E
for guidance.
Note: If an applicant’s profile is left in an “open” or a temporarily disqualified status (3T), then
the final medical qualification determination cannot be made, and neither box will be checked in item 74.
(51) Item 75. I have been advised of my disqualifying condition(s); items 75a, SIGNATURE
OF EXAMINEE; item 75b: DATE. This section will be signed and dated by the applicant on the date of
the examination when the applicant has been determined to be medically disqualified due to a disqualifying
condition (DQ). If an applicant becomes disqualified after supporting medical documentation review or
when the applicant is not present, the DQ letter must be sent to the applicant. The phrase “applicant notified
by letter” will be recorded in the applicant signature block (item 75a). The letter must be dated with the
date the applicant was determined to be medically disqualified. A copy of the letter will be placed in the
applicant’s medical packet and maintained in the MEPS medical office file under Record Number 40/500A,
“General Medical Services Files” (see Appendix A,
Section III) for 2 years, then destroyed.
(52) Item 76: PHYSICAL PROFILE. (See Paragraph 11-2
on Profiling.)
(53) Item 77: SIGNIFICANT OR DISQUALIFYING MEDICAL DIAGNOSES. MEPS will
use item 77 for listing medically disqualifying conditions only. Record all “CD” medical conditions listed
in SECTIONs VII and IX of the DD Form 2807-2
, as well as those identified during the medical
examination, and temporary disqualifications. List item number (17 through 72) from the DD Form 2808
(e.g., for self-harm use item 40 Psychiatric, for overweight use item 54 Weight). Use common medical
terminology for the condition, list the corresponding Accession Policy (AP) approved ICD code, and the
profile series (e.g., S3P, P3T) for each medical condition. Annotate the RBJ date for all temporary
disqualifications. Place a check mark in the disqualified box. The profiler will then record their initials.
Note: If a temporarily disqualifying condition (TDQ) has resolved, check the qualified box for the
condition, and line out and initial the disqualified check mark. The medical condition is recorded in this
item as succinctly as possible given the limited line space. For instance, “Acne” is written in item 77 and
“Extensive cystic acne on back, shoulders, and chest” is written in item 89. For each disqualifying medical
condition listed, the profiling provider should cite the corresponding DoDI 6130.03
section in item 89.
If a waiver is approved for a disqualifying condition, record the Service issuing the waiver and the date that
the MEPS received it. If the waiver is denied, complete item 87 but leave waiver block in item 77 blank.
(54) Item 78: SUMMARY OF MEDICAL DIAGNOSES. A medical condition that is under
evaluation (identified as O for “open” PULHES) will be listed under this item. Also, any other diagnoses
thought by the medical provider to be significant (but not disqualifying) are recorded in this space.
Statements should be preceded by the corresponding item numbers as described in item 77, if applicable.
If additional space is necessary, item 89 will be used for documentation. If an “open” condition is

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
73
subsequently determined to be disqualifying, it will then be annotated appropriately by completing an
additional row in item 77.
(55) Item 79: RECOMMENDATIONS. This block is used to document a brief plan of action for
each “open” condition. When the plan of action for a particular item has been completed, write the word
“done” and initial for each item. Provide all important additional details (results of lab tests or consults,
dates, etc.), explanation, and/or discussion with a dated and signed entry for each in item 89 or SF 507
and
indicate in this box “see item 89” or “see SF 507”.
(56) Item 80: MEPS WORKLOAD. Enter the work identification code (WKID), status (ST), and
date. The MEPS Medical NCOIC/SUPMT or trained medical technician will complete item 80, and date
and initial each entry. If there are more than six WKID and ST entries, then record additional entries in item
73 or on the SF 507
.
(57) Item 81: MEDICAL INSPECTION DATE. Enter the date of the medical inspection,
followed by the applicant’s height (HT), weight (WT), percent body fat (%BF), if required, and maximum
authorized weight (MAXWT) in the appropriate columns. For HCG results (female applicants only), enter
“POS” for a positive result and enter “NEG” for a negative result. After the inspection is conducted and
any new information is annotated, the provider will check qualified or disqualified as appropriate,
print/stamp and sign their name. When conducting a medical inspection, and there is a “3” in the PULHES,
block 81 is checked as “disqualified.” Applicants with approved waivers remain disqualified.
(58) Items 82a and b: TYPED OR PRINTED NAME OF PHYSICIAN OR EXAMINER
AND SIGNATURE. These items must be completed by the interviewing provider and signed on the date
of the interview.
(59) Item 83a and b, or Item 84a and b: If a different provider conducts the medical examination,
then the examining provider will print/stamp and sign their name in items 83a and b. If more than one
provider participates in the medical examination of the applicant, for example a second provider oversees
the ortho/neuro exam, then the second provider prints/stamps and signs their name in items 84 a and b.
Note: If the medical examination was done by a non-profiling provider, i.e., DPC-1 or DPC -2,
then a profiling provider will review the record for completeness and then prints/stamps and signs their
name in items 84a and b.
(60) Items 85a and b: Once the medical processing of the applicant is complete, the profiling
provider will review the medical packet. This provider will then print and sign their name (bottom-line) in
items 85a and b once the PULHES has been completed and item 74 has been checked. If there is a “3T” or
an “O” in the profile, then the PULHES is not complete and the DD Form 2808
should not be bottom-lined.
Note: The reviewing profiler may be the same person listed in items 82a/b and/or 83a/b.
(61) Item 86 a, b, c: The medical staff member that performs the administrative review of the
medical packet on the date of the initial medical examination will complete these items after reviewing the
forms to ensure that any identified deficiencies or errors are corrected appropriately.
(62) Item 87: WAIVER GRANTED. If a waiver request was approved, the profiler will check
“Yes”, and will record both the name of the individual from the SMWRA approving the waiver and the
date of the waiver. The profiler will also complete item 77 as above. If additional space is required (for

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
74
example, multiple waivers), use item 89 or an SF 507. If a waiver request was disapproved, and the Service
submits a copy of the documentation from the SMWRA to the Medical Department for review, then the
profiler will check “No”. The waiver documentation from the SMWRA, if provided to the MEPS, becomes
part of the medical packet.
(63) Item 88: NUMBER OF ATTACHED SHEETS. The number of pages of supporting medical
documentation submitted on the day of or after the medical examination will be annotated in item 88. The
DD Form 2807-2
and supporting prescreen documentation will not be accounted for in this block.
(64) Item 89: ADDITIONAL REMARKS (extension of blocks 44, 73, 77, 78 or 79).
(a) The provider will use this space to:
1. Document additional information or supply details to provide clarification of the
medical decision-making process.
2. Summarize the results of a test or consultation.
3. Document significant interval history including new findings on inspection.
4. Document any other medical/profiling information deemed significant in order to
render a medical qualification determination.
(b) Additionally, “Drug Test Specimen ID Label” can be placed in this block if there is no
space under item 73.
(c) Date, stamp/print name, and sign name under every entry. When appropriate, supply
corresponding item number from items 17-43. An SF 507
can be used if additional space is required.
11-2. Profiling and Qualification Determination
a. The physical profile serial system is used by the provider performing accession medical evaluations
in making the qualification determination, and is recorded on the DD Form 2808
. The system is based
primarily upon the function of body systems and their relation to military duties. For the purpose of the
accession medical evaluation, the functions of the various organs, systems, and integral parts of the body
are considered. Since the analysis of the individual's medical, physical, and mental status play an important
role in assignment and welfare, not only must the functional grading be executed with great care, but clear
and accurate descriptions of any deviations from medical standards, as defined in the
DoDI 6130.03-V1,
will be provided. In developing the system, the functions have been considered under six factors designated
“P-U-L-H-E-S” in order to classify individuals according to their functional abilities. The letter designators
are to be considered for the following factors:
(1) P—Physical capacity or stamina. This factor, general physical capacity, typically includes
conditions of the heart, respiratory system, gastrointestinal system, genitourinary system, nervous system,
allergic, endocrine, metabolic and nutritional diseases, diseases of the blood and blood forming tissues,
dental conditions, diseases of the breast, and all other organic defects and diseases that do not fall under
other specific factors of the system (e.g., underweight/overweight, underheight/overheight).

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
75
(2) U—Upper extremities. This factor includes the hands, arms, shoulder girdle, and upper spine
(cervical, thoracic) with regard to strength, range of motion and general efficiency.
(3) L—Lower extremities. This factor includes the feet, legs, pelvic girdle, lower back
musculature and lower spine (lumbar and sacral) with regard to strength, range of motion and general
efficiency.
(4) H—Hearing and ears. This factor includes auditory acuity as well as diseases and defects of
the ear.
(5) E—Eyes. This factor includes visual acuity as well as diseases and defects of the eye.
(6) S—Psychiatric. This factor includes personality, psychiatric and any substance abuse
disorders.
(7) X–Air Force Incremental Lifting Device. This is not used by the MEPS Medical Department.
(8) D–Drugs. This is not currently used for MEPS processing.
b. For applicants who are processing under the DoD accession medical standards (DoDI 6130.03-
V1), each letter designator must be assigned a numerical designator for evaluating the individual’s
functional capacity in each of the six factors. The following numerical designators O, 1, 3T or 3P will be
used for accession purposes.
(1) O—Open status. This designator is used when further supporting medical documentation is
required in order to render a medical qualification determination. A Med Read Cover Sheet will be provided
by the Medical Department to the SL specifying the documentation being requested (see Paragraph 11-4
).
UMF 40-1-2-R-E, Record of Medical Examination/Treatment may be given to the applicant to assist in
procuring the additional supporting medical documentation from their provider(s).
(2) 1—Qualified. This designator will be used when the applicant meets the medical accession
standards, as defined by the current version of the DoDI 6130.03-V1
.
(3) 3T—Temporarily disqualified (TDQ). This designator is used for a medical condition (e.g.,
acute self-limiting upper respiratory infection) or physical condition (e.g., exceeding a Service-specific
maximum weight) that is expected to resolve. The applicant must be given an RBJ date based on the
condition’s expected resolution timeframe and/or regulatory guidance. J-3/5/7 MD reserves the right to
adjust any RBJ date.
(4) 3P—Disqualified (DQ). This designator is used for a medical condition that is listed in the
current version of the DoDI 6130.03-V1
as not meeting the medical standards for appointment, enlistment
or induction into the Military Services.
Note: To ensure the right profile designator is entered into USMIRS, a hierarchy will be established: “3P”
supersedes a “3T”, which supersedes an “O”. Recording the profile in this hierarchical order will ensure
the correct profile is entered into USMIRS by the medical technician.
c. A single medical condition will not have two numerical designators. For example, when an
applicant has a history of asthma that was not disclosed on prescreen, the profiling provider should not

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
76
annotate “3P/O” under the P - factor. Only the “O” designator should be assigned for this condition until
supporting medical documents are received, reviewed and a medical qualification determination is
rendered.
When several medical conditions are identified, then multiple numeric designators may be used for
annotation under a single letter factor. If this occurs, the profiling provider will use the appropriate number
designators for each condition.
(1) For example, an applicant who has a history of moderate mitral regurgitation (“3P”), is
overweight (“3T”), and has a history of asthma that was not disclosed on prescreen and additional
documentation was requested (“O”), would have the following profile:
Figure 11-1. Example of Applicant Profile with “3P” for moderate mitral regurgitation, “3T” for
overweight, and “O” for medical records concerning his asthma.
P
U
L
H
E
S
Initials
Date
3P/3T/O
1
1
1
1
1
CMO
YYYYMMDD
Figure 11-1. Example of Applicant Profile with “3P” for moderate mitral regurgitation, “3T” for
overweight, and “O” for medical records concerning his asthma.
The profiling provider will ensure that the disqualifying conditions (‘3P” and “3T”) are documented in item
77, with an RBJ date calculated for being overweight (“3T”). In addition, the profiler should annotate
specific recommendations for the “open” (“O”) or “TDQ” conditions in item 79 or item 89 if necessary. In
this example, item 79 would read:
“28: Submit all medical records regarding treatment for asthma, and all records from the past 5 years”
“54: overweight RBJ 16 days to lose 4 pounds (YYYYMMDD)”
For a “DQ” condition, in this case moderate mitral regurgitation, the following should be annotated under
item 89:
“27: moderate mitral regurgitation, CD IAW 5.11.b(3), I34.0.”
(2) This documentation method ensures that any provider reviewing the medical packet will be
able to understand the previous provider’s intentions.
(3) As illustrated in Figure 11-1
above, once the applicant has submitted the supporting medical
documentation, and it is determined that the remote history of asthma is “NCD”, the profile should be
changed to P = “3P/3T” for mitral regurgitation and overweight (
Figure 11-2, line 2). Once the applicant
meets the Service specific weight/body fat standards (Figure 11-2, line 3), the profiling provider will change
the profile to “3P” for mitral regurgitaion.
Figure 11-2. Example of Applicant Profile Continued
P
U
L
H
E
S
Initials
Date
3P/3T/O
1
1
1
1
1
CMO
YYYYMMDD
USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
77
3P/3T
1
1
1
1
1
CMO
YYYYMMDD
3P
1
1
1
1
1
CMO
YYYYMMDD
Figure 11-2. Example of Applicant Profile Continued
(4) In Figure 11-2
above, as the steps are completed, item 79 would read:
“28: Submit all medical records regarding treatment for asthma, and all records from the past 5 years
DONE, PROVIDER INITIALS”
“54: RBJ 16 days to lose 4 pounds (and give the date) DONE, PROVIDER INITIALS”
(5) It is a Service-specific function to refer cases of medically disqualified applicants to the
Service Medical Waiver Review Authority (SMWRA) for a medical waiver review and decision. This
decision is based on the guidance and specific needs of the Service. The medical packet submitted for a
medical waiver consideration must have a final closed profile (no “O” or “3T” designators). The final
medical disqualification determination must be rendered, and item 74 must be completed. Also, the
DD
Form 2808 should be “bottom-lined” (items 85a and b must be completed).
Note: Incomplete medical records, with incomplete item 74, containing numerical designator of “3T” or
“O” in item 76, and not bottom-lined, should not be submitted for medical waiver consideration.
d. Applicants previously separated or discharged from the Military for any medical reason with or
without disability are not medically qualified for accession.
e. When there is a difference of interpretation of the medical accession standards IAW the
DoDI
6130.03-V1 between MEPS providers, the CMO is the final local authority. If the issue is not resolvable
at the local level, the MEPS will submit a MOC ticket to J-3/5/7 MD for further guidance.
f. Temporary profiles issued at one MEPS may be removed at another MEPS if the condition for
“TDQ” has resolved.
g. “3P” profiles issued at one MEPS may be changed at another MEPS for one of the following
reasons:
(1) The profile was originally given for a condition that is no longer disqualifying IAW the
DoDI
6130.03-V1.
(2) The J-3/5/7 MDC (or their designee) concurs that the original profile determination was
incorrect.
h. When changing a physical profile (e.g., from a disqualified or open status to a qualified status) or
correcting an error in the profile, the entire profile will be annotated in the next row and the profiling
provider will record their initials and the date in the designated items.
i. If more than the five rows are needed to annotate changes to an applicant’s profile, indicate in item
76 after the words “PHYSICAL PROFILE” that additional profiles are recorded in item 89. If space is not
available in item 89, use an SF 507.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
78
11-3. Medical Waivers
a. A medical waiver is a Service decision to waive an accession medical standard for a pre-existing
condition which is disqualifying for Military Service IAW DoDI 6130.03-V1
. Each DOD Component may
initiate and request a medical waiver for a disqualified applicant. Each DOD Component’s waiver authority
for medical conditions, i.e., the SMWRA, will make a decision based upon all available information
regarding the issue or condition as well as the specific needs of the Military Service. The medical waiver
documentation is considered supporting medical documentation and will be reviewed IAW the review
timeline in
Appendix F, and will be included in the applicant’s medical packet.
b. Medical Waiver Considerations: The role for medical waiver determination is reserved solely for
the DoD Components IAW the DoDI 6130.03-V1
.
(1) MEPS medical providers do not have medical waiver authority for any condition and are not
authorized to make any specific recommendations for or against a medical waiver.
(2) The medical packet generated by the MEPS Medical Department should paint a clear and
succinct picture of each medical condition in order to enable the SMWRA to make their medical waiver
decision.
(3) If the MEPS accession medical examination expires (2 years after completion), then the
associated medical waivers also expire.
(4) Medical waivers granted by one Service are not valid for another Service.
c. SMWRA Courtesy Consultation/Ancillary Services Requests: For guidance on courtesy
consultation/ancillary service requests see Chapter 13
.
d. Resolving Differences of Interpretations of Accession Medical Standards:
Disagreement may arise between the SMWRAs and the MEPS profiling provider’s interpretation
of the medical qualification standards as listed in the DoDI 6130.03-V1
. If a waiver discrepancy or dispute
occurs, then the applicant will not process further until a final disposition decision is determined. In these
cases the CMO will do the following:
(1) Attempt to resolve the case at the MEPS level by discussing the case with the SMWRA.
(2) If the SMWRA and the CMO are unable to resolve the case, then the MEPS will submit a MOC
ticket to J-3/5/7 MD for assistance with resolution. The MOC ticket will be submitted with all pertinent
details of the case and if requested, the applicant’s medical records will be sent to J-3/5/7 MD via encrypted
email.
e. A current list of the SMWRA members and contact information is located on SPEAR
for
consultation as needed.
11-4. Medical Read
A medical read (med read) is any non-MEPS generated supporting medical documentation (other than
consultations, ancillary service results, and medical waivers) that has been requested and/or submitted
following the initial medical examination. A med read occurs when the prescreen process does not provide

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
79
adequate information to render a medical qualification determination on a pre-existing medical condition
which is subsequently identified at the time of the medical history interview or during the medical
examination. A med read will be conducted as follows:
a. When a provider determines that med read documents are required in order to render a medical
qualification determination, the applicant’s profile will be placed in an open status under the appropriate
PULHES letter designator in item 76 of the DD Form 2808
(Physical Profile box). This will be entered
into USMIRS.
b. The additional supporting medical documentation will be requested by the MEPS provider using
the fillable electronic “Medical Read Cover Sheet” (see Appendix G
) and a copy will be submitted to the
SL for action.
c. The Medical Department will submit the coversheet to the SL using one of the following methods
(see Appendix I
for guidance on establishing an encrypted e-mail of direct prescreen coversheet exchange):
(1) The Medical Department may give the med read cover sheet to the applicant for hand carrying
to their SL after check out from the Medical Department.
(2) The Medical Department may send it to the SL via:
(a) Outlook encrypted email
(b) Shared network folder
(3) The Medical Department may gather all med read cover sheets from all applicants during
medical check-out and:
(a) Personally deliver all medical read cover sheets to the appropriate SL
(b) Establish a med read cover sheet SL pick up point: In this case the Medical Department
will establish a specified location in a secure area to which the SLs can be given access. Copies of med
read cover sheets will be separated by Service (i.e., in a stackable/hanging paper tray) and covered with a
DD Form 2923
, Privacy Act Cover Sheet. The Medical Department will be overall responsible for the
time(s), place, and the way SLs pick up med read cover sheets as long as PII and PHI is protected and does
not interfere with applicant medical processing.
Note: No matter the method, the med read cover sheet must be delivered/available to the SL on the same
day that the applicant processes. It is up to the MEPS to determine what process is best for them based on
facility layout and size, staffing, workload, etc.
d. The med read cover sheet is only to be used when supporting medical documentation is requested
in order to complete the medical examination and render a medical qualification determination IAW
DoDI
6130.03-V1, and will not be used for consultation or waiver results.
e. Prior to submission of the med read packet, the Service will complete the SL portion of the cover
sheet, and will number the med read documents (including the coversheet) as follows: page #/total number
of pages submitted.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
80
f. The med read packets may be submitted by the SL either to the files room or directly to the Medical
Department as follows:
(1) If med read is submitted to the MEPS files room (similar to the prescreen process) then the
files room personnel will do the following:
(a) Pull the applicant medical record, and place the med read cover sheet and additional
documents in it (loosely; not pronged down). The medical record, the med read coversheet, and the
requested additional document are referred to as a med read packet.
(b) Sign out the med read packet to the Medical Department.
(c) Place the med read packet(s) in an area where they may be picked up by a medical
technician. This may be done throughout the MEPS workday either randomly or at established time(s) that
best suits the overall MEPS workflow.
(2) Med read coversheets and attached supporting medical documentation may be submitted
directly to the Medical Department by the SL, either periodically throughout the day or at established time
frames. Medical personnel will then:
(a) Take all med read coversheets with attached additional documents to the files room.
(b) Charge out the appropriate medical record from the files room.
(c) Place the med read cover sheet and additional documents in the appropriate medical record
creating a med read packet.
(d) Take the med read packet to the Medical Department for review by MEPS providers.
g. There is no requirement to update USMIRS (with WKIDs or N statuses) upon receipt of the med
read packet (other than the record being charged out).
h. The Medical Department will annotate the number of the med read pages received (including the
cover sheet) in item 88 of the DD Form 2808
.
i. The med read packet will be reviewed IAW the timeline in Appendix F
based upon the number of
pages submitted.
j. The MEPS provider will review the supporting medical documentation and summarize all pertinent
medical information on the DD Form 2808 item 89 (or SF 507
).
(a) If the provider review generates an additional request for more supporting documentation, then
the applicant’s profile will be left in an open status. A new “Medical Read Cover Sheet” will be completed
by the provider and returned to the Service for action.
(b) Upon receipt of the new med read documents, the SL will calculate a new timeline based on
the total number of newly submitted pages. For example, if the initial med read had 30 pages of supporting
documentation and the new submission has 24 additional pages, then the total # of pages used for
calculation is 24 (instead of 54).

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
81
k. When no further supporting medical documentation is required in order to render a qualification
determination, then the provider will update the physical profile in item 76, and render a qualification
determination in item 74 of the DD Form 2808
. Items 77 and 78 will be updated as needed, and items 85
a and b will be completed.
l. The MEPS Medical Department will update USMIRS accordingly.
m. The completed packet will be returned to the files room.
11-5. Notification of Disqualified Applicants
USMEPCOM is not a medical treatment facility, therefore further diagnosis and treatment cannot be
provided to the medically disqualified applicant. Furthermore, USMEPCOM is not financially responsible
for costs associated with any necessary follow-up evaluation and/or treatment based on the applicant’s
screening evaluation.
a. If the applicant is present when the medical disqualification determination is rendered, the MEPS
medical provider will explain to the applicant the nature of the medical disqualification. The applicant must
be informed of any serious medical condition and whether or not this condition needs immediate/urgent
medical attention. If during the MEPS accession examination a medical condition is found that requires
further evaluation and/or treatment, then the applicant will be referred to their health care provider.
Additionally, the applicant should be advised that the government will not cover any costs of non-MEPS
directed evaluation and/or treatment for their medical issue. The applicant will sign item 75a and enter the
date in item 75b.
b. If a disqualified applicant is not present when the medical qualification determination is rendered,
the CMO/ACMO/MO/FB-CMO will send the applicant a “Disqualification (DQ) Letter”, to advise them
of the medical disqualification. The DQ letter will be sent only for a disqualifying medical condition. The
medical provider will annotate in item 75a on the DD Form 2808
“Applicant notified by letter”, and enter
the date of the notification in item 75b. If the applicant is a minor, a separate DQ letter will be sent to the
applicant’s parent/guardian.
c. If a serious medical condition is identified by the MEPS Medical Department and the applicant is
present, they should be notified of such condition by the CMO/ACMO/MO/FB-CMO and advised to seek
further care. The provider should make appropriate annotation under item 89 on the DD Form 2808 or
SF
507 that the applicant was notified and advised to seek further care. If the applicant is not present, an attempt
to contact the applicant via phone in addition to sending a “Serious Medical Condition Letter” must be
made as soon as the information is reviewed by the MEPS. Appropriate annotations should be made in item
89 or on an
SF 507. The letter should be sent according to the following:
(1) A copy of the “Serious Medical Condition Letter” must be sent via certified mail to the
applicant with the serious medical condition. When the signed acknowledged receipt is returned, it must be
included in the medical administration file.
(2) The “Serious Medical Condition Letter” and all supporting medical documentation is
authorized to be sent via government-contracted, next day delivery service.
(3) An applicant who has been notified in person must still be sent a certified letter.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
82
d. A copy of all letters sent to the applicant will be placed in the applicant’s medical packet and in a
medical administration file for two years. Templates for both letters can be found on SPEAR
and are in the
Appendix E. Templates should also be saved in several Medical Department local share drives in the event
of connectivity issues.
e. Templates of the letters provided in Appendix E
are the only templates that have been officially
approved by USMECOM for the purpose of applicant notification, and may not be altered locally.
11-6. Air Force X-Factor Testing
a. All Air Force applicants receive an X-Factor code for Air Force Specialty Code (AFSC) processing.
The Service performs this testing themselves. The MEPS Medical Department staff are not authorized
to conduct or provide medical coverage during the X-Factor testing.
b. For applicants who have a TDQ or DQ in the Hearing (H), Vision (E), and/or Psychiatric (S)
categories of the PULHES, MEPS providers may annotate on item 89 of the DD Form 2808
: "DQ condition
does not preclude X-Factor testing." For applicants who have a TDQ or DQ in the Physical Condition (P),
Upper (U), and Lower (L) factors of the PULHES, MEPS providers may annotate on item 89 of the
DD
Form 2808: “Medical Waiver permission needed for X-Factor”.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
83
Chapter 12
Orthopedic/Neurologic
12-1. Orthopedic/Neurologic Screening Examination
The orthopedic/neurological examination (ortho/neuro or ONE) may be performed individually or in groups
to afford accurate and detailed observation of applicants. This screening is part of the applicant’s accession
medical evaluation. Trained MEPS personnel will verbally describe and/or physically demonstrate each
maneuver, freeing the examining provider to observe the maneuvers. This can also be accomplished by
using the Ortho/Neuro DVD. The demonstrator must be the same biological sex as the applicants being
tested. The demonstrator will notify the examining provider if a suspected abnormality is observed in an
applicant. The provider has the option to lead the session. A provider must be in the room while the
ortho/neuro maneuvers are being completed by the applicants.
Note: The blood pressure, heart rate, and medical history interview must be completed and a negative HCG
result must be documented prior to the ONE.
a. The ONE is a series of maneuvers intended to identify orthopedic or neurological abnormalities
that may require a focused examination by the MEPS medical provider or by a MEPS-directed consultant.
It is not an exercise or strength test. An applicant must not be medically disqualified solely based on
difficulty or inability to perform a maneuver. Difficulty or inability to perform a maneuver may indicate
an underlying medical condition. The applicant may be medically disqualified for Service due to the
underlying condition IAW DoDI 6130.03-V1
.
b. The purpose of this examination is to observe for:
(1) Abnormalities in constitution, posture, habitus, and gait
(2) Deformities, particularly of the extremities
(3) Range of Motion (ROM) of joints
(4) Muscle absence, decreased muscle bulk, or muscle atrophy
(5) Muscle strength
(6) Coordination
(7) Missing and/or incomplete digits, extra digits, or digit deformities
(8) Skin eruptions and other skin abnormalities such as scars, eschars, and skin grafts
(9) Apprehension, reluctance, or inability to perform a prescribed maneuver because of fear that it
will produce pain or dislocate a joint
(10) Other abnormalities
c. The ONE begins with the provider, trained MEPS personnel, or the ortho/neuro DVD asking all
applicants, as a group, if they have had any of the following:
(1) Current or recent injuries

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
84
(2) Cardiovascular/heart problems
(3) Recent surgery
d. If the additional history requires further questioning, it must be done in private. Instruct applicants
to immediately report any pain, numbness, or other problems that develop during the examination.
e. Trained MEPS personnel must verbally describe and/or physically demonstrate each movement, as
described below. The provider must be able to closely observe each applicant during every prescribed
maneuver. The maximum number of applicants allowed in the ortho/neuro room is determined by the
physical layout and size of the room. There will no more than 8 applicants per provider in the ortho/neuro
lineup.
f. While providers and/or trained MEPS personnel may choose to exercise their discretion by varying
the order of ONE movements, all maneuvers must be accomplished with all applicants.
g. The recommended sequence for the ONE maneuvers are as follows:
(1) Arch and feet examination
(a) APPLICANTS: Stand relaxed with arms to the side, heels together, feet spread at least 90
degrees for inner arch evaluation, thereby simultaneously evaluating the required minimal 60 degree
individual hip abduction requirement.
(b) PROVIDER: Observe each applicant for:
1. General body habitus
2. Clinically significant scars and skin abnormalities
3. Pes planus, Pes cavus, hallux valgus, hammertoes, and other foot deformities
(2) Arm circles
(a) APPLICANTS: Make full arm circles by extending arms forward, rotating above the head,
back, and down to complete full circles. Repeatedly mimic swimming backstrokes by simultaneously
rotating both fully extended arms backward from each shoulder (liked paired windmills) by circularly
rotating both shoulders backwards while maintaining fully extended and locked elbows above the head, back,
and down to complete full circles. Repeat until instructed to stop.
(b) PROVIDER: This is a provocative test intended to aggravate or induce shoulder
subluxation and shoulder pain in those applicants with shoulder problems or concealed history thereof.
Observe each applicant for:
1. Symmetry and coordination of shoulders, clavicles, and arms
2. Subluxation of shoulders
3. General coordination and balance

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
85
4. Facial grimacing / Facial Apprehension Sign
5. Impaired shoulder abduction to less than 90 degrees
6. Impaired shoulder forward elevation to less than 90 degrees.
(3) Arms out and Flex elbow/touch shoulder
(a) APPLICANTS: Fully extend arms out laterally at right angles to body, make fists with
thumbs pointing up and elbows locked. Flex elbows and touch thumbs to shoulder. Repeat rapidly until told
to stop.
(b) PROVIDER: This is a provocative test intended to aggravate or induce elbow subluxation
and elbow pain in those applicants with elbow problems or concealed history thereof. Observe each
applicant for:
1. Impaired elbow extension failing to fall within the 0 – 15 degree range
2. Impaired elbow flexion failing to meet or exceed 135 degrees
3. Elbow subluxation
4. Uncoordinated movement
5. Deltoid weakness
(4) Arm flap
(a) APPLICANTS: Extend arms to the ceiling and lower sharply to side of the body without
slapping the sides. Repeat until told to stop (applicants need to face away from the examiner in order to
have scapulae observed).
(b) PROVIDER: Observe each applicant for:
1. Winging of the scapula
2. Full range of shoulder excursion to no less than 180 degrees
3. Position and movement of the scapula
4. Muscular Atrophy of the paraspinal musculature
5. Muscular Atrophy of the shoulder girdle
6. Subluxation of the shoulders
(5) Swan dive or cheerleader Y
(a) APPLICANTS: Begin by extending both arms in front at shoulder level, with both palms

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
86
together and with both thumbs pointing upward. Then, perform a forceful sweeping shoulder hyper-
abduction posteriorly throwing both shoulders to the rear, both beyond and slightly above shoulder level,
while simultaneously standing on tip toes, thereby raising the applicant’s body as the arms hyper-abduct,
and then returning the feet to a standing foot level position as the hands return in front of the nose with the
extended and locked elbow position maintained. Repeat until instructed to stop.
(b) PROVIDER: This is a provocative test intended to aggravate or induce shoulder
subluxation and shoulder pain in those applicants with shoulder problems or concealed history thereof.
Observe each applicant for:
1. Symmetry and coordination of shoulders, clavicles, and arms
2. Subluxation of shoulders
3. General coordination and balance
4. Facial grimacing / Facial Apprehension Sign
5. Impaired individual shoulder abduction to less than 90 degrees (R.O.M. for both
shoulders together less than 180 degrees)
6. Impaired individual shoulder forward elevation to less than 90 degrees (R.O.M. for
both shoulders together less than 180 degrees)
(6) Bend over for spine exam
(a) APPLICANTS: Stand relaxed, extend arms above head, locking thumbs together; bend
over forward and touch floor with fingertips, if able, keeping the knees straight. Bend forward at the waist
touching the floor with both hands, so that the spine may be palpated.
(b) PROVIDER: Observe each applicant for:
1. Scoliosis angle exceeding 30 degrees in the frontal (coronal) plane
2. Thoracic kyphosis angle exceeding 50 degrees in the lateral (sagittal) plane
3. Possible pelvic tilt
4. Possible leg length discrepancies exceeding 2 inches or causing limping
(7) Toe crunch and ankle rotation
(a) APPLICANTS: Stand up straight, extend one leg forward, lifting foot from the floor, toes
down, then up; then relax toes and rotate foot at the ankle. Repeat until told to stop (repeat for other leg
when instructed).
(b) PROVIDER: Observe each applicant for:
1. Inability to dorsiflex the ankle to at least 10 degrees upward

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
87
2. Inability to plantarflex the ankle to at least 30 degrees downward
3. Inability to circularly rotate the ankle at least 5 degrees
4. Uncoordinated movements and/or imbalance
5. Open or unhealed wounds
(8) Kicks forward and backward
(a) APPLICANTS: Repeatedly mimic a series of forceful heel strikes, also known as “can
crushes”. Do not touch or hit the floor with the heel of the foot. When directed, begin by
1. Flex right thigh at least 90 degrees at hip, bringing the knee up, with at least 10 degrees
of ankle dorsiflexion of the same ankle; flex at the knee; then forcefully lower the foot, leading with the
heel, kicking down and forward. Repeat until told to stop. Then repeat the maneuver with the knee up and
flexed, this time kicking down and rearward. Repeat until told to stop.
2. Repeat these maneuvers with opposite leg.
(b) PROVIDER: This is a provocative test intended to aggravate or induce knee subluxation
and knee pain in those applicants with knee problems or concealed history thereof. Observe each applicant
for:
1. Limited Hip Flexion with incapacity to achieve the 90 degree hip flexor minimum
2. Limited Knee Flexion with incapacity to achieve the 110 degree knee flexion minimum
3. Limited Knee Extension with incapacity to lock the knee at 0 degrees knee extension
4. Anterior Knee Subluxation when attempting to extend and lock the knee forwardly at
0 degrees
5. Posterior Knee Subluxation when attempting to extend and lock the knee rearwardly
at 0 degrees
6. Apprehension to BRISKLY perform the maneuver
7. Primary Knee Joint Pain manifesting as Facial Discomfort or Facial Grimacing
8. Hesitancy to perform the maneuver
9. Knee joint integrity and stability
10. Inability to upwardly dorsiflex the ankle to at least 10 degrees
(9) Tiptoe walk and Heel walk
(a) APPLICANTS: Stand on toes as high as possible, and walk on tiptoes five steps forward.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
88
Turn 180 degrees and return walk on tiptoes five steps to original position. Then walk five steps forward
on your heels maintaining both toes and forefeet as high as possible. Turn 180 degrees and return walk on
your heels five more steps to original position.
(b) PROVIDER: Observe each applicant for:
1. At least 30 degrees of plantar flexion
2. At least 10 degrees of ankle dorsiflexion
3. Plantar Flexor weakness
4. Foot Drop weakness
5. Spastic Weakness with or without clonus
6. Uncoordinated limb movement (from Appendicular Ataxia)
7. Uncoordinated torso movement (from Truncal Ataxia)
8. Atrophy and/or muscle wasting
(10) Squats
(a) APPLICANTS: Repeatedly mimic the motion of a baseball catcher by alternating between
standing straight and squatting positions several times.
(b) PROVIDER: Observe each applicant for:
1. Pain from the hips, knees, or ankles upon squatting and standing
2. Lateral patellar motion
3. Integrity of the knees and hips
4. Hesitancy to fully squat or to stand
5. Imbalance
(11) Duck walk
(a) APPLICANTS: Duck walk five steps forward while maintaining balance in a squatting
position. Applicants are to keep their rear end low to the floor without touching the floor with their hands
at any time. Each leg movement has three distinct components of motion, namely 1) leading with the heel,
then 2) rolling from the heel of the same foot to the toes of the same foot, and finally 3) side shifting one’s
body weight to same leg in a waddling twisting motion; followed by a pivot/turn and duck walking back
five steps to original position.
(b) PROVIDER: Observe each applicant for:

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
89
1. Medial knee (medial collateral ligament and/or medial meniscal) pain brought on by
initiating a heel motion
2. Lateral knee (lateral collateral ligament and/or lateral meniscal) pain brought on by
initiating a shifting of body weight laterally (initiating a waddling motion)
3. Patellar subluxation
4. Inability of each hip joint to rotate at least 60 degrees with the combined internal and
external waddle motion
5. Inability of each hip to abduct at least 45 degrees lateral to applicant’s neutral centerof
mass
6. Incapacity to flex each hip individually at least 90 degrees
7. Incapacity to flex each knee individually at least 110 degrees
8. Shortening of the Achilles’ Tendon(s)
9. Tendonopathy of the Achilles’ Tendon(s)
10. Plantar Fasciitis
11. Symptomatic Plantar Warts
12. Deconditioning
13. Uncoordinated movements
14. Imbalance
(12) Knee drop
(a) APPLICANTS: Applicants form a row with their feet together and simultaneously squat
with both knees together. One at a time, each applicant drops onto the floor while hitting both knees
simultaneously upon the floor.
(b) PROVIDER: Observe each applicant for:
1. Apprehension to simultaneously drop onto both knees
2. Knee and/or hip pain
3. Hesitancy to have both knees simultaneously strike the floor (involuntary guarding)
4. Tibial Tuberosity pain (Symptomatic Osgood-Schlatter’s Disease)
5. Facial grimace

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
90
(13) Knee walk
(a) APPLICANTS: Applicants walk forward five steps on their knees and stop.
(b) PROVIDER: This is a provocative test intended to aggravate or induce knee pain and
symptomatic Osgood-Schlatter’s disease. Observe each applicant for:
1. Posterior knee subluxation
2. Tibial Tuberosity pain (Symptomatic Osgood-Schlatter’s Disease)
3. Knee pain
4. Apprehension
5. Facial grimace
6. Hesitancy to crawl on their knees
(14) Stand up from kneeling position
(a) APPLICANTS: From the kneeling position, applicants tuck their toes under both feet
(namely, dorsiflex their toes) and, when instructed to rise, then one applicant at a time will rise to standing
position in one smooth motion, without taking any extra steps or hops and without touching their hands to
the floor. Applicant may separate feet for better balance.
(b) PROVIDER: Observe each applicant for:
1. Rigid great toes and/or additional rigid toes
2. Rigid ankles unable to dorsiflex at least 10 degrees
3. Uncoordinated movements
4. Imbalance
5. Apprehension to stand because of anticipated pain will be stopped by the provider prior
to attempting the maneuver.
6. Deconditioning
(15) Sole of foot examination
(a) APPLICANTS: In a standing position, flex the knee and grab an ankle with the
corresponding hand so that the sole of the foot may be inspected (repeat for the other ankle/foot).
(b) PROVIDER: Observe each applicant for:

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
91
1. Plantar warts
2. Tinea pedis or unguim
3. Open or unhealed wounds
(16) Repeat number 15 with the other foot
(17) Palms up/down
(a) APPLICANTS: Facing the examiner, flex elbows to right angles with elbows touching
the torso with all fingers separated and extended, first palms up and then palms down:
(b) PROVIDER: Observe each applicant for:
1. Missing digits, incomplete digits, extra digits, or digit deformities
2. Restricted supination surpassing 45 degrees of impaired motion
3. Restricted pronation surpassing 45 degrees of impaired motion
4. Skin eruptions, including eczema, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, tinea versicolor, ashy
dermatosis, lichen planus, and other skin abnormalities
(18) With palms up, repeatedly flex and extend fingers (make a fist). Repeatedly open and close
until instructed to stop.
(19) Turn palms down and extend fingers, with elbows remaining at right angles against the body.
(20) Turn palms up and touch each fingertip in turn to the thumb tip; continue until told to stop.
(21) Turn palms down, fingers extended, and repeatedly flex and extend hands up and down at the
wrists. Repeat until told to stop.
(22) Turn palms down, fingers extended, and repeatedly move hands left and right at the wrists.
Repeat until told to stop.
PROVIDER: For maneuvers 18-22 above observe each applicant for:
1. Impaired Up Down Wrist Range of Motion less than 60 degrees
2. Impaired Left Right Wrist Range of Motion less than 30 degrees
3. Impaired Pronation greater than 45 degrees (from the vertical plane)
4. Impaired Supination greater than 45 degrees (from the vertical plane)
5. Inability to touch the thumb to any of the fingertips

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
92
6. Compromised finger dexterity
7. Inability to clench a fist
8. Median Nerve Neuropraxia
9. Ulnar Nerve Neuropraxia
10. Radial Nerve Neuropraxia
11. Muscle atrophy
(23) Brisk walk
(a) APPLICANTS: Walk briskly, one by one, in a straight line toward the examiner; stop in
front of the examiner, turn, and walk away from the examiner.
(b) PROVIDER: Observe each applicant for:
1. Limping
2. Gait apraxia or imbalance
3. Deconditioning
4. Lower extremity pain
5. Spasticity/hyperreflexia at the ankles
(24) Optional Maneuver (if scapula issue discovered during “arm circles” maneuver)
(a) APPLICANT: Assume a half push up hold position on the floor. An acceptable alternative
is to stand upright and lean into a wall at a 45 degree angle with elbows flexed at least to 45 degrees.
(b) PROVIDER: Observe each applicant for:
1. Winging of the scapula
2. Full range of elbow flexion to no less than 130 degrees
3. Position and movement of scapulae
4. Muscular Atrophy of the paraspinal musculature
5. Muscular Atrophy of the shoulder girdle
6. Posterior Subluxation of the shoulders

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
93
Chapter 13
Consultations
13-1. Consultants
a. MEPS medical providers may request consultation from specialty consultants, either military or
civilian. Consultation results are considered supporting medical documentation. The consultant must be
board certified/board eligible (BC/BE) in their specialty with an active medical license in good standing or
an advanced practitioner working under their supervision, and will assist the MEPS provider in making the
qualification determination by providing an expert medical opinion regarding the specific medical
condition. All consultations will be completed in accordance with the current contract. Consultation results
will be reviewed IAW the review timeline in the Appendix F
.
b. Government providers are employed by USMEPCOM, trained to perform accession medical
evaluations, and will not conduct specialty consultations themselves.
c. FBPs are trained and contracted to perform accession medical evaluations only, and will not
conduct specialty consultations themselves.
d. MEPS Medical Departments should use contracted consultants for applicant consultations.
Consultations may be coordinated and obtained from a local Military Treatment Facility (MTF), if
available. The following medical consultation specialties are included in the medical referrals contract:
Allergy, Audiology, Cardiology, Dental, Dermatology, Otorhinolaryngology (ENT), Gynecology, Internal
Medicine, Neurology, Ophthalmology, Optometry, Orthopedics, Podiatry, Psychiatry, Psychology,
Pulmonology, and Urology.
e. If a contracted consultation cannot be obtained due to provider non-availability or an available
appointment is not within the contract timeline, then the MEPS may utilize the Government Purchase Card
(GPC) to obtain the consultation without prior J-3/5/7 MD approval. The MEPS will submit a MOC ticket
to J-3/5/7 MD for tracking.
f. If a requested specialty is not a contracted service, then the MEPS Medical Department must
submit a MOC ticket to J-3/5/7 MD for review and approval prior to scheduling an appointment.
g. Before utilizing a non-contracted consultant, the MEPS will verify the consultant’s BC/BE status
and that their medical license is in good standing. Utilization of advanced practitioners working under the
supervision of a BC/BE consultant for the purpose of seeing MEPS applicants is authorized with use of the
GPC.
h. Consultation for a radiology report may be requested if the MEPS provider is not comfortable with
this responsibility. X-rays will not be ordered or performed on pregnant female applicants.
i. Consultation for EKG interpretation may be requested if the MEPS provider is not comfortable
with this responsibility.
j. Any condition which is disqualifying per the DoDI 6130.03-V1
for a “history of” does not require
any further consultation to determine improvement or resolution for the purpose of rendering a medical
qualification determination.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
94
k. The following invasive or other special tests/procedures ARE NOT AUTHORIZED TO BE
ORDERED OR PERFORMED at the MEPS either to render a qualification determination or as a courtesy
consultation for the SMWRAs:
(1) Any invasive procedure to include endoscopy, biopsy, surgical excision, electrophysiology,
ablations, nerve conduction studies, or vascular catheter placements, with the exceptions of allergy skin
testing, cerumen removal and phlebotomy.
(2) Any invasive testing to include chemical testing/provocations such as methacholine challenge
test, mannitol bronchoprovocation testing, exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, oral challenge testing or
contrast studies [e.g., nuclear medicine scan, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI), etc.].
(3) Any testing or procedure that may pose harm to the applicant such as cardiac stress tests,
pulmonary exercise test, etc.
(4) Diagnostic imaging and testing such as non-contrast MRIs, neuropsychiatric evaluations,
holter/event monitoring, 24-hour continuous blood pressure monitoring, etc.
13-2. Consultation Process
a. No medical testing/consultations will be scheduled until the applicant receives a qualifying Armed
Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) score.
b. Consultations will not be scheduled if there is a valid RBJ date, or until a temporarily disqualifying
condition has resolved.
c. Consultations will not be scheduled for applicants in order to test or re-tested to determine
qualification for special duty or special programs.
d. Consultations will not be ordered by the MEPS for applicants who are identified on exam to have
a potentially serious medical condition. PCP evaluation for definitive diagnosis and treatment should not
be delayed.
e. The profile of applicants who need consultation(s) in order to render a medical qualification
determination will be left in an open “O” status under the appropriate factor designator letter.
f. All consultation data will be entered into USMIRS upon initiation, and updated once the
consultation has been completed. An applicant who is scheduled for a consultation will be projected at the
MEPS IAW UMM 680-3-1
.
g. Specialty consultations and ancillary test results are supporting medical documents and will be filed
in the applicant’s medical packet.
h. Consultation results are valid as long as the condition for which it was obtained has not changed or
until the MEPS medical examination expires.
i. It is acceptable to provide copies of appropriate medical records in a sealed envelope to a consultant
in order to assist them with completing the evaluation.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
95
j. The results of the consultation will not be given directly to the applicant by the consultant. The
result of the contracted consultation will be available to the MEPS Medical Department in the contractor’s
portal within three (3) business days.
k. Reviews of consultation results will be completed IAW the review timeline in the Appendix F
.
l. The MEPS provider will summarize the pertinent medical information from the consult on
DD
Form 2808 item 89 (or SF 507).
m. When a medical qualification determination is rendered in item 74 of the DD Form 2808
, the MEPS
provider will also update the physical profile in item 76. Items 77 and 78 will be updated as needed, and
items 85a and b will be completed.
n. The number of pages of consultation documentation will be annotated in item 88 of the
DD Form
2808 and will be included in the medical packet.
o. The Medical Department will update USMIRS to include updating the PULHES as applicable.
p. Consultation appointment management:
(1) The MEPS Medical Department will establish a local policy for the management of
consultation appointments.
(2) The MEPS Medical Department should designate an individual to contact the SL to confirm the
applicant’s availability and desire to complete the consultation, in order to decrease the consultation no-show
rate. Each MEPS Medical Department will obtain the applicant’s email address and cell phone number
from either the applicant or SL prior to scheduling an appointment with the vendor. The applicant’s email
address and cell phone number will be recorded on the SF 513 (Medical Record Consultation Sheet).
(3) The first missed consultation appointment by the applicant may be rescheduled at the request of
the Recruiting Service. If a second consultation appointment is missed, the MEPS Commander will notify
the appropriate IRC level Commander in writing or by email that the applicant’s processing has been placed
in an ‘N’ status. Further appointments will not be scheduled unless a written request is provided by the
IRC-level Commander. For applicants with two or more missed appointments, the use of the GPC card will
not be authorized in order to expedite the consultation. If the applicant misses a third appointment, further
processing will be discontinued, unless approved by J-3/5/7 MDC or their designee.
q. The CMO will review all consultation requests. All consultation requests will be written
professionally and legibly. The MEPS provider will state on the SF 513 exactly what services are being
requested from the consultant. Include in the request the appropriate AP approved ICD code(s) for the
condition.
r. The SMWRA may request additional consultations or ancillary services (courtesy consultations) in
order to assist them in making a medical waiver decision. Courtesy consultation requests will be reviewed
by the CMO who will determine if the requested medical services are indicated. If necessary, the CMO
may obtain further guidance from J-3/5/7 MD physicians. If issues arise at any point during this process, a
MOC ticket may be submitted to J-3/5/7 MD. (See Paragraph 13-1i
. for a list of unauthorized special
tests/procedures.)

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
96
Note: A medically disqualified applicant’s physical profile (item 76 on the DD Form 2808) will remain
unchanged as “3P”. The profile will not be changed to “O” or “3P/O” due to the courtesy consultation
request by the SMWRA.
13-3. Payment of Consultants
a. Contracted consultants are paid a negotiated rate under the Medical Specialty Consultation contract.
b. Non-contracted consultants will be reimbursed by utilizing the GPC which will be completed by
using the Standard Form 1034
, Public Voucher for Purchases and Services Other Than Personal or GPC.
Prior to requesting GPC use, the MEPS medical department must verify the consultant’s BC/|BE status and
the status of their medical license. Also, they will verify that the requested services are covered by the
contract, but not available from a contracted provider, prior to using the GPC. In some cases, non-contracted
consultants require payment for missed appointments. This type of payment should be negotiated by the
local MEPS prior to scheduling the applicant’s appointment.
Note: If a non-contracted consultation has a combined cost of more than $1,500.00 (test and
consultation), J-3/5/7 MD approval is required before scheduling the appointment.
c. All vendor consultation vouchers must be kept on file for one year.
13-4. Payment of Ancillary and Laboratory Services
a. Authorized ancillary and laboratory services should be ordered through the locally contracted
service provider. If the authorized service is unavailable through the contracted service provider, it may be
obtained from a local non-contracted service provider via locally negotiated rates with the Government
Purchase Card (GPC) or SF 1034 (Public Voucher for Purchases and Services Other Than Personal).
In
some cases, facilities require payment for missed appointments. This type of payment should be negotiated
by the MEPS prior to scheduling the applicant’s appointment.
b. All vendor consultation vouchers must be kept on file for one year.
13-5. Consultation Timeframes
The contractor shall make every effort to schedule and complete consultations IAW the current contract
timelines. The MEPS will order consultations and all associated services according to the following:
a. MEPS personnel will submit referrals for scheduling between 0800-1600 local time Monday
through Friday.
b. All laboratory services are considered same day walk-ins and will be ordered via vendor portal
using “Order Wizard”. Only those services listed in the portal may be ordered. When ordering ancillary
labs, the MEPS must enter referring provider’s name and NPI number. If an applicant requires a laboratory
service that is not listed in the contracted portal, the MEPS Medical Department must submit a MOC ticket
to obtain J-3/5/7 MD approval prior to ordering the excepted laboratory service using the GPC.
c. Standalone ancillary (non-laboratory) services must be ordered via the vendor portal. Ancillary
and laboratory service results will post to the vendor portal within three working days following the
scheduled appointment.
d. The contractor should complete consultation services listed in Paragraph 13-1 within 15 business

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
97
days. Consultation results will post to the vendor portal within three working days after completion of the
consultation.
e. The MEPS must complete a Specialty Consultation Contract/Ancillary Services Contract
Performance Report (UMF 40-1-5
) anytime the contractor is not performing to the established contractual
standards. Examples include not meeting contractual timelines, invoice errors and/or not receiving the
requested consultation. The completed form must be sent to the consultation Contracting Officer
Representative (COR) in A&C SSO.
13-6. Consultation MOC Ticket Procedures
The MEPS Medical Department will notify J-3/5/7 MD via a MOC ticket for situational awareness if they
receive a response from the vendor portal or from the scheduling staff representative that the consultation
request cannot be scheduled IAW the established timelines of the consultation contract or the contracted
provider is not available. No prior J-3/5/7 MD approval is necessary for the MEPS to utilize the GPC in
order to obtain contracted services.
13-7. Transportation
a. Transportation to/from consultations, ancillary services, and laboratory services scheduled by the
MEPS, will be provided by the MEPS IAW UMR 715-4.
b. USMEPCOM is responsible for transportation costs for applicant transportation to medical
consultation, ancillary, and laboratory appointments if the transportation is provided by MEPS contracted
transportation services.
c. Recruiters are authorized to transport applicants directly to and from medical consultations and
ancillary services. In addition, applicants are authorized to transport themselves directly to and from
medical consultations and ancillary services. USMEPCOM is not responsible for transportation costs
incurred by applicants or Recruiting Services who do not utilize MEPS contracted transportation services,
and will not reimburse transportation associated costs (e.g., parking fees, tolls, fuel, mileage, etc.).
d. Use the following guidance to record in USMIRS the Travel Mode of the applicant transportation
to the consult facility:
(1)
“G” for Government Recruiter transportation to a consultation
(2)
“P” for Private applicant transportation to a consultation
(3)
“O” for Other MEPS Transportation to a consultation
e. The Recruiting Service transporting an applicant to and from a medical consultation assumes
responsibility for the safety and security of the applicant. The Recruiting Service will ensure the applicant
arrives and is picked up in a timely manner from the consultation location.
f. The sponsoring Service will ensure that the applicant’s attire is IAW current USMEPCOM policy
on applicant dress and hygiene standards.
g. The sponsoring Service will ensure that the applicant has the required photo identification when
lodging at the CLF IAW current USMEPCOM policy.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
98
h. An applicant will be checked in/out IAW UMM 680-3-1 only when physically present at the MEPS.
In this case the applicant will be checked-out to a "CON" status in USMIRS when departing the MEPS for
a consultation appointment and will be checked-in upon return.
i. An applicant who is staying at the contract lodging facility (CLF) and is a scheduled holdover for
a next day consultation must utilize the contracted transportation to the MEPS. As above, specify the Travel
Mode in the projection.
(1) Recruiters are not authorized to pick up applicants from the CLF.
(2) After an applicant arrives and checks in at the MEPS, Recruiters are then permitted to transport
the applicant to the consultation.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
99
Chapter 14
Medical Check Out
Any time an applicant leaves the MEPS Medical Department, the applicant will be biometrically checked
out of the Medical Department using e-Security. The applicant’s medical packet will be reviewed for
completeness at the time of checkout.
Note: The applicant will not hand carry their medical packet out of the Medical Department (excluding
shipping applicants) to operations/SLs. After check-out, if the medical packet needs to be transferred from
the Medical Department to operations/SLs for any reason, only MEPS staff will hand carry the packet.
14-1. Shipping Applicant Check Out
a. The shipping applicant’s medical packet must be reviewed at QRP prior to shipping inspection. At
the time of check-out, the medical technician will review the day-of medical data in the medical packet to
ensure that all data is present and that the applicant is medically qualified to ship.
b. The medical technician will assign a WKID based on the PULHES. USMIRS will be updated with
the applicant’s height, weight, body fat (if applicable), HCG (for females), and waiver (if applicable). A
current 680-3ADP may be printed and added to the applicant’s medical packet.
c. The complete original medical packet will be given back to the shipping applicant.
14-2. Inspection Check Out
a. For applicants undergoing inspection, their medical packet would have previously been reviewed
at QRP. A review of why the applicant is returning must be made to expedite medical processing.
b. The medical technician will assign a WKID based on the PULHES, and the most recent data from
the applicant’s packet will be transcribed into USMIRS. A current 680-3ADP may be printed and added to
the applicant’s medical packet.
c. When finished processing through the Medical Department, applicants may receive a copy of the
DD Form 2808
, stamped or printed, "Working Copy", and any pertinent medical documents.
14-3. Accession Medical Examination Check Out
a. The applicant will report to the medical control desk with their medical packet. The medical
technician will assign a WKID based on the PULHES and the data from the applicant’s packet will be
transcribed into USMIRS. A current 680-3ADP may be printed and reviewed against the DD Form 2808
and corrected in USMIRS if necessary.
b. A thorough quality check will be done on the medical packet before the applicant leaves the
Medical Department. Instructions for completing the quality check can be found in the TSJTS
.
c. For further MEPS processing, applicants will receive a copy of the DD Form 2808, and the
UMF
40-1-15-E (SHSQ), stamped or printed "Working Copy", and any pertinent medical documents.
d. Once medical processing is complete, the MEPS Medical Department will keep the original
medical jacket (DA Form 3444, DA Form 8005, or other Two-Sided folder) to include all forms in a locked

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
100
cabinet until the HIV and drug results are annotated on the DD Form 2808 IAW UMR 40-8, except if the
record is requested by the files room for immediate transfer to another MEPS due to a change in the
permanent ownership of the record. In this case, the drug result will be posted by the gaining MEPS. Contact
J-3/5/7 MD HIV/DAT Program Office to obtain the lab result source document.
14-4. Temporary Check Out
If the applicant has to leave the Medical Department for a short period of time (but is not leaving the
premises), they must check out with a medical technician. The medical technician must take control of the
applicant’s medical packet.
14-5. Reconciliation
a. Reconciliation is the process whereby the daily transactions performed in the MEPS Medical
Department are compared with computer generated products and data is reentered when needed.
b. The Medical NCOIC/SUP MT must ensure medical reconciliation has been accomplished each
morning and before COB. They must also ensure that all required medical transactions, including medical
examinations, have been entered and committed in USMIRS IAW UMR 680-3.
c. The Medical Department is responsible for reconciliation on a daily basis. The UMF 727-E,
Processing List will be used to reconcile the daily transactions against the data in the electronic system.
14-6. Common USMIRS Entries
See the list of common USMIRS transaction codes and their meanings located on
SPEAR J-3/5/7 Medical
Division page.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
101
Chapter 15
Inspections
After an accession medical examination has been started for an applicant, there may be a situation where
the applicant is required to return to the MEPS for further medical processing. This is called an inspection.
15-1. Inspection of an Applicant Medically Qualified for Service
a. Fully medically qualified applicants may be required to return to the MEPS for one of the following
reasons:
(1) Greater than 30 days have elapsed since the medical examination or last inspection, the
applicant requires further processing, and is not currently in the DEP (for AD applicants), or accessed (for
Reserve and National Guard applicants).
(2) The applicant returns for entry onto Active Duty or Active Duty Training (ADT). This is
commonly called “shipping.” Inspection of a shipping applicant is required if more than 72 hours have
elapsed since the medical examination or last inspection. When a non-processing training day or holiday
falls on a Monday or Friday (only), the shipping inspection will be valid for a maximum of 96 hours.
Note: A shipping inspection is not required for applicants entering AD when on orders to proceed from
school or home directly to duty (hometown/direct shippers).
b. Elements of inspections of medically qualified applicants include the following:
(1) Current height and weight: If the measured height differs by 1 inch or more from the height
previously recorded on the DD Form 2808
, the MEPS medical staff will re-measure the height, ensuring
proper quality control procedures are followed (refer to Chapter 8 for height/weight instructions).
(2) Temperature (shipping applicants only). (See Chapter 8
for further guidance.)
(3) Significant interval history since last accession medical exam, such as:
(a) Surgeries
(b) Medical treatments, hospitalizations or ER visits
(c) Any visits to behavioral health professionals
(d) Injuries
(e) Drug or alcohol-related legal issues
(f) New wounds, to include recent tattoos or piercings
(g) Encounters with law enforcement agencies other than minor traffic tickets
c. An inspection of a medically qualified applicant will be performed by a provider. Each applicant
will be inspected with clothing removed (except for authorized undergarments) to evaluate for any interval

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
102
changes from the previous examination/inspection. Hands and feet are to be inspected for any lesions or
abnormalities that may interfere with training.
d. For a female applicant a urine HCG test will be performed, and the results recorded on the
DD
Form 2808 in item 81 (HCG block). If the urine HCG test is positive, the applicant will be informed by the
provider that the test indicates that she may be pregnant. The applicant is disqualified and should be
instructed to see her primary care provider.
e. The results of the inspection will be entered on the DD Form 2808
, item 81 (item 89 may also be
used if necessary). When disqualifying conditions are discovered upon inspection, they will be explained
to the applicant and documented in items 76, 77, 78 and 79 with the appropriate recommendations. (See
Chapter 21 for further guidance).
Note: Any significant findings on the inspection must be discussed in private and not in a group setting,
and annotated on the DD Form 2808
in item 89.
15-2. Inspection of an Applicant Not Medically Qualified for Service
An applicant who is not medically qualified for Service may be required to return to the MEPS for one of
the following reasons:
a. When an applicant is temporarily disqualified and returns to the MEPS for re-evaluation to clear
an RBJ date, i.e., to document resolution of a temporary medical condition.
b. When an applicant’s profile has been left in an “open” status and returns to the MEPS for any of
the following reasons:
(1) To complete a deferred medical examination.
(2) To complete a consultation, ancillary service, or any other non-MEPS medical services.
(3) To repeat DAT or HIV testing.
Note: The elements of the inspection of an applicant not medically qualified for Service will be determined
by and limited to the reason for the return to the Medical Department.
15-3. When a Medical Inspection is NOT Required
An inspection is not required for the following:
a. A medically qualified applicant who meets all 3 of the following:
(1) Returns to the MEPS for further processing
(2) Is currently in the DEP or assessed in a Reserve or National Guard component (any service)
(3) Is not shipping (e.g. the applicant returns for additional aptitude testing).
b. A medically qualified applicant who meets all 4 of the following:
(1) Returns to the MEPS for further processing

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
103
(2) Is NOT in the DEP
(3) Is not shipping
(4) 30 days or less has elapsed from the initial medical exam or subsequent inspection (e.g., the
applicant returns to enter the DEP or assess in a Reserve or National Guard component of any Service).
c. An applicant returns to the MEPS for non-medical processing prior to the assigned RBJ date.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
104
Chapter 16
Special Medical Examinations
16-1. Released From Active Duty
This is an Army Reserve (USAR) and Army National Guard (ARNG) program which allows USAR and
ARNG soldiers that have been medically released from Initial Entry Training (IET) or Advanced Individual
Training (AIT) to have time to receive treatment and recover at their home station/state unit for an injury
or medical condition that occurred during training. Soldiers in the Released From Active Duty (REFRAD)
program will be given a return date and/or recalled to training by their respective Service. Pregnancy is not
a REFRAD eligible medical condition, the respective Service must take appropriate administrative action.
An accession medical examination will be performed to ensure that the medical condition has resolved and
that the REFRAD Soldier meets accession standards for the purposes of completing IET and AIT. They
will be referred to the MEPS by USAREC/NGB recruiters for a medical evaluation. The REFRAD applicant
must be identified as a REFRAD through the QRP process.
The DD Form 2807-2
, along with appropriate supporting medical documentation pertaining to the treatment
and recovery from the medical condition, must be submitted as a complex prescreen for review. The MEPS
provider will determine if any additional documentation is needed for the REFRAD Soldier prior to the
MEPS medical examination.
If the REFRAD prescreen is incomplete, the MEPS will return it to the appropriate SL with instructions
detailing what further action(s) need to be taken.
When the REFRAD prescreen review has been completed and the REFRAD Soldier is authorized by a
MEPS provider to process (PA), the applicant will be projected by the SL with REFRAD annotated in the
remarks of the projection.
16-2. Service Members Processing for Commission and Warrant Officer
These candidates will be processed according to accession standards using Prior Service height/weight
standards. Service-specific instructions may accompany these candidates and will be incorporated into the
MEPS medical evaluation process.
16-3. Dis-enrolled Reserve Officers’ Training Corps
a. Dis-enrolled Reserve Officers’ Training Corps (DROTC) applicants include those students who
dis-enrolled from ROTC or a US Military Academy, and who are being ordered to AD in order to fulfill a
Service obligation as an enlisted member.
b. Applicants processing through the DROTC program will be processed according to accession
standards for enlistment.
c. DROTC applicants may be processed as No-Med Required (B0M0) only if they provide a
separation examination, annual periodic health assessment (PHA), or separation health assessment (SHA)
accomplished prior to discharge that is within 15 months of MEPS processing.
d. MEPS will process Army DROTC as Prior Service (PS) applicants. The respective cadet command
must provide them a copy of their AD orders prior to the MEPS medical exam.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
105
e. MEPS will process DROTC applicants using PS height/weight/body fat standards, unless projected
differently by the particular recruiting Service.
16-4. Army Airborne Screening
a. Airborne screening is a MEPS process for all Army components and assists the SL with contracting
certain applicants for an airborne related MOS. This screening will only be performed at the request of the
SL for an applicant with an existing Airborne reservation. The MEPS Medical Department should develop
an Airborne screening process that best fits their daily workflow. The Airborne screening will occur after an
accession medical examination has been completed. In some instances, the Airborne screening may be
performed while the medical examination is being conducted if the Medical Department authorizes it.
Note: MEPS personnel are not authorized to conduct Airborne screenings on current Active Duty Service
Members, with the exception of Blue to Green candidates.
b. Airborne MOS eligible applicants must have an SF 507 Airborne Training Checklist
(found on
SPEAR under airborne) that will be used to perform MEPS Airborne screening. This checklist is to be used
as a supplement to the DD Forms 2807-2 and 2808, and will become part of the applicant’s medical packet.
The CMO will ensure that all FBPs are trained on the proper use of this checklist.
c. The MEPS Medical Department will not request additional procedures, testing, or consultations,
solely in order to determine Airborne qualification. The condition(s) requiring additional testing or
consultation will be annotated on the Airborne Training Checklist and in item 79 of the DD Form 2808
.
d. Airborne screenings will include:
(1) Completion of the SF 507 Airborne Training Checklist by the examining provider
(2) Observation by the examining provider of tympanic membrane mobility of both ears during
the Valsalva maneuver, and annotating the results in item 72b on the DD Form 2808
(3) Applicant completion of the color vision test (PIP or Red/Green test)
Note: The MEPS medical provider will note a failed color vision for Airborne screening in item 79 of the
DD Form 2808
, any additional condition(s) that prevent the applicant from being screened for Airborne
consideration will be documented in item 89.
e. If the applicant passes the MEPS screening for Airborne training, the medical provider will write
or stamp “Airborne Screened” in item 78 of the DD Form 2808
followed by the provider’s initials and date.
f. If the applicant does not meet accession medical standards due to a TDQ or a DQ condition, then
they are not eligible to undergo Airborne screening at the MEPS, even with an approved medical waiver.
Any condition that prevents the applicant from being screened for Airborne consideration will be
documented in item 89 of the DD Form 2808
.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
106
16-5. Army Blue to Green
a. The purpose of the Army Blue to Green program is to transfer current Air Force and Navy Service
Members into the Army with no break in service.
b. The Army SL will project the applicant with no testing and/or medical required (B0M0).
c. If the Army Blue to Green candidate will be attending IET, the candidate must receive a full
accession medical examination (B0M0 not authorized).
16-6. Military Accessions Vital to National Interest Recruitment Program
a. The Secretary of Defense authorized the Services to implement a program temporarily permitting
enlistment of certain legal non-immigrant aliens into the Military with certain skills as Health Care
Professionals (HCP) and personnel with Critical Foreign Language skills. USMEPCOM and the Services
require alternative processing procedures to ensure efficient implementation of this program.
b. If the applicant does not comprehend English well enough to complete medical processing, refer to
Paragraph 3-9
for guidance on deferring the medical exam. Use of the RAT for the purpose of evaluation
of English language proficiency is not authorized. For specific information on the Military Accessions
Vital to National Interest (MAVNI) program, refer to
UMR 601-23.
16-7. General Officer
a. Senior Officers (O-6 promotable/select and above) of the ARNG are eligible to undergo a MEPS
medical evaluation for promotion to a General Officer (GO) rank.
b. The MEPS Medical Department will make arrangements with the Senior Officer for the medical
examination appointment, and will advise the Senior Officer to complete the applicant’s portion of the
DD
Form 2807-1. The DD Form 2807-2 is only used for accession purposes, and should not be used for the GO
processing. The form and required medical records must be brought to the MEPS by the officer on the date
of the examination.
c. The GO medical examination will not be scheduled on any of the Services’ mission days. The
CMO/ACMO/MO, along with the MEPS Commander, will determine the best date/time to conduct the GO
medical examination so as not to interfere with normal daily processing at the MEPS.
d. The MEPS Medical Department must submit a request via MOC ticket to J-3/5/7 MD for
authorization to conduct a GO medical examination. The MOC ticket must state that the CMO/ACMO/MO
is available to conduct the examination, and which dates are being considered.
e. Scheduling of the GO examination must be approved by the USMEPCOM Chief of Staff.
f. When the MEPS receives the approval to perform the GO examination, the MEPS Medical
Department will notify the Battalion Commander of the pending date and time of the examination, and
advise the Battalion Commander that there is no requirement for them to be present at the MEPS on day of
GO medical examination.
g. The GO processor must be projected a minimum of 24 hours in advance. The Senior Officer will

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
107
be projected/processed as “Special Category”.
h. Every GO medical examination will be processed as a VIP, and will have individualized
processing. The GO medical examination will be completed at the MEPS and recorded on the
DD Form
2808, but the profile section will be left blank. The GO medical examination must be conducted by a
CMO/ACMO/MO (FB-CMO is not authorized to conduct the examination).
i. A DD Form 2807-1, DD Form 2808
, and all supporting medical documentation must be completed
and reviewed by the MEPS CMO/ACMO/MO for accuracy and completeness before submitting to the J-3/5/7
MD for profiling. Once review is completed, a copy of all documentation must be sent via encrypted email
to
osd.north-chicago.usmepcom.list.hq-j7-memd-physicians@mail.mil for profiling by the J-3/5/7 MDC or
the Command Surgeon.
j. Once the J-3/5/7 MDC or the Command Surgeon has completed the profile section on the
DD Form
2808, any pages that have been updated will be returned to the MEPS and are now considered original
documents.
k. The MEPS will then ensure that the medical record is complete, and return it to the files room to
be forwarded to the SL.
16-8. Overseas Applicants
a. Overseas processors are defined as applicants that process at a Military Treatment Facility (MTF)
outside the continental United States (OCONUS) where no MEPS are available. OCONUS medical
examinations are accepted by all Services for accession. No additional medical examination/inspection is
required by USMEPCOM. Accession data for overseas processors will be entered in USMIRS.
b. Overseas processors are authorized to be placed in a “no medical required” (B0M0) status so that
their enlistment information is available for accession into the Military. This can only be done after the
overseas medical examination data is entered into USMIRS. The overseas processor packet will be
submitted and processed as follows:
(1) Overseas recruiters will submit (scan) accession documents, to include the DD Forms 2807-2
,
2807-1 (if used) and 2808 to MEPS SL.
(2) The MEPS files room will take permanent ownership of the overseas documents and create a
MEPS medical packet.
(3) The files room (processing section) will route the overseas documents to the appropriate section
for USMIRS data entry. The Medical Department will enter the medical examination results into USMIRS
as a “4” transaction (B040 “outside MEPS physical”). The MEPS Medical Department will enter the data
from the DD Form 2808
as is. In cases where a medical test was not done (i.e., vision, hearing) the entry
in USMIRS will have an entry that starts with a 9.
(4) Once the data is entered in USMIRS, the overseas applicant will be processed in a “no medical
required” status. (See Paragraph 2-11d
.)
c. Refer to UMR 40-8
for more information on HIV/DAT requirements. Contact J-3/5/7 MD for
additional guidance.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
108
16-9. Non-MEPS Medical Applicants (Other than Overseas Processors)
Non-MEPS medical applicants are applicants that have undergone a medical examination at a location other
than the MEPS. Non-MEPS medical examinations must be reviewed and approved by the
CMO/ACMO/MO/FB-CMO before data can be entered into USMIRS using the “B040P” transaction. If
the non-MEPS medical applicant requires further MEPS medical processing they must have a medical
inspection.
16-10. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Applicants
a. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) medical examinations have time-
sensitive deadlines. J-3/5/7 MD receives a list of NOAA candidates twice per year (spring and fall) and
determines the closest MEPS to the applicant’s address for in-person processing. J-3/5/7 MD will notify
MEPS Commanders and Medical NCOIC/Supervisory Medical Technician and will provide them with the
candidate’s name and contact information for medical examination scheduling. The email will include
instructions on how to process the candidate.
b. The MEPS Commander will be responsible for establishing a workable process for the MEPS
Medical Department to contact NOAA candidates within 48 hours (2 business days) in order to determine
the date and time for the candidate to schedule their medical examination at the MEPS. Additionally, MEPS
Medical Department personnel must inform MEPS operations personnel of the agreed upon date so they
can enter the projection into USMIRS (using Code ZZZ). An information sheet on how to complete the
NOAA candidate medical examination can be found on
SPEAR J-3/5/7 Medical Division page under
General Information.
c. Once the NOAA medical examination has been completed, the MEPS Medical Department must
contact J-3/5/7 MD to conduct a review of the documentation to ensure that all medical processing is
complete and accurate prior to the candidate leaving the MEPS on the day of the medical examination.
16-11. Public Health Service Applicants
a. The MEPS are authorized to conduct physicals for all Public Health Service (PHS) applicants. The
PHS applicant will need to be projected in USMIRS with Code ZPZ. The projection may be entered by any
Service. Submission of the DD Form 2807-2
as a prescreen is not required. The applicant will complete the
DD Form 2808 and DD Form 2807-1 during the medical brief. The MEPS provider may do an
individualized ortho/neuro exam if preferred.
b. The following will be the only tests conducted at the MEPS for these applicants:
(1) Urine Protein/Glucose/HCG Testing
(2) Height/Weight/Body Fat (leave min/max WT and Max BF blank)
(3) Blood Pressure, heart rate, and temperature
(4) Vision – Distance/Near/Heterophoria/Color/Depth Perception/IOP
(5) Hearing - one test only (If applicant receives an H3 result there is no need to re-test the PHS
applicant)

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
109
c. All other tests and exams found on the PHS medical data checklist are not authorized to be
done either at the MEPS or via consult. The applicant will be responsible for obtaining those tests at their
own expense.
d. Specialty consults are not authorized for these applicants.
e. The MEPS provider will document any medical conditions disclosed during the examination in
items 78 and/or 89. Items 74, 76, and 77 should be left blank because the qualification determinations for
these applicants will be made by PHS Physical Examination Branch. For USMIRS entry, the MEPS Medical
Department enter the examination data and use Open PULHES. Do not enter them into e-Security.
f. The MEPS Medical Department will provide the original documents to the applicant on the day of
examination, and is not required to keep copies. The MEPS Medical Department will ensure that the
medical record has been signed out “off-site” in USMIRS.
16-12. Reserve Officer Training Corps and Service Academy Cadets/Midshipmen
a. ROTC and Service Academy (SA) applicants will receive head-of-line privileges IAW
UMR 601-
23.
b. Services may use MEPS for pre-contract or pre-commissioning medical examinations for ROTC
and SA applicants. The Department of Defense Medical Examination Review Board (DoDMERB) remains
the agency responsible for the determination of medical qualifications for ROTC and SA applicants.
c. MEPS will perform the pre-commissioning or pre-contract medical examination to accessions
standards. The DD Form 2807-2
, current ROTC physical (if available), medical records (in accordance with
prescreen SOP), etc., must be provided for QRP in advance of the projected processing date.
d. SA Cadets/Midshipmen will be processed using PS height/weight standards.
16-13. Individual Ready Reserve
a. Any member of any Service Individual Ready Reserve (IRR) is authorized to enlist or commission
into active, reserve, and guard components of any Service without restriction, and regardless of time
remaining on their Military Service Obligation.
b. PS documentation is required IAW UMR 601-23
.
c. IRR applicants processing back into the Military (any Service/component) will receive an accession
or commissioning medical examination IAW DoDI 6130.03-V1
and UMR 40-1 under PS HT/WT standards
for the Service for which they are processing.
Note: MEPS Medical Departments must communicate with SLs to ensure that the applicant is authorized
to process.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
110
Chapter 17
Quality Review Program
17-1. Quality Review Program
a. Quality Review Program (QRP) will be accomplished 48 hours before the applicant processes at the
MEPS. Medical Department personnel will ensure that the applicant’s electronic data record is reviewed
(in USMIRS) in conjunction with the applicant's packet. A MEPS Medical Department representative will
be assigned to participate in QRP IAW UMM 680-3-1
and local MEPS policy.
b. All Hometown and Direct Ship applicant records must be reviewed at QRP for completeness and
potentially expired medical examinations in USMIRS no earlier than 30 days prior, but not less than 5 days
prior to applicant shipping.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
111
Chapter 18
Fee Basis Providers
18-1. Fee Basis Provider Responsibilities
a. Fee Basis Providers (FBPs) are contracted medical providers who augment the MEPS Medical
Department. They are trained and qualified to perform accession medical evaluations. They may be
requested by the MEPS as necessary to assist the government providers (CMOs/ACMOs/MOs) in
conducting accession medical processing.
b. FBPs are trained IAW the UMR 40-2
. They achieve increasing levels of responsibility as
designated by their Defined Provider Category (DPC) level upon recommendation for advancement by their
home MEPS CMO and upon approval by the Command Surgeon or their designee. DPC advancement
correlates with the following increasing levels of responsibility:
(1) DPC-1 is granted by the Command Surgeon or their designee after review of credentials and
prior to beginning training. This level enables the FBP to begin training at the MEPS.
(2) DPC-2 is granted by the the Command Surgeon or their designee after review of the successful
completion of the initial training. This level enables the FBP to perform medical examinations and review
supporting medical documentation
(3) DPC-3 is granted by the Command Surgeon or their designee after review of the
recommendation by the CMO that the FBP has demonstrated proficiency in the medical examination,
documentation review and the application of medical qualification standards. This level enables the FBP
to render a medical qualification determination and to profile applicants.
(4) DPC-4 is granted the Command Surgeon or their designee after review of the recommendation
by the CMO that the FBP has achieved expert management of medical processing. This enables the FBP
to function as a Fee Basis CMO (FB-CMO).
Note: The CMO/ACMO/MO (if available) is responsible for rendering a medical qualification
determination and assigning an appropriate physical profile. It is the CMO’s responsibility to ensure that
the profiling providers are familiar with the contents of the current version of DoDI 6130.03-V1
and this
regulation.
c. A FB-CMO functions as the CMO in a limited capacity. When a government provider is absent
from the MEPS, then the MEPS may request a FB-CMO from the contractor. Only FBPs with a DPC-4
level may be designated as the FB-CMO. FB-CMOs will:
(1) Conduct applicant processing
(2) Be administratively responsible for the MEPS Medical Department
(3) Respond to requests from the MEPS Commander (e.g., to attend meetings)
(4) Provide technical advice and medical guidance to the Medical Department. Medical processing
questions that cannot be resolved at the local level will be referred to a J-3/5/7 MD physician.
Note: MEPS are not authorized to request a FB-CMO when a government provider is physically present

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
112
at the MEPS, unless the only government provider physically present is unavailable due to previously
scheduled and approved provider training.
18-2. Requesting FBPs
FBPs may be requested as necessary to assist government providers in processing applicants. The MEPS
Medical Department personnel will utilize the FBP IV Application to order FBPs. In the application the
MEPS must indicate the government provider availability to process applicants for each processing day. If
the government provider is not available, the MEPS Medical Department personnel must update the
planning calendar to correctly reflect scheduled absences as soon as they become aware of the requested
time off. The FBP IV Application calculates the number of FBPs authorized based on anticipated workload,
government provider availability, set number of walk-ins, and a percentage of workload for review of
supporting medical documentation. The FBP IV Application must be used to request approval from A&C
SSO for any additional FBP requirements (e.g., using Service over-projection percentages). MEPS Medical
Department personnel may request an additional FBP to allow the CMO to conduct scheduled initial
training for providers. In the request justification area, the specific reason why the additional FBP is being
requested must be stated. If the CMO is physically present at the MEPS, but using “other” as reason to
request additional FBPs coverage, then the request justification area must state the specific reason why the
CMO is unavailable to process applicants. In these instances prior coordination and approval from J-3/5/7
MD is required.
Note: The FBP IV Application determines the next two processing days by interface with USMIRS for
MEPS open/closed schedule information. MEPS personnel must accurately indicate in USMIRS when the
MEPS is open and closed in order for the FBP IV Application to make accurate projections.
18-3. Placing Daily FBP Requests in the FBP Application
For each day a MEPS is open and processing applicants, the MEPS Medical Department personnel must
complete a Daily FBP Schedule Request two business days in advance. The daily FBP request is the
government order for services under the FBP contract.
a. If either FBP IV or USMIRS is down, the MEPS will use the Computation Formula for MEPS FBP
Requirements (available on SPEAR), and email the request by 1400 local time to A&C SSO and the
designated contractor, or as directed by A&C SSO. An FBP order must be sent even for days when there is
no requirement for the FBPs. A by name request for a specific FBP can only be made in cases when a
particular FBP requires training or an evaluation. Coordination for CMO availability must be completed
prior to scheduling the training and/or evaluation.
b. In the FBP IV application, each MEPS has until 1430 local time to submit the daily FBP order. The
MEPS Medical Department personnel should wait until all projections are entered into USMIRS after QRP.
If the order is submitted prior to the completion of QRP, it must be reviewed at the 24-hour mark. For
example, if Wednesday’s projection was submitted on Monday, a quick review of the order should be done
Tuesday morning to ensure there were no last minute changes to Wednesday’s projections.
c. If a Daily FBP Schedule Request has been submitted to the contractor and the Medical Department
becomes aware of the FBP requirement change, the MEPS Medical Department personnel must email
another request to the FBP COR A&C SSO and the contractor. The MEPS Medical Department will then
call the contractor’s scheduler to verify receipt of the request (if after hours, use the scheduler’s cell phone
number). Additionally, if the requirement for FBPs changes, causing a reduction in the need for providers,
the MEPS Medical Department personnel must utilize the FBP IV Order Screen to adjust the FBP Count
to reflect the number of providers actually needed on a given day. If additional support is needed, the MEPS
Medical Department personnel must request more providers via the FBP IV Workload screen. The request

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
113
must be approved by the A&C SSO prior to coordinating additional support with the vendor. MEPS medical
staff are required to include comments/justifications any time additional providers are needed. If the change
happens on the morning of the processing day, the MEPS Medical Department personnel must immediately
call their FBP scheduler and the FBP COR to notify them of the issue. An email will then be sent to the
contractor and FBP COR A&C SSO.
Note: Requests for additional FBP support, outside the allotted points indicated on the FBP IV Workload
screen, must be authorized by FBP COR A&C SSO before coordinating additional support with the vendor.
Requests for additional FBP support can be made up to 12 hours before a provider is needed.
d. If the MEPS Medical Department personnel determine that the need for provider support is less
than what has already been confirmed, they will immediately notify FBP COR A&C SSO and the
vendor/scheduling POC. The FBP Adjusted Order Count should be updated only if the provider scheduled
to work has been canceled prior to their arrival for work. To use this function, log into the FBP IV
Application Order Details screen and enter the number of FBPs actually required. This box is used to
remove FBP slots for any given work day, and does not impact FB-CMO slots if any are present. Adjusting
the FBP order to reduce the amount of providers needed will not be utilized when the vendor is unable to
fill a request for FBP support. Do not adjust the order count if the vendor cannot fill the request. Doing this
will negatively impact the Command fill rate, which limits USMEPCOM’s ability to hold the vendor
accountable.
e. The FBP Application allows users to create ‘Auto Process’ requests for future dates where FBP
support is anticipated. These automatic requests will not be used on a routine basis because they may not
capture any subsequent changes. This function is intended for emergency situations or extenuating
circumstances only. The expectation is for MEPS Medical Department personnel to review the daily FBP
orders to ensure efficient use and accurate ordering of the FBP resources. For example, if the MEPS has
a high “no-show” rate, the FBP order may be lowered by one provider because the provider is not needed.
In other cases, the MEPS may be behind on medical prescreen processing and needs to request an additional
FBP to review prescreens. Overall, a review of each order must be completed by the MEPS Medical
Department personnel to ensure the order is correct.
f. After duty hours, if the MEPS is notified of an issue with a provider, they should contact the FBP
scheduler via cell phone. For example, a provider’s family calls on a Saturday stating the FBP has a medical
emergency and can’t work the following week. The MEPS medical staff would then call their FBP
scheduler to notify the scheduler of the issue.
g. Depending on the issue, the MEPS medical staff must also call the FBP COR A&C SSO for
situational awareness or to intervene on behalf of the MEPS to resolve an issue. For example, only the FB-
CMO was requested and on the processing day, the provider does not arrive; therefore, no government or
contract providers are available at the MEPS.
h. The MEPS medical staff must document the impact on the medical mission by submitting an Impact
Statement form via email to the FBP COR A&C SSO when the number of providers who report for work is
less than the number of providers requested/authorized. Examples of impact include MEPS government
personnel working overtime in order to process applicants; Marine applicants not shipping until the next
week; Services asked to move applicants to another processing day, “Service slice” being implemented; no
applicants can undergo medical examinations or inspects that day, etc. The email must be sent within one
business day after the processing day in question for all situations except when there are no providers. In
this situation contact the FBP COR immediately. The Impact Statement form can be found on SPEAR.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
114
18-4. FBP Provider Work Record
a. The FBP Provider Work Record (PWR) is the official document for tracking FBP work hours.
Medical NCOIC/SUP MTs will be designated by the MEPS Commander to act as FBP Government Points
of Contact (GPOC). GPOCs will act as an ACOR at their MEPS and are responsible for general FBP
performance oversight, to include FBP work records/timekeeping, etc.
b. Medical NCOIC/SUP MTs will maintain a three ring binder or clipboard approximately 8.5 by 11
inches and clearly label it “FBP Provider Work Record”. The “MEPS FBP Contract – Provider Work
Record” is UMF 40-1-12
(MEPS Fee Basis Provider Work Record). It is the only authorized provider work
record to be used at the MEPS for the FBPs. UMF 40-1-12 will be placed in the binder. Copies of PWRs
will be kept on file for one year. The appropriate UMF 40-1-12 will be labeled (MEPS Name, Month, Date,
Day) each day and placed in the binder or clipboard before FBPs arrive to work. All entries made on the
UMF 40-1-12 will be printed legibly in black ink only. Each completed UMF 40-1-12
must match the data
entered into the FBP IV Application Provider Work Record screen.
c. Only the MEPS Medical Department personnel may complete the “Time In, Time Out, Total Hours
Worked” columns on the UMF 40-1-12.
FBPs are not authorized to sign in each time they arrive at the
MEPS, or sign out each time they leave the MEPS.
d. The FBPs will report to work at the time scheduled by the contractor and no earlier than 15 minutes
before their scheduled start time. If FBPs report for work earlier than 15 minutes before their scheduled
time, or they report late for work, the MEPS will immediately complete and submit a Contractor Provider
Quality Management Form (UMF 40-2-4-E
). Increments of 15 minutes will be calculated and recorded on
the UMF 40-1-12 as follows:
(1) Between 1 and 7 minutes: after the hour, 15, 30, and 45 minutes after the hour - round
backwards
(2) Between 8 and 14 minutes: after the hour, 15, 30, and 45 minutes after the hour - round forward
(3) Examples
(a) A FBP arriving at 0501 would be recorded as 0500 on the PWR because for 1 minute after
the hour, round back.
(b) A FBP arriving at 0607 would be recorded as 0600 on the PWR because for 7 minutes after
the hour, round back.
(c) A FBP arriving at 0717 would be recorded as 0715 on the PWR because for 2 minutes after
15 after the hour, round back.
(d) A FBP arriving at 0835 would be recorded as 0830 on the PWR because for 5 minutes after
30 after the hour, round back.
(e) A FBP arriving at 0652 would be recorded as 0645 on the PWR because for 7 minutes after
45 after the hour, round back.
(f) A FBP departing at 1314 would be recorded as 1315 on the PWR because for 14 minutes
after the hour, round forward.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
115
(g) A FBP departing 1423 would be recorded as 1430 on the PWR because for 8 minutes after
15 after the hour, round forward.
e. The night before the next processing day, or early in the morning on the processing day prior to
FBP arrival for work at the MEPS, the Medical NCOIC/Sup MT or the alternate scheduling POC will
complete a UMF 40-1-12
for the next/same day. The PWR must clearly indicate the MEPS name, the
month, and the day, and the information contained on the PWR prior to any FBPs arriving at the MEPS.
f. When the FBP arrives to work for the first time each day, the Medical NCOIC/Sup MT will print
the FBP’s first and last name (in that order), and enter the time rounding back or forward as described above
on the “Time In (1)” column on the UMF 40-1-12
for the appropriate date/day. The Medical NCOIC/Sup
MT needs to print the FBP’s name legibly. If they remain at work all day, then depart, the Medical
NCOIC/Sup MT will sign out in the “Time Out 1” column rounding back or forward as described above.
Then the Medical NCOIC/Sup MT will calculate “Total Hours Worked” (in 15 minute increments) and
record this number in the appropriate column of the PWR. The PWR will either be updated with new names
or the names will be removed if no longer needed. The 15 minute increments will be recorded as: 00 minutes
= .00 hours, 15 minutes = .25 hours, 30 minutes = .50 hours, 45 minutes = .75 hours. The PWR comment
section must contain comments as to the type of position the FBP is filling: FBP-CMO, FBP, or training.
Other comments may also be included to clarify specific details e.g., “No lunch taken”, “FBPs sent home
due to weather”, etc.
g. At the end of each day, the Medical NCOIC/Sup MT will calculate and record the number of total
hours worked that day and will annotate it in the “Total Hours Worked” Column. The Medical NCOIC/Sup
MT will then sign or print their initials in the appropriate column verifying the information they recorded
is truthful and accurate.
h. All FBPs who work four consecutive hours will be allowed to take a 30 minute unpaid lunch break,
if desired.
i. When the FBP signs-in for work and subsequently they stop working or leave the MEPS (e.g.,
taking a lunch or other break), the FBP will be signed in and out each time they arrive, and each time they
stop working or leave work. Examples include:
(1) Lunch break: The FBP reports to work and is signed in. The FBP stops work to eat lunch and
must be signed out. FBP returns to work and is signed in again. FBP leaves work for the day and is signed
out.
(2) Split work session with lunch: FBP would like to work, but needs to take an hour off in the
middle of the work session. The FBP must receive permission ahead of time from the CMO or FB-CMO
to do this. The FBP reports to work and is signed in. The FBP stops work to eat lunch and is signed out.
The FBP returns to work and is signed in again. The FBP leaves work for pre-approved personal business
and is signed out after letting CMO or FB-CMO know they are leaving. The FBP returns to work from
personal business and is signed in. The FBP completes work and is signed out for the day.
18-5. FBP Provider Work Record Verification
a. Periodically throughout the day, and at the end of each workday, the medical NCOIC/SUP MTs
(or the alternate scheduling POC in their absence) will review the PWR to ensure FBPs are correctly signed
in and out, and times are accurately recorded. For each FBP, they will also review and ensure that the “Total

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
116
Hours Worked” column has been properly calculated and recorded on the PWR. The MEPS Commander
has overall responsibility for releasing the FBPs, but may delegate this responsibility to the OPSO, CMO,
ACMO, MO, FB-CMO, or the Medical NCOIC/Sup MT. If, for any reason, the FBP does not appropriately
complete their work and leaves the MEPS, a UMF 40-2-4-E
should be immediately completed and
submitted to the J-3/5/7 MD.
b. At the end of each work day, the Medical NCOIC/SUP MTs (or the alternate scheduling POC in
their absence) will review the PWR to verify that the recorded information is correct and accurate. This
includes all of the following:
(1) The MEPS name, month, year, and date are properly filled in, and the correct day of week is
circled. The month and date listed on the PWR must properly correspond to the day of the week circled.
(2) All entries are legibly made in black ink only.
(3) For each FBP who worked that day, their name is recorded with first name first, then last name.
(4) Each time the FBP reported to work, and stopped working, they were appropriately signed in
and out on the UMF 40-1-12.
(5) All signed in and out times listed for the FBPs are in military time format.
(6) Validate that the “Total Hours Worked” were properly calculated and entered on the UMF 40-
1-12 by the MEPS medical personnel. If not, the verifier may correct this entry only by following the guidance
directly below for “correcting UMF 40-1-12 errors”.
(7) Ensure that appropriate comments are listed under the “Comments” column on the same row
as the FBP’s name, e.g., if the FBP worked as the FB-CMO that day, “FB-CMO” is listed.
c. The PWR cannot be verified until the last FBP signs out for the day. The PWR must not be verified
until all the information above is correct. If there are problems identified on the PWR they must circled on
the form and corrected as soon as possible. Initials and a date for any corrections made to the PWR must
be included. The PWR must not be submitted until it has been properly verified.
d. After all the information listed above is verified and correct, the Medical NCOIC or Sup MT (or
the alternate scheduling POC in their absence) will sign or print their initials, and record the date and time
in the appropriate blocks at the bottom of the PWR. Verification of the PWR validates that the information
directly above was appropriately reviewed and is correct.
e. The PWR also includes additional information that needs to be accurately and legibly recorded
each processing day in order to monitor contract compliance. The following information will be recorded
on the PWR prior to its submission:
(1) Date/Time that the Daily FBP Schedule Request was sent via FBP IV application or by email
to the contractor for the FBPs who worked on the day the PWR is being completed (for most days, the date
would be the previous processing day).
(2) Number of FBPs requested on the Daily FBP Schedule Request (this will always be the number
of FBPs the MEPS needs based on the workload projection, not the number of FBPs the MEPS thinks the
contractor will send to the MEPS).

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
117
(3) Number of FBPs the contractor scheduled (number of FBPs the contractor fills in on the Daily
FBP Schedule Request and sends back to the MEPS).
(4) Number of FBPs who actually reported to work that day.
f. After the PWR has been properly validated, the MEPS staff will electronically scan the PWR into
a PDF document and upload the document to the corresponding Provider Work Record screen in the FBP
Application. Scanned PWRs must be uploaded to the FBP Application at the end of each processing day,
and no later than the 16th day of the month for the 1st through 15th of the month and no later than the 1st
day of the following month for the 16th through the last day of the month. A&C SSO personnel will lock
the PWR for invoicing purposes bi-weekly, so it is critical for MEPS medical personnel to upload PWR
PDF files on time.
g. If the FBP is required to work after all the MEPS Medical staff have departed for the day, the OPSO
will ensure additional non-medical MEPS staff are properly trained in the Provider Work Record
verification process, so that the process described above is completed the same processing day in which the
work occurs.
h. An error on the PWR, must be corrected as follows:
(1) Draw a single line through the error – do not make more than one line through it.
(2) Print “error” as close as possible to the error with the line through it.
(3) The individual making the correction will place their initials by the error.
(4) Print the correct information.
i. The MEPS will maintain the PWR on file in the Medical Department under RN 40-1a/500A,
“Professional Consultant Records” (see Appendix A
, Section III).
j. The FBPs are paid only for the actual hours worked. There are two exceptions:
(1) If a MEPS closes on short notice, and the FBP was not contacted and reported for work
(2) If the FBP reports for work, and is sent home within one hour after reporting to work due to
the MEPS decreased workload. In this case, the FBP will be paid for one hour of work.
(3) Any other unusual circumstances must be coordinated with the FBP COR A&C SSO.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
118
Chapter 19
Medical Training Program
19-1. General
Training is a critical part of having a successful Medical Program. All MEPS Medical Department
personnel will be trained on how to perform all functions of their position description.
19-2. Initial Lead/Medical Technician Training
Initial Training: The Medical NCOIC/SUP MT must establish an initial training program based on a 90 day
training plan. On the Medical Department employee’s start date (or non-medical employee assignment
date), a training plan must be discussed and the employee must be informed of the required training on
medical functions, to be completed within the first 90 days of employment.
a. All functional areas in which the new employee must complete training are located on TSJTS found
on SPEAR.
b. The Medical NCOIC/SUP MT will assign a medical staff member as a trainer to the new employee
to train them on all the medical functions found on the TSJTS
, and to familiarize the employee with MEPS
specific processes. The Medical NCOIC/SUP MT may authorize the trainer to utilize other medical staff
members or rotate trainers so that more than one medical staff member is assigned to train the new
employee.
c. The trainer will provide a progress report to the Medical NCOIC/SUP MT on TSJTS completion at
the 30 and 60 day mark after the employee’s start date. All TSJTS training, as well as training in all medical
tasks, must be completed within 90 days of their start date and documented in the employee’s training
record. They must also become familiar with the UMR 40-1,
40-2, 40-8, 40-9, and the DoDM 6440.02
Clinical Laboratory Improvement Program prior to their 90 day mark.
d. After the 90 day training period, the Medical NCOIC/SUP MT will draft a Confirmed Training
Order (CTO) that will be signed by the MEPS Commander and kept in the employee training record.
Note: While the employee is in their initial training cycle, they will be operating under the CTO (both
UMR 40-1 and UMR 40-8
) of their trainer. It is imperative that all employees designated as trainers
understand that if a new employee makes critical errors, the trainer(s) can be held dually responsible,
resulting in possible disciplinary action including and up to their CTOs being revoked.
19-3. Initial Medical NCOIC/Supervisory Medical Technician Training
The MEPS Medical Department will notify J-3/5/7 MD via email of the arrival of a new NCOIC/SUP MT.
The Medical NCOIC/SUP MT will have their initial training reviewed and signed by J-3/5/7 MD MMA,
or their designee, during an Individual Training Visit (ITV).
a. Initial 60 day training for the NCOIC/SUP MT will be completed by the Medical Department Lead
Medical Technician (LMT)/Medical NCO.
b. The LMT/Medical NCO will complete all TSJTS training within 60 days of their start date and
ensure the training is recorded in the official training record.
c. Medical NCOIC/SUP MT must read UMR 40-1, 40-2, 40-8, 40-9, 601-23 and DoDM 6440.02
Clinical Laboratory Improvement Program prior to their 90 day mark.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
119
d. J-3/5/7 MD or their designee will provide the following via email:
(1) An open book/regulation pre-test that must be completed prior to the ITV.
(2) Information on the dates and times the ITV will be conducted. The Medical NCOIC/SUP MT
will inform J-3/5/7 MD or their designee if the dates of the visit need to be adjusted due to their availability
during this week. It is imperative that the Medical NCOIC/SUP MT is present for training to maximize the
training time, as a standard ITV is only 3 full working days long.
e. Upon completion of the ITV, a signed training checklist will be completed and placed in the
Medical NCOIC/SUP MT official training record.
f. After the ITV training checklist is signed, a CTO will be drafted, signed by the MEPS Commander,
and kept in the Medical NCOIC/SUP MT’s training record.
g. The Medical NCOIC/SUP MT is authorized a five day crosswalk at another MEPS. The J-3/5/7 MD
or their designee can assist a Battalion/MEPS Commander with selecting a MEPS for the crosswalk visit,
and Battalion Commanders can coordinate with other Battalion Commanders if a MEPS outside their
Battalion is recommended.
h. A MEPS Commander can request an ITV through J-3/5/7 MD for LMTs, Medical NCOs, or other
personnel detailed into the Medical NCOIC/SUP MT position.
19-4. Confirmed Training Orders
A CTO is required for initial training that must be signed off by the MEPS Commander. A signed/initialed
appointment order by the Commander confirms that the employee is fully trained on specific duties and
understands the additional regulatory and/or legal standards of these particular duties. CTOs will remain in
effect throughout the period of employment at the MEPS unless otherwise revoked by the MEPS
Commander.
a. The CTOs will be initiated after the employee has completed their 90 day training and the Medical
NCOIC/SUP MT must ensure the employee has completed all training per medical TSJTS
s and associated
regulations. The signing of the CTO’s indicate that ALL initial training has been completed. CTOs should
not be signed until the employee completes all training on the CTO and all medical
TSJTS.
b. The Commander will review the CTO to ensure that the training tasks have been completed, and
that the trainee and trainer have initialed on the Trainee/Trainer lines of the CTO. Once the review is
complete, the MEPS Commander will initial and sign the CTO.
c. The CTO will then be signed and dated by the employee, and the completed CTO will be filed in
the employee training record.
d. The types of required training listed on the CTO can be found in Paragraph 19-5
.
Note: For sustainment training, the Medical NCOIC/SUP MT must establish a training calendar IAW UMR
350-1, Command Training Program. The training calendar must include, at a minimum, one hour of
uninterrupted training per week. Training completion will be documented in the employee training record.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
120
19-5. Required Medical Training of All Medical Technicians
a. The following Medical Technician training is required to be reviewed and signed by the MEPS
Commander on a 40-1 CTO, is conducted IAW the TSJTS
s and associated regulations, and is governed by
UMR 350-1 and UMR 350-2:
(1) Body Fat Technician- Authorized to conduct body fat taping procedures on all applicants using
the Gulick II measuring tape.
(2) Chaperone- Authorized to observe an applicant during the medical examination process when
the provider and applicant are of a different biological sex or when requested by the applicant or medical
provider.
(3) Cerumen Removal- Authorized to conduct cerumen removal on an applicant.
(4) Medical Briefer- Authorized to give the USMEPCOM standardized medical brief to applicants.
(5) Standard Precautions (gloves and bloodborne pathogens) - Understands the minimum standard
precautions needed to conduct medical processing where there is a risk of bloodborne pathogen exposure.
(6) Urine Protein/Glucose/HCG- Authorized to test, read and annotate results of all urine protein,
glucose, and HCG testing on applicants. This includes performance of the QC on all these tests and proper
annotation on laboratory QC control logs.
b. Weekly medical training will be conducted using the most current TSJTS
s.
c. FY quarterly medical training will include the HIV and Drug TSJTS
and PowerPoint presentations
(HIV/Drug page on SPEAR).
d. Twice-a-year training will include the following:
(1) CLIP/CAP (specific for urine protein/glucose/HCG).
(2) A mock drill for a HIV-positive applicant (5D).
(3) A mock drill for manual processing of an applicant.
e. Annual refresher training will include the following:
(1) Body Fat Technician
(2) Cerumen Removal
(3) Chaperone
(4) Medical Briefer
(5) Standard Precautions (bloodborne pathogens) to include review of Safety Data Sheets (SDS)
(6) Breathalyzer (ref. UMR 40-8
)

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
121
Note: A guide to assist the Medical NCOIC/SUP MT and Medical Technicians in creating the Medical
Department training record can be found on SPEAR.
The set-up of an internal Medical Department training
record will not replace the unit training record, but is meant to give the Medical NCOIC/SUP MT a
comprehensive document of all medical (and other) training in order to assist with HQ USMEPCOM visits.
All training that is in the Medical Department training record must also be present in the unit training record,
which is overseen by the MEPS Senior Enlisted Advisor (SEA).
19-6. Chief Medical Officer Quarterly Review
a. The CMO will conduct a quarterly review of the Medical Department in the first month of each
quarter of each fiscal year using the CMO Quarterly Review Checklist found on SPEAR.
It is up to the
CMO to decide if they want to complete a section, several sections or the entire checklist during their
quarterly review. Once complete, the CMO will review findings with the Medical NCOIC/SUP MT and
determine if any training is required. Training will be conducted in the deficient areas within the same
quarter of the CMO review. Training rosters will be attached to the report and will be annotated in each
employee’s training record.
b. After training has been completed, the report will be sent to the MEPS Commander for review and
signature. The Commander must sign the report during the same quarter that the quarterly review was
completed. After the report has been signed by the CMO and Commander, it must be maintained in the
command training record for two years. The report will be available for review during inspections and Staff
Assistance Visits.
c. In the absence of the CMO, the ACMO or MO may complete the quarterly review. If there is no
government provider at the MEPS, the MEPS Commander will coordinate with J-3/5/7 MD to develop a plan
for quarterly review/training. In instances where training requirements cannot be met each quarter, the
MEPS Commander will complete a memorandum (example on SPEAR
under the Provider Training) and
forward it for review and concurrence by the J-3/5/7 MD. The memorandum will be retained on file for
review by Staff Assistance Visit and Inspector General Personnel. The Medical NCOIC/SUP MT will
perform a limited review consisting of medical technician processing areas and provide training as needed.
d. The CMO quarterly review report/Commander’s memorandum (to include attached training rosters
if applicable) will be filed in the Medical Department under RN 1-201a/800D, Inspection, Survey, and SAV
Files – CMO Quarterly Review (see Appendix A
, Section III).
19-7. Mandatory USMEPCOM Provider Medical Training and Documentation
a. This mandatory training is intended to give the MEPS medical provider guidance on the medical
examination process specific to the MEPS.
b. All MEPS providers must have documented mandatory training on the following tasks:
(1) Cerumen Removal Program
(2) Chaperone
(3) Accession medical examination and profiling as described in Chapter 11
of the current UMR
(4) Standard Precautions

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
122
c. This mandatory training is not a component of the Provider Quality Management Program (PQMP)
and will be conducted after the medical provider has been approved to work at the MEPS. It contains
instructions on how these specific duties are to be performed, and is based on policy adapted to support the
unique USMEPCOM accession mission. The new provider will have 90 days to initially complete the
mandatory USMEPCOM medical training. It will be done during their in-processing and orientation stage
after they are approved to work at the MEPS.
d. Initial Provider Training: The provider will be given an initial 90 day time frame to complete all
four mandatory USMEPCOM medical tasks. This time will start on the first day of the provider working
at the MEPS. Because FBPs work on an intermittent schedule, the Medical Department is authorized to
specifically request the FBP, by name, in order to accomplish this training during the initial training time
frame.
(1) The Medical Department NCOIC/SUP MT will inform the new provider of the medical tasks that
they must be trained on within the first 90 days of employment.
(2) As the new provider completes their initial PQMP training, the NCOIC/SUP MT will ensure
these USMEPCOM specific mandatory tasks are completed.
(a) If the provider is an ACMO/MO or FBP, the NCOIC/SUP MT will ensure training is
completed with oversight from the CMO.
(b) If the provider is a CMO, the NCOIC/SUP MT will ensure training is completed with
oversight from the MEPS Commander.
(3) The NCOIC/SUP MT will provide the following to the new provider:
(a) Cerumen Removal TSJTS
.
(b) Chaperone TSJTS
.
(c) A copy of Chapter 11
of this UMR explaining accession medical examination and
profiling.
(d) Standard Precautions TSJTS
.
Note: Training in these tasks also requires a review of the corresponding regulatory standard. The MEPS
CMO and/or NCOIC/SUP MT can add MEPS-specific local policy as it relates to the training task (e.g.,
location of the supplies, chaperone rosters etc.)
(4) There is no requirement to further test the provider’s knowledge on these tasks. The provider-
in-training should be encouraged to seek further clarifications from the CMO or NCOIC/SUP MT if they
don’t understand the training content. The NCOIC/SUP MT will ensure the provider has access to review
anything associated with the task they are training on, i.e., equipment, additional instructions, and
documents.
(5) Once the provider has read the TSJTS
s they will sign and date in the “Trainee Signature” block.
They will do this for each TSJTS and return to the NCOIC/SUP MT.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
123
(6) Once the NCOIC/SUP MT has all four signed TSJTS
s, they will draft the Initial Training
Document (ITD). The TSJTSs will only be used to record the actual date that the provider completed the
task. Once the ITD has been drafted, and dates and initials have been annotated, the TSJTSs may be
discarded/deleted.
(7) Completing the ITD- This is a signed training document that indicates that the provider has
completed initial training. An ITD should not be drafted until all the mandatory training duties have been
completed. A provider without an ITD is considered to be in their initial training phase. The ITD will be
completed as follows:
(a) Must be on the MEPS letterhead in the ITD MFR format found on SPEAR
.
(b) The date of the ITD will be the day the NCOIC/SUP MT drafts the document after all the
initial training TSJTS
s have been completed (the ITD date will be on or after all the training dates on the
ITD).
(c) The NCOIC/SUP MT will annotate the training dates and have the provider initial as the
trainee after each duty. The NCOIC/SUP MT will then initial as the trainer. All four areas must be initialed.
(d) The CMO will be the final training authority, and will initial after the provider and
NCOIC/SUP MT have initialed. The MEPS Commander will initial for the CMO.
(e) The CMO (or MEPS Commander for the CMO) will sign the ITD.
(f) The provider will then print, sign, initial and date the ITD after the CMO (or Commander)
signs.
(g) The signed ITD will be put in Section 3 of the provider six part folder (6PF). The ITD
serves as a consolidated document for initial provider mandatory training that was conducted and
completed. The ITD will stay in the 6PF for the duration of the provider’s employment and will never be
removed.
(h) The ITD is good for one year from the date it was drafted (not the individual training dates).
Mandatory USMEPCOM provider training is recurrent and must be done annually (due to possible updates
to the duties) prior to expiration, and documented on an Annual Training Document (ATD)
e. Annual Training- The provider must complete annual refresher training on all four USMEPCOM
mandatory medical tasks. The Medical Department can specifically request the FBP, by name, in order to
complete this training before the previous training expires.
(1) The Medical Department NCOIC/SUP MT will inform the provider that mandatory
USMEPCOM training is due and wll ensure the specific USMEPCOM mandatory training is completed.
(a) If the provider is an ACMO/MO or a FBP, the NCOIC/SUP MT will ensure training is
completed with oversight from the CMO.
(b) If the provider is a CMO, the NCOIC/SUP MT will ensure training is completed with
oversight from the MEPS Commander.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
124
(2) List of training material is provided in Paragraph 19-7d(3)
.
(3) Once the provider has read the TSJTS
s they will sign and date in the “Trainee Signature” block.
They will do this for each area and return to the NCOIC/SUP MT.
(4) Once the NCOIC/SUP MT (or assigned representative) has signed all four areas, they will draft
the Annual Training Document (ATD). The TSJTS
s will only be used to record the actual date that the
provider completed the task. Once the ATD has been drafted and dates and initials have been annotated,
the
TSJTSs can be discarded/deleted.
(5) Completing the ATD- This is a signed training document that indicates that the provider has
completed annual mandatory USMEPCOM refresher training. The ATD is completed in the same
MFR format as the ITD.
(a) Must be on the MEPS letterhead in the ATD MFR format found on SPEAR
.
(b) The date on the ATD will be the day the NCOIC/SUP MT drafts the document after all
four areas have been completed (the ATD date should be on or after all the training dates on the ITD).
(c) The NCOIC/SUP MT will annotate the training dates and have the provider initial as the
trainee after each task. The NCOIC/SUP MT will then initial as the trainer.
(d) The CMO (or Commander) will be the final training authority and initial after the provider
and NCOIC/SUP MT have initialed.
(e) The CMO (or Commander) will sign the ATD.
(f) The provider will then print, sign, initial and date the ATD after the CMO (or Commander)
signs.
(g) The signed ATD will be placed in Section 3 of the provider 6PF. The ATD will stay in the
6PF for a year. When a new ATD is completed, the previous ATD will be pulled out and discarded (the
old ATD is similar to an expired CPR card. Once a new one is completed the previous one is invalid and
does not need to stay in the record).
f. MEPS providers do not complete a UMR 40-1 CTO or a UMR 40-8 CTO, but must complete an
ITD and the annual ATD. A CTO is used for Medical Technicians.
Note: It is preferred for the provider to complete all the training requirement described on the ITD and
ATD in one day (especially FBPs). The minimum requirement is for the provider to read the TSJTS
s and
have an understanding of the policy. Therefore, it is common to see all of the training dates be the same on
the ITD/ADT.
19-8. MEPS Medical Provider Six Part Folder Requirements
a. The MEPS are to use a 6PF for all medical providers working at the MEPS. These folders must be
kept in a secure and locked file cabinet. These files are only accessible by authorized medical supervisory
personnel in the MEPS, which includes any medical staff designated by the CMO/NCOIC/SUP MT (e.g.,
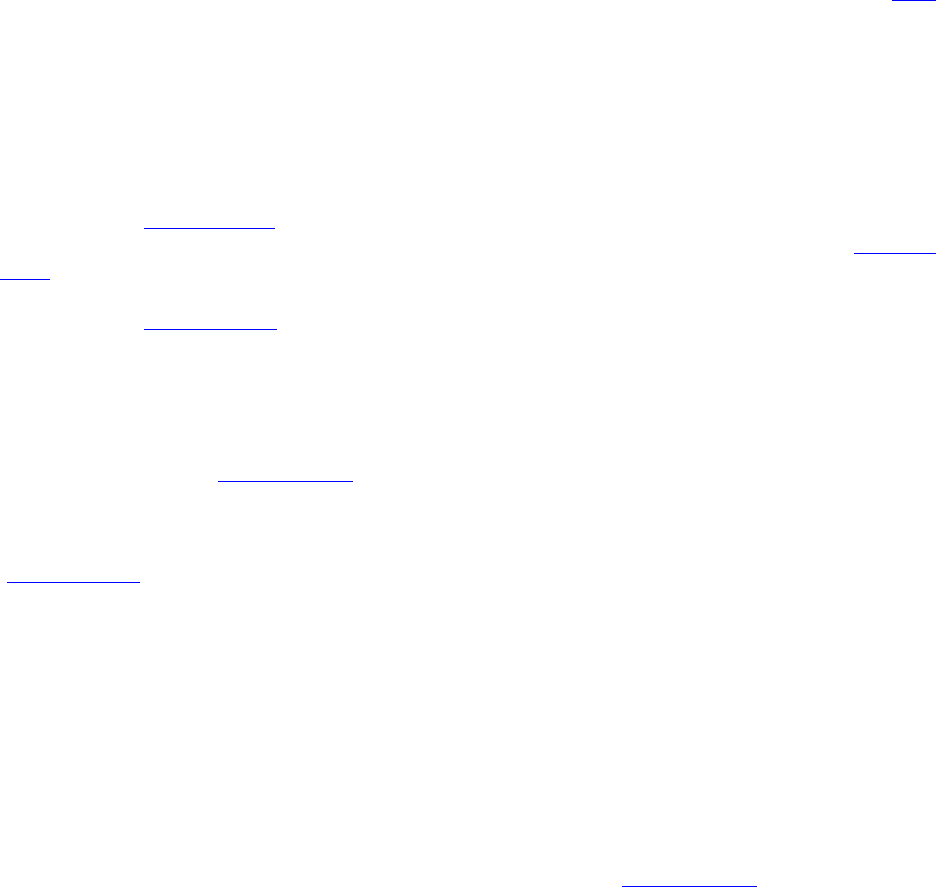

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
125
medical training NCO). The MEPS Commander may access the provider 6PF. Providers may review their
folder. However, the folder cannot be removed from control of the MEPS medical staff.
b. The provider 6PF will be set up as follows:
(1) Section 1 – Mandatory USMEPCOM Provider Documentation
(a) UMF 40-2-1-E
Medical Provider Initial Application – The previous initial application form
(UMF 40-1-7-E) is no longer used, however, the UMF 40-1-7-E will be grandfathered and a new UMF 40-
2-1-E will not be completed.
(b) UMF 40-2-4-E
Contract Provider Quality Management Form (if applicable) – This form
is used for FBP evaluations. If a form has been submitted to the USMEPCOM Provider Review Panel
(PRP) for review and signature, a copy of the form will be placed in the 6PF as a placeholder until return
of the signed form from the PRP. Once the signed copy is received, remove the placeholder and replace
with the completed document.
Note: The UMF 40-2-3-E
Provider Clinical Assessment and Qualification for government
providers (CMO/ACMO/MO) may have performance and evaluation annotations on them, and will be sent
directly to the MEPS Commander (or the CMO if the evaluation is for an ACMO). These forms must be
kept in their government personnel folder, but a copy may be placed after the Provider Initial Application
(
UMF 40-2-1-E or UMF 40-1-7-E) in their individual 6PF.
(2) Section 2 – Mandatory Licensure Information
(a) Current Medical License
(b) Current Basic Life Support (BLS) card
Note: The FBP will provide all updated copies of medical licenses and BLS cards to the FBP
COR A&C SSO, who will then forward these documents to the MEPS. All expired licenses and BLS cards
will be removed from the 6PF and returned to the provider.
(3) Section 3 – Mandatory Medical Training Documentation (Paragraph 19-7
)
(a) Annual Training Document (ATD)
(b) Initial Training Document (ITD)
Note: Once completed, the ITD will never be removed from the provider 6PF as long as they
are contracted/employed at the MEPS. Refresher training will be completed annually thereafter and
documented on the ATD. When a new ATD is completed, the old ATD will be removed.
(4) Section 4 – Mandatory Non-Medical Training Documentation (only applicable if the provider
has a CAC/PIV card and computer access)
(a) Mandatory MEPS IT classes
(b) DD Form 2875, System Authorization Access Request

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
126
Note: Once completed, the DD Form 2875 will permanently remain as a reference. All IT
training can be accessed through the SPEAR J-1 webpage. Refresher training will be mandated through the
USMEPCOM annual training calendar. If a provider has a CAC/PIV card and has computer access they
must complete these USMEPCOM required courses. When the new training is completed, the old
certificates will be removed and replaced with current certificates.
(5) Section 5 – Physical Examination (FBPs only)
(a) Occupation Physical Examination Certificate (OPEC) - Renewal will occur every two
years from the last day of the FBP’s initial qualification month. FBP COR A&C SSO will send the OPEC
to the MEPS from the contracting agency.
(b) Other FBP medical documentation (i.e., X-ray reports, lab results etc.)
Note:
If the OPEC contains Hepatitis B/Tetanus information, a copy will also be made and placed in the
provider’s individual health record. CMOs/ACMOs/MOs will not have an OPEC, and this section of their
6PF will be empty. CMOs/ACMOs/MOs will have an employee health record with Hepatitis B and Tetanus
information (or UMF 40-9-1-R-E declination) IAW UMR 40-9
.
(6) Section 6 – Miscellaneous Training Documentation
(a) USMEPCOM Training Day Medical Documentation
(b) PQMP Training Documents
(c) Other Medical Training Documentation
1. Non-PQMP training given by another provider.
2. General USMEPCOM medical training by MEPS medical staff (overseen by medical
NCOIC/SUP MT).
3. Expired training documentation (over 2 years) will be removed and returned to the
provider.
c. The provider 6PF must be updated with new training requirements, current licenses, BLS cards,
USMEPCOM forms and FBP OPECs. These documents will be sent via outlook email or the USMEPCOM
Command Message System. Medical documents and required training will be placed in the appropriate
6PF section.
d. The Command Surgeon Office will archive the USMEPCOM copy of the provider’s 6PF upon
notification from the FBP vendor that a provider no longer works for them. The MEPS is then required to
scan the FBP's individual health record to the FBP COR A&C SSO for archival purposes IAW UMR 40-9
.
When the scanned copies are received, the FBP COR A&C SSO will notify the MEPS to destroy the
provider’s original 6PF and their health record.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
127
Chapter 20
Medical Equipment, Supplies, and Cleaning
For any equipment that falls under the Medical Standby Equipment Program (MEDSTEP) located on the
Medical Materiel Allowance List (MMAL), reference the Equipment Maintenance Program TSJTS
for
instructions on exchanges and replacements.
20-1. Audiometric Equipment Calibration and Audio Booth Maintenance
a. For validation of audiometric reference thresholds of audiometers in the audio room, the MEPS
must file the electroacoustical calibrations (completed by Tobyhanna) and the DD Form 2217
(Biological
Audiometer Calibration Check) which is completed by using the Bio-Acoustic Simulator (BAS). The
MEPS must establish a primary baseline calibration with a BAS once machines are received from Tobyhanna
and document the results on a
DD Form 2217.
b. An electroacoustical calibration will be performed annually on audiometers. The supporting
medical maintenance operations division operated by the United States Army Medical Materiel Agency
(MMOD-PA) will perform the calibration. Audiometers will be calibrated to American National Standards
Institute (ANSI) S3.1-1999 standards. A DD Form 2163 (Medical Equipment Verification/Certification)
label, indicating the date of the last electroacoustical calibration, will be prominently displayed on the
audiometers. The calibration verification demonstrates that the audiometer meets specific requirements
stated in the applicable sections of ANSI S3.1-1999. The electroacoustical calibration is valid for one year
plus a one-time extension of up to 30 days. The electroacoustical calibration paperwork must be filed with
the DD Form 2217
.
c. Upon receipt of replacement audiometers, an initial (baseline) calibration check will be performed
using a BAS. A bioacoustic calibration check, using the same BAS that was used for the primary check,
will be completed every calendar week. The weekly calibration check will be recorded on DD Form 2217
.
If an audiometer fails the calibration check (greater than ± 5db), ensure that the headsets have been correctly
placed on the simulator and that connectors are fully plugged in before repeating the test with the BAS. If
the repeated test fails, the failure must be noted in the ‘Remarks’ block on the
DD Form 2217, and the
audiometer will be taken offline. Follow the Equipment TSJTS for further troubleshooting. Contact the
biomedical technicians (biomeds) at MMOD-PA via their hotline phone number for troubleshooting
assistance and for a possible replacement audiometer. File electroacoustic calibration records with DD
Form 2217 under RN 40-61i/500A, Medical Equipment Maintenance –
DD Form 2217 (see Appendix A,
Section III).
d. The ambient background noise check (sound level) of the audio booth ensures the environment
within the booth is sufficiently quiet to perform hearing tests. The appropriate supporting Army Medical
Treatment Facility (MTF) is responsible for overall booth maintenance as well as measuring ambient noise
with a sound level meter annually or when changes in ambient noise are reasonably suspected (for example,
highway construction next to MEPS). Sound level certification is valid for one year plus a one-time
extension of up to 30 days from the date of issuance and must be prominently displayed outside the audio
booth. Allowable background noise levels for audiometric testing rooms are as follows:

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
128
Figure 20-1. Background Noise Levels
Figure 20-1. Background Noise Levels
e. The interiors of audiometric testing environments will be illuminated with low wattage bulbs (less
than 60 watts) or light emitting diode technology to reduce heat radiation.
f. Audiometers are calibrated to a specific headset. The headset that was calibrated to the audiometer
is the only authorized headset for that specific audiometer. If the headset becomes unusable, the audiometer
will no longer be used for testing applicants and must be reported to Tobyhanna. When an audiometer is
replaced or exchanged, the companion headset must accompany the audiometer with which it was
calibrated.
g. Ensure audiometers are connected to the battery backup uninterrupted power supply (UPS) outlets
with surge protection.
20-2. Height/Weight Measurement Equipment
a. Height measurement devices will be the wall-mounted type, SECA MDL 222 or SECA MDL 216.
The device must be properly installed and verified for accuracy after installation. The MEPS Medical
Department is to attach a level perpendicular (only for SECA MDL 222) to the wall to ensure the measuring
device is level.
b. The MEPS Medical Department will check monthly that the height measurement devices are still
securely mounted to the wall.
Figure 20-2. Height Device
Figure 20-2. Height Device

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
129
c. Weight measurement digital scale accuracy will be confirmed daily by a medical technician using
the 25-pound weight issued with the scale and documented per Height/Weight/Body Fat/BMI TSJTS.
Should the scale fail the daily accuracy confirmation or appear to be unserviceable, contact the biomeds at
MMOD-PA via their hotline phone number for troubleshooting assistance and for a possible replacement
scale.
20-3. Gulick II Tape
This is the only tape in the MMAL
authorized for measuring Service applicants’ body circumference in
order to calculate body fat percentage. It is made of a non-stretchable material, and will be 1/4- to 1/2-inch
wide (not exceeding 1/2 inch). It is spring loaded to ensure the same amount of pressure is applied to each
applicant uniformly. Further instructions on using the Gulick II tape may be found in the
Height/Weight/Body Fat/BMI TSJST and the manufacturer’s instructions.
20-4. Proteinuria Qualitative Test
a. Qualitative urine tests for protein will be done using the Siemens Uristix (stock number 6650-00-
226-1203). When a medical technician opens a new bottle, the date and their initials must be annotated on
the side of the bottle. Refer to MMAL
for Uristix ordering information.
b. The MEPS Medical Technician must complete quality control tests whenever a new Uristix bottle
is first opened and every 30 days thereafter until the Uristix bottle is empty, expired, or no longer passes
the controls.
c. Record all quality control test results/Uristix bottle lot number and open date on (UMF 40-1-8
).
The UMF 40-1-8 will be maintained on file for two calendar years from the date of last test in the Medical
Department, then destroyed. File under RN 40-24a2/500A, “Medical Laboratory Performance Files” (see
Appendix A, Section III).
20-5. Glycosuria Qualitative Test
a. Qualitative urine tests for glucose will be done using the Siemen Uristix (stock number 6650-00-
226-1203). When a medical technician opens a new bottle, the date and their initials must be annotated on
the side of the bottle. Refer to MMAL
for ordering information for Uristix.
b. The MEPS Medical Technician must complete quality control tests whenever a new Uristix bottle
is first opened and every 30 days thereafter until the Uristix bottle is empty, expired, or no longer passes
the controls.
c. Record all quality control test results/Uristix bottle lot number and open date on (UMF 40-1-8
).
The UMF 40-1-8 will be maintained on file for two calendar years from the date of last test in the Medical
Department, then destroyed. File under RN 40-24a2/500A, “Medical Laboratory Performance Files” (see
Appendix A, Section III).
20-6. Pregnancy Test
a. The authorized pregnancy test kit for MEPS use is the QuickVue+® One-Step HCG Combo test
kits (stock number 6550-01-591-0962) listed on the MMAL.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
130
b. The MEPS must follow the instructions contained in the product package insert of the authorized
pregnancy test kit.
c. The MEPS will acquire HCG Urine (Pregnancy) control set, NSN 6550-01-506-4951 for completion
of external QC checks.
d. Controls will be run and documented in a control log (UMF 40-1-6
) whenever a new box of test
kits is first opened and every 30 days thereafter until the box is empty, expired, or no longer passes the
controls.
e. The logs must be maintained in the Medical Department under RN 40-24a2/500A, “Medical
Laboratory Performance Files” (see Appendix A, Section III
) and will be maintained on file for two
calendar years from the date of last test in the Medical Department,. Use control information established
by the Center for Clinical Laboratory Medicine in
DoDM 6440.02 (Clinical Laboratory Improvement
Program). Ensure the expiration date has not passed.
20-7. Safety Data Sheets
Please refer to UMR 385-1
and OSHA Hazard Communication Standard 29 CFR 1910.1200 a2 and CFR
1910.1200 h1 for more information on the requirements for Safety Data Sheets.
20-8. Virtual Medical Library
The Army Medical Department online library in Army Knowledge Online is available to anyone with a
Common Access Card. It can be accessed through the following link: https://medlinet.amedd.army.mil
/. A
free subscription to UpToDate.com is included with this access. Instructions on how to access the online
library and additional medical resources can be found on
SPEAR.
20-9. Cleaning of the Medical Department
a. The MEPS must provide a safe and sanitary environment for all applicants and employees.
b. Routine cleaning and disinfection of frequently touched surfaces is important. Cleaning will be
done daily by the local MEPS housekeeping department and medical personnel. Routine cleaning should
primarily be directed toward those items that have been in direct contact with the applicant or in contact with
the applicant’s excretions, secretions, blood, or body fluids.
c. Cleaning and disinfecting will be performed as follows:
(1) Select EPA-registered disinfectants, and use them in accordance with manufacturer
instructions.
(2) For cleaning and maintaining medical equipment and follow the equipment manufacturers’
instructions. In the absence of manufacturers’ cleaning instructions, the following procedures will be
adhered to:
(a) Clean medical equipment surfaces with a detergent/disinfectant.
(b) Do not use alcohol to disinfect large environmental surfaces.
(3) Use barrier protective coverings for noncritical surfaces that are touched frequently with gloved

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
131
hands during the delivery of applicant care likely to become contaminated with blood or body substances
or difficult to clean (e.g., computer keyboards).
(4) Keep housekeeping surfaces (e.g., floors, walls, tabletops) visibly clean on a regular basis and
clean up spills promptly.
(5) Use a one-step process and an EPA-registered detergent/disinfectant designed for general
housekeeping purposes in Medical Department areas where uncertainty exists as to the nature of the soil on
the surfaces (e.g., blood or body fluid contamination versus routine dust or dirt).
(6) Detergent and water is adequate for cleaning surfaces in non-medical processing areas (e.g.,
administrative offices).
(7) Clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces (e.g., doorknobs, exam tables, light switches,
and surfaces on and around toilets) on a more frequent schedule than minimal-touch housekeeping surfaces.
(8) Clean walls, blinds, and window curtains in Medical Department areas when they are visibly
dusty or soiled.
(9) Avoid large-surface cleaning methods that produce mists or aerosols, or disperse dust in
Medical Department areas.
(10) Prepare cleaning solutions daily or as needed, and replace with fresh solution.
(11) Change the mop head at the beginning of each day, or after cleaning up large spills of blood
or other body substances.
(12) Clean mops and cloths after use and allow to dry before reuse; or use single-use, disposable
mop heads and cloths.
d. MEPS Medical Departments must properly maintain their work area to present a professional and
safe environment for applicants while they are conducting medical processing. This includes removing
unnecessary obstructions and clutter. The MEPS Medical Department must not place unnecessary
equipment and supplies placed in hallways, examination and ortho/neuro rooms, and the laboratory.
e. All Medical Department personnel, FBPs, ASTs, and any non-Medical Department personnel
assigned to duty in the Medical Department (i.e., chaperones, QC officers), must complete training on
Standard Precautions for Infection Control in the MEPS, IAW Paragraph 19-5
of the current regulation.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
132
Chapter 21
Shipping Disruptions
During shipping inspection, new medical information may be obtained which may change the qualification
status of an applicant who is shipping. A shipping applicant may be found to have a disqualifying condition.
Disqualification of an applicant during a medical shipping inspection is a highly disruptive event,
significantly impacting the applicant and family, and their Service Recruiting and Training Commands.
Examples of shipping disruptions include a change in the interim medical history, a new disclosure, and/or
a medical condition not previously identified during the qualification medical evaluation.
21-1. Medical Qualification Status Change of a Shipping Applicant
a. The MEPS Operations Department or SL will provide the shipping applicant’s medical record to
the MEPS Medical Department for review.
b. When a temporarily disqualifying condition is identified during the shipping inspection, e.g.,
fever, open wound, recent injury or current illness, the applicant will be further evaluated by the MEPS
CMO/ACMO/MO/FB-CMO. The MEPS provider will do the following:
(1) Document the results of the inspection in item 81 on the DD Form 2808
.
(2) Change the PULHES to “3T”. Do NOT change item 74.
(3) Update items 77 and 79 with the applicant’s temporarily disqualifying condition, and enter
“RBJ date.” All updates to the paper record must be entered into USMIRS.
(4) Ensure the applicant is placed in an “N” status with comment “DO NOT SHIP UNTIL
CLEARED BY MEPS CMO”.
(5) Ensure the medical technician changes the WKID in USMIRS.
(6) Send the applicant to the SL for further processing.
Note: For any applicant whose shipping was stopped due to illness or injury, the applicant must return to
the MEPS Medical Department for inspection after RBJ date prior to shipping.
c. When a disqualifying condition is identified during the shipping inspection, the applicant will be
further evaluated by the MEPS CMO/ACMO/FB-CMO. The MEPS provider will do the following:
(1) Document the results of the inspection in item 81 on the DD Form 2808
.
(2) Change the PULHES to “3P”.
(3) Update items 77 and 79 with the applicant’s disqualifying condition. All updates to the paper
record must be entered into USMIRS.
(4) Change item 74(a) to “IS NOT MEDICALLY QUALIFIED”.
(5) Ensure the applicant signs and dates in items 75(a) & (b) after informing the applicant of the
disqualification determination

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
133
(6) Ensure the medical technician changes the WKID in USMIRS.
(7) Contact the SMWRA in order to discuss a possible same day waiver decision.
(a) If medical referral services are requested by the SMWRA (i.e., courtesy consultation), the
provider will leave PULHES as “3P” (do not change to “O”), and will follow the guidance in
Paragraph
13-2q.
(b) If medical referral services are not requested by the SMWRA, and a waiver decision is
received by the MEPS, then the provider will document the waiver decision in item 87, and 77 if applicable.
(8) Notify the SL of the SMWRA decision and send the applicant to the SL for further processing.
(9) If there is disagreement between the SMWRA and the CMO, then MEPS will notify J-3/5/7
MD via MOC ticket for assistance.
d. When a potentially disqualifying medical condition is identified during the shipping inspection,
the applicant will be further evaluated by the MEPS CMO/ACMO/MO/FB-CMO in order to determine if
continued shipping is warranted. If additional evaluation or documentation is required, then the MEPS
provider will do the following:
(1) Change the physical profile to “O” in item 76.
(2) Document the necessary action(s) required to render a medical qualification determination in
item 79.
(3) Obtain additional consultation evaluation IAW Chapter 13
guidance, if necessary.
(4) Obtain additional documentation by completing a med read coversheet with a list of the
required documents IAW Appendix F
, and forward to the SL for action.
(5) Ensure that the medical technician changes the WKID in USMIRS.
21-2. Differences of Interpretations of Accession Medical Standards for Shipping Applicants
a. Between MEPS Providers- In situations where the provider performing the shipping inspection
disagrees with a prior medical qualification determination due to a difference in interpretations of accession
medical standards, the providers will do the following:
(1) Attempt to resolve the case at the MEPS level by discussing the case with the MEPS provider
who rendered the prior medical qualification determination, if that provider is available.
(2) If the prior provider is not available, the case should be discussed with the CMO/ACMO/FB-
CMO.
(3) If the case is resolved after discussion, and the applicant is disqualified, then follow instructions
per Paragraph 21-1c
.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
134
(4) If the MEPS providers are unable to resolve the case, then the MEPS will submit a MOC ticket
and call J-3/5/7 MD for assistance with resolution. The MOC ticket will be submitted with all pertinent
details of the case and, if necessary, the applicant’s medical records will be sent to J-3/5/7 MD via encrypted
email.
(5) For contract providers at a MEPS without a CMO, the contract provider will direct the MEPS
Medical Department to submit a MOC ticket with all pertinent details of the case, and will call J-3/5/7 MD
to discuss the case before disqualifying the applicant.
b. Between MEPS Providers and SMWRAs- In situations where a SMWRA disagrees with a
medical disqualification determination rendered by a MEPS provider, the CMO will do the following:
(1) Attempt to resolve the case at the MEPS level by discussing the case with the SMWRA.
(2) If the case is resolved and the applicant is disqualified, then follow instructions per
Paragraph
21-1c.
(3) If the SMWRA and the CMO are unable to resolve the case, then the CMO will submit a MOC
ticket and call J-3/5/7 MD for assistance with resolution. The MOC ticket will be submitted with all
pertinent details of the case and if necessary, the applicant’s medical records sent to J-3/5/7 MD via
encrypted email.
21-3. No Shipping on (Working) Copies
a. The SL is responsible for ensuring original documents are available before projecting the applicant
for shipping.
b. When original medical documents are not available, the applicant must complete a new medical
examination, including DAT and HIV testing. The applicant will be allowed to ship once the new medical
examination and negative DAT and HIV results are completed.
c. Medical documents marked as “working copy" are NOT authorized for inclusion into the
applicant's enlistment packet. If there is doubt concerning authenticity or legibility of medical documents, the
MEPS will conduct a new medical examination.
d. For guidance regarding shipping on copies for National Guard and Reserve, see UMR 55-2.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
135
Chapter 22
Medical Emergencies in the MEPS
22-1. Medical Emergencies in the MEPS
The MEPS Medical Department will evaluate any applicant who becomes ill or is injured while at the
MEPS.
a. The CMO, ACMO, MO or FB-CMO will determine if emergency medical treatment is necessary
for any illness and/or injury that occurs at the MEPS. MEPS personnel will only provide life-sustaining
emergency procedures (BLS) until Emergency Medical Services arrive. The CMO, ACMO, MO or FB-
CMO is authorized to contact the receiving Emergency Department physician in order to provide the details
of the illness or injury, if required.
b. If the applicant is at an outside facility for a consultation, the contracted consultant will determine
if emergency treatment is necessary for any illness or injury that occurs at their facility.
Note: The Recruiting Service is responsible for arranging the applicant’s transportation after discharge
from the local medical treatment facility.
c. The MEPS Commander or their designee will submit a station advisory report (STAR) IAW UMR
380-1 (USMEPCOM Security Program), using the station advisory reporting network (STARNET).
d. MEPS will not advise an applicant on the coverage of cost of a medical claim. Any claims
associated with injuries sustained at a MEPS or a consultant’s office shall be addressed IAW UMR 27-1.
e. Each MEPS will implement their own Falls Prevention Program which should include, but is not
limited to, the AWARE Program which may be found on the SPEAR. This Falls Prevention Program should
be implemented with consideration of available personnel, furniture, work space, floor plan, and work flow
of the MEPS. The Falls Prevention Program should include policy adjustments (work flow) as well as
engineering (arrangement of furniture) adjustments in lieu of personnel or equipment shortfalls.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
136
Appendix A
References
Section I
Publications referenced in, or related to this regulation
DoDI 1308.3
DoD Physical Fitness and Body Fat Program Procedures
DoDI 6130.03-V1
Medical Standards for Miitary Service: Appointment, Enlistment, or Induction
DoDM 6440.02
Clinical Laboratory Improvement Program (CLIP) Procedures
UMR 25-50
Official Mail and Distribution Management Program
UMR 25-53
PII and PHI Incident Reporting and Breach Notification
UMR 27-1
Military Justice and Legal Services
UMR 40-2
Provider Quality Management Program
UMR 40-8
DoD HIV Testing Program and Drug and Alcohol Testing Program
UMR 40-9
Bloodborne Pathogen Program
UMR 55-2
Recruit Travel
UMR 350-1
Command Training Program
UMR 350-2
Training Documentation
UMR 380-1
USMEPCOM Security Program
UMR 385-1
Safety and Occupational Health Program

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
137
UMR 601-23
Enlistment Processing
UMR 680-3
United States Military Entrance Processing Command Integrated Resource System (USMIRS)
UMR 715-4
Applicant Meals and Lodging Program
Section II – Forms
Forms referenced in or related to this regulation
CLMS Form 2
Clinical Laboratory Improvement Program – Change Request Form
DD Form 1966
Parental Consent
DD Form 2005
Privacy Act Statement - Health Care Records
DD Form 2217
Biological Audiometer Calibration Check
DD Form 2807-1
Report of Medical History
DD Form 2807-2
Accessions Medical History Report
DD Form 2808
Report of Medical Examination
DD Form 2923
Privacy Act Cover Sheet
SF 507
Medical Record
SF 513
Medical Record Consultation Sheet
SF 1034
Public Voucher for Purchases and Services Other Than Personal
UMF 40-1-4
MEPS Refractive Eye Surgery Worksheet
UMF 40-1-5
Specialty Consultation Contract/Ancillary Services Contract Performance Report

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
138
UMF 40-1-6
HCG Control Log
UMF 40-1-8
Uri-Stix Control Log
UMF 40-1-11
Blood Pressure Measurement Worksheet
UMF 40-1-12
MEPS Fee Basis Provider Work Record
UMF 40-1-15-E
Supplemental Health Screening Questionnaire
UMF 40-1-18
Uri-Stick Control Log
UMF 40-2-1-E
Medical Provider Initial Application
UMF 40-2-3-E
Provider Clinical Assessment and Qualification
UMF 40-2-4-E
Contract Provider Quality Management Form
UMF 40-8-1-E
DAT/HIV Acknowledgement
UMF 40-9-1-E
Hepatitis B and Tetanus Vaccination Declination
UMF 601-23-E
Report of Additional Information
UMF 601-23-1
QRP Discrepancy Sheet
UMF 680-3-2-E
QRP Discrepancy List
UMF 680-3A-E
Request for Examination
UMF 727-E
Processing List (PL)

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
139
Section III
Recordkeeping Requirements
RN 1-201a/800D: “Inspection, Survey, and SAV Files – CMO Quarterly Review” PA: N/A
Keep in office file for 2 years, then destroy. (Referenced in Paragraph 19-6d
)
RN 11-2a3/800B: “Management Control Program” PA: N/A
Keep in office file until next management control evaluation, not more than 6 years, then destroy.
(Referenced in Appendix B-6
)
RN 40/500A: “General Medical Services Files” (may insert applicant info to file by applicant) PA: N/A
Keep in office file for 2 years, then destroy. (Referenced in Paragraph 11-1d(51)
)
RN 40-1a/500A: “Professional Consultant Records” PA: A0040-1DASG
Upon transfer or termination of individual, keep in office file for 1 year, or no longer needed for
conducting business, then destroy.
(Referenced in Paragraph 18-5i
)
RN 40-24a2/500A: “Medical Laboratory Performance Files” PA: N/A
Keep in office file for 2 years, then destroy. (Referenced in Paragraphs 20-4c, 20-5c, 20-6e
)
RN 40-61i/500A: “Medical Equipment Maintenance - DD Form 2217” PA: N/A
Keep in office file for 2 years, then destroy. (Referenced in Paragraph 20-1c
)

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
140
Appendix B
Internal Control Evaluation Checklist - Medical
B-1. Function. The function covered by this checklist is medical processing at the MEPS.
B-2. Purpose. The purpose of this checklist is to assist MEPS Commanders in evaluating the key internal
controls identified below. It is not intended to cover all controls.
B-3. Instructions. Answers must be based on actual testing of key management controls (e.g., document
analysis, direct observation, and sampling). Answers that indicate deficiencies must be explained and
corrective actions indicated in the supporting documentation. These controls must be evaluated at least
every 2 years. Certification that the evaluation has been conducted must be accomplished on DA Form 11-
2-R, Management Control Evaluation Control Evaluation Certification.
B-4. Questions
a. Are the providers reviewing the medical prescreen forms correctly? (Chapter 2)
b. Is the chaperone/consent stamp filled out correctly? (Chapter 3
)
c. Are applicant packets reviewed for minor and prior service documentation upon medical check-in?
(Chapter 4
)
d. Is the medical briefing conducted properly? (Chapter 5
)
e. Are the medical technicians conducting hearing and vision testing on all applicant physical
examinations? (Chapters 6 and 7
)
f. Are all applicants shipping from the MEPS having temperature taken? (Chapter 8
)
g. Is current CLIP certification on file? Is a laboratory director identified? Is semi-annual CAP testing
performed and results on file? (Chapter 9
)
h. Are the providers conducting the applicant interviews properly? (Chapter 10
)
i. Are the applicants and medical staff completing DD Form 2807-2
(Accessions Medical History
Report), DD Form 2808 (Report of Medical Examination), and UMF 40-1-15-E (Supplemental Health
Screening Questionnaire) correctly? (Chapter 11)
j. Is notification of disqualified applicants being conducted? (Chapter 11
)
k. Are the providers making medical qualification/disqualification determinations according to
current policy? (Chapter 11
)
l. Does the provider/technician/demonstrator ask all applicants as a group, prior to beginning the
orthopedic/neurologic maneuvers, if they have had any of the listed medical conditions? (Chapter 12
)
m. Is the exact purpose of the consult relayed to the consultant by the MEPS medical provider on the
SF 513? (Chapter 13
)

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
141
n. Is a medical technician completing the required daily quality review process on all applicant records
projected to process at the MEPS? (Chapter 17
)
o. Are the daily FBP requests accomplished? Are typical “no show” rates taken into consideration
when determining the number of FBPs requested? (Chapter 18
)
p. Are the work hours used for invoice reconciliation and fill rate data verified as accurate in the FBP
applications? ( Chapter 18
)
q. Are the medical technicians receiving the required medical training as outlined in this regulation
and the training SOP? (Chapter 19
)
r. Is audiometric equipment calibrated and maintained? (Chapter 20
)
s. Are the protein/glucose/HCG tests QCed (not expired) and then performed by a trained medical
staff member? Are test controls analyzed and documented as recommended by the manufacturer? Is
laboratory documentation (controls/logs) retained for at least two years in Medical Department? (Chapter
20
)
t. Are recruits that have sworn in and are now accessed to their respective Service who become ill
and/or injured, whether still at the MEPS or a MEPS-sponsored facility (such as the contract hotel), or
returns to the MEPS after beginning transport from their place of departure for recruit training/duty station
returned to the MEPS medical department for evaluation? (Chapter 21
)
B-5. Comments
Users may submit comments to
HQ USMEPCOM, ATTN:
J-3/5/7 MD 2834 Green Bay Road North Chicago, IL 60064-3091
B-6. DA Form 11-2
DA Form 11-2
is designed to document any management control evaluation. Evaluations of the MEPS
Medical Department area must be documented on this form. Fill in the appropriate items, as needed. The
assessable unit is the MEPS Medical Department. The methodology used to conduct the evaluations could
be the Internal Control Evaluation Checklist questions (B-4 above) and other methods used to review
this area (e.g., manufacturer’s instructions). Block 6 lists who completed the evaluation and when it was
conducted. Block 7 is used to document and explain the methods used for evaluating this functional area.
Item 8 is competed by the assessable unit manager (e.g., Commander). File completed
DA Form 11- 2
under RN 11-2a3/800B, “Management Control Program” (see Appendix A, Section III).

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
142
Appendix C
Glossary
Section I Abbreviations
ABHA
Applicant Behavioral Health Assessment
ACMO
Assistant Chief Medical Officer
A&C SSO
Acqusitions and Contracting Special Staff Office
ACOR
Alternate Contracting Officer Representative
ADT
Active Duty for Training
AFSC
Air Force Specialty Code
AFVT
Armed Forces Vision Tester
AIT
Advanced Individual Training
ANSI
American National Standards Institute
AP
Accession Policy
ARNG
Army National Guard
ATD
Annual Training Document
BAS
Bio-Acoustic Simulator
BAT
Breath Alcohol Test
BLS
Basic Life Support

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
143
BP
Blood Pressure
CAP
College of American Pathology
CD
Considered Disqualifying
CLF
Contract Lodging Facility
CLIP
Clinical Laboratory Improvement Program
CMO
Chief Medical Officer
COR
Contracting Officers Representative
CR
Closing Review
CTO
Confirmed Training Orders
DAT
Drug and Alcohol Test
DD or DoD
Department of Defense
DoDI
Department of Defense Instruction
DoD ID
Department of Defense Identification
DoDMERB
Department of Defense Medical Examination Review Board
DPC
Defined Provider Category
DQ
Disqualified

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
144
DROTC
Dis-enrolled Reserve Officer Training Corps
EKG
Electrocardiogram
ELS
Entry-Level Separation
EPTS
Existed Prior to Service
ETP
Exception to Policy
FB-CMO
Fee Basis Chief Medical Officer
FBP
Fee Basis Provider
GPC
Government Purchase Card
GPOC
Government Point of Contact
HIPAA
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
HIV
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
HR
Heart Rate
HT
Height
HTP
Hometown Physical
IAW
In Accordance With
ICD
International Classification of Diseases

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
145
IET
Initial Entry Training
IOP
Intraocular Pressure
IRC
Inter-service Recruitment Committee
IRR
Individual Ready Reserve
ITD
Initial Training Document
ITS
Information Technology Specialist
ITV
Individual Training Visit
J-1/MEHR
J-1/Human Resources Directorate
J-3/5/7 MD
J-3/5/7 Medical Division
J-4/MEFA
J-4/Facilities and Acquisitions Directorate
JKO
Joint Knowledge Online
MEB
Medical Evaluation Board
MEPS
Military Entrance Processing Station
METR
Medical Evaluation Treatment Records
MLTS
Medical Leadership Training Seminar
MMA
Medical Management Analyst
MMAL
Medical Materiel Allowance List

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
146
MO
Medical officer
MOC
Military Entrance Processing Command Operations Center
MTF
Military Treatment Facility
MRV
Medical Reassessment Visit
NCD
Not Considered Disqualifying
NCOIC
Non-Commissioned Officer in Charge
NG
National Guard
NP
Nurse Practitioner
ONE
Orthopedic/Neurological Examination
OPSO
Operations Officer
OPTEC
Stereoscope Vision Testing
OSHA
Occupational Safety & Health Administration
PA
Physician Assistant
PCP
Primary Care Provider
PDRL
Permanent Disability Retirement List
PEB
Physical Evaluation Board

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
147
PHA
Periodic Health Assessment
PIP
Pseudoisochromatic Plate
POC
Point of Contact
PS
Prior Service
PQMP
Provider Quality Management Program
PWR
Provider Work Record
QRP
Quality Review Process
RAT
Reading Aloud Test
RJ/RBJ
Return Justified/Reevaluation Believed Justified
ROTC
Reserve Officer Training Corps
SAV
Staff Assistance Visit
SMA
Sector Medical Asset
SMO
Sector Medical Officer
SMWRA
Service Medical Waiver Review Authority
SOP
Standard Operating Procedure
SPEAR
Sharing Policy Experience and Resources (USMEPCOM intranet)
STAR
Station Advisory Report

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
148
STARNET
Station Advisory Report Network
SUP MT
Supervisory Medical Technician
TDQ
Temporary Disqualification or Temporarily Disqualified
TDRL
Temporary Disability Retired List
TSJTS
Training Standardization Job Task Sheets
UMF
USMEPCOM Form
UMQP
USMEPCOM Medical Qualification Program
UMR
USMEPCOM Regulation
USAR
United States Army Reserve
USMEPCOM
United States Military Entrance Processing Command
USMIRS
United States MEPCOM Integrated Resource System
VA
Department of Veterans’ Affairs
WKID
Work Identification Code
WT
Weight
6PF
Six Part Folder
Section II Terms
Accession Medicine

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
149
Accession medicine is the practice of performing medical evaluations as defined in chapter 11 in this
regulation in order to render a medical qualification determination for accessing applicants into the Armed
Forces according to standards established by the DoDI 6130.03-V1.
Assistant Chief Medical Officer
Government civil service medical provider located at MEPS in the Medical Department. The ACMO uses
their professional training and judgment to apply medical qualification standards set forth by the
Department of Defense policy. The ACMO is supervised by the CMO, under the administrative control of
the Commander, within the rules and regulation of USMEPCOM. After initial training, ACMOs are
expected to achieve DPC-4 level proficiency.
Audiogram
A hearing test or the printed test results from the audiometer.
Bottom-Line
The signature by the profiling provider on an applicant’s physical when PULHES are complete.
Chaperone
A MEPS employee or contractor who is trained and authorized to observe the medical examination of an
applicant of the same biological sex when the provider and applicant are different biological sexes or when
requested by the applicant or medical provider.
Chief Medical Officer
Government civil service medical provider who supervises the Medical Department at each MEPS or
processing facility. The CMO uses their professional training and judgment to apply medical qualification
standards set forth by the Department of Defense policy. The CMO functions under the supervision and
administrative control of the MEPS Commander, within the rules and regulation of USMEPCOM. After
initial training, CMOs are expected to achieve DPC-4 level proficiency.
Confirmed Training Orders
Appointment orders signed by the MEPS Commander that confirm the employee is fully trained in and
authorized to perform all duties identified on the CTO.
Disqualified
Applicant does not meet established criteria under the standards prescribed by the DoDI 6130.03-V1 or the
sponsoring Military Service.
Fee Basis Chief Medical Officer
A FB-CMO is a contracted provider who functions as the CMO in a limited capacity. When a government
provider is absent from the MEPS, then the MEPS may request a FB-CMO from the contractor. An FB-
CMO must have achieved a DPC-4 level proficiency.
Fee Basis Provider
Fee Basis Providers (FBPs) are contracted medical providers who augment the MEPS Medical Department.
They are trained and qualified to perform accession medical evaluations. They may be requested by the
MEPS as necessary to assist the government providers (CMOs/ACMOs/MOs) in conducting accession
medical processing IAW current policies.
Front-Loading

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
150
Front loading refers to medical tests that are authorized to be performed before the Medical Brief but are
not authorized during “night” aptitude testing timeframes.
Hometown Shipper
An individual who has been authorized by their Service to ship from their hometown to a
Reception/Training Center or other duty location without returning to the MEPS. Also known as a “direct
shipper” for the National Guard.
Individual Training Visit
A visit by a J-3/5/7 MD staff member or their designee to provide guidance, training and assistance to a
newly assigned MED NCOIC or Supervisory Medical Technician in a particular MEPS.
Medical Non-Commissioned Officer in Charge (NCOIC)/Supervisory Medical Technician (SUP
MED)
Individual (Government employee) responsible for the administrative operation of the MEPS Medical
Department and general supervision of paraprofessional staff (lead medical technicians, medical
technicians) conducting medical testing.
Medical Officers
Government civil service medical provider who is an advanced practitioner (NPs/PAs) who supports and
assists the CMO with the execution of the UMQP as indicated by the CMO and as outlined in this regulation.
MOs are expected to achieve DPC-3 level proficiency.
Medical Provider
Medical practitioners performing accession medical evaluations within USMEPCOM. Includes
government and contracted physicians, certified nurse practitioners, and physician assistants.
Medical Read (Med Read)
A “med read” is any applicant supporting medical documentation, not including consult and waiver results,
which has been requested and/or supplied following the initial physical examination.
Medical Reassessment Visit
A visit by a Sector Medical Asset or USMEPCOM HQ staff member(s) to improve the unsatisfactory
functional areas within 90 days of a “Not-In-Compliance” IG inspection.
Medical Waiver
A Service decision to waive a medical standard for a pre-existing condition which is disqualifying for
Military Service IAW DoDI 6130.03-V1.
N Status
This indicates the applicant has been placed on administrative hold, pending resolution of a discrepancy or
that additional enlistment paperwork may be required. MEPS personnel will notify the appropriate
recruiting Service liaison/guidance counselor that until the disqualifying discrepancy and/or condition is
cleared, the applicant is ineligible for further enlistment processing. If the medical examination was initiated
while the applicant was in an “N” status, the medical examination will be completed. Upon completion of
the medical examination, the applicant will be placed in an “N” status until cleared for further processing.
No-show
An individual projected for processing who fails to arrive on the scheduled date at the prescribed time.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
151
Overseas Processor
Applicants processing outside the continental United States, Alaska, Hawaii, or Puerto Rico.
Profiler
Government or contracted provider who has achieved at least DPC-3 level proficiency.
Projection
The scheduling of an individual applicant for entrance processing at a USMEPCOM Processing Location.
Return justified/reevaluation believed justified
A term applied to an individual found temporarily disqualified for Military Service, due to an administrative
(e.g., overweight) or temporary medical condition, and whom MEPS personnel believe should be
reevaluated at a later date.
Sector Medical Assets
Includes Sector Medical Officers and Management Program Analysts
Shipper
A recruit who has enlisted and is en route from home or the MEPS to an initial entry training site.
Shipping Applicant
An applicant who is projected for a shipping inspection to enter on Active Duty/Active Duty Training at
the MEPS prior to shipping to a basic training site.
Staff Assistance Visit
A visit by a Sector Medical Asset or USMEPCOM HQ staff member to provide guidance, training and
assistance to the MEPS staff departments on how to meet the standards required to operate effectively
within a particular functional area.
Walk-In
An individual who has been previously determined to be processing authorized (“PA”), arrived at the MEPS
early enough to attend the medical brief in order to receive accession medical examination and/or
processing, but was not scheduled by name with the MEPS prior to close of business on the preceding
workday.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
152
Appendix D
Proteinuria/Glycosuria
D-1. Proteinuria:
An applicant with a urine dipstick positive for protein (including trace) will be further evaluated according
to the following:
a. With Hypertension:
(1) If an applicant is hypertensive with a systolic blood pressure > 180 and/or diastolic > 120, then
processing is discontinued and the applicant will be left in an “open” status. As this is considered
hypertensive emergency, the MEPS will contact emergency services to transport the applicant to the
nearest Emergency Department.
(2) If an applicant is hypertensive with a systolic blood pressure >140 but <180 and/or diastolic
>90 but <120, then processing is discontinued, the applicant’s profile will be left in an “open” status, the
applicant will provided a UMF 40-1-11
for BP evaluation, and the applicant will be referred to the PCP for
urgent evaluation of elevated BP and proteinuria.
b. Without Hypertension:
If an applicant is normotensive, then the applicant should be given the opportunity to provide another
urine sample before the end of the processing day.
(1) If the second test shows negative or trace results, then the applicant is qualified.
(2) If the repeat dipstick result is 1+ or greater, or if the applicant is unable to provide a second
urine sample on the same processing day, then a random urine protein/creatinine ratio must be obtained
(more than 48 hours after last strenuous activity) in order to render a qualification determination IAW
DoDI
6130.03-V1. If the protein/creatinine ratio is disqualifying for proteinuria, then the applicant will be DQ’d
and should be refered to their PCP for further evaluation.
D-2. Glycosuria:
An applicant with a urine dipstick positive for glucose must be evaluated by the MEPS profiling provider
for symptoms of possible uncontrolled diabetes.
a. If the applicant is symptomatic for possible uncontrolled diabetes (e.g., polyuria, polydipsia,
polyphagia, blurred vision), then the applicant’s profile will be left in an “open” status and the applicant
immediately referred to the nearest Emergency Department.
b. If the applicant is asymptomatic, a urine dipstick may be repeated on the same day, and if the
repeat test remains positive for glucose, then the applicant is disqualified for current persistent glycosuria
IAW the DoDI 6130.03-V1
. The applicant should then be referred to their PCP for further evaluation and
definitive diagnosis.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
153
Appendix E
Letters
Figure E-1. USMEPCOM Authorized Serious Medical Condition Letter
Month Day, Year
(Insert Applicant Name)
(Insert Applicant Street Address)
City/State/zip code
Dear Mr./Mrs./Ms. (Insert Applicant Name):
Based upon your recent Military entrance medical examination and the medical
documentation that is enclosed, you have been found to have a potentially serious medical
condition. You will need to go to a (insert medical provider or emergency department,
depending upon acuity of the condition) as soon as possible for evaluation of (insert explanation
of condition). Ensure that you bring the enclosed documentation with you to the (insert
appointment or emergency department). Upon evaluation and documented resolution of this
condition, you may return to the MEPS for reevaluation for qualification, at your Service’s
discretion.
Sincerely,
(Insert CMO Name)
Chief Medical Officer
Enclosures: (insert description of medical documentation)
cc:
MEPS Commander
Figure E-1. USMEPCOM Authorized Serious Medical Condition Letter

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
154
Figure E-2. USMEPCOM Authorized Medical Disqualification Letter
Month Day, Year
(Insert Applicant Name)
(Insert Applicant Street Address)
City/State/zip code
Dear Mr./Mrs./Ms. (Insert Applicant Name):
Based upon your recent military entrance medical examination, you have been found
medically disqualified for entry into the Armed Forces of the United States. The reason for your
medical disqualification is the finding of (Insert medical condition). Although this condition may not
affect your current or future employability in civilian life, it is considered disqualifying for military
service in accordance with section (cite section(s) of the DoDI 6130.03-V1) of Department of
Defense Instruction (DoDI) 6130.03 Volume 1, “Medical Standards for Military Service:
Appointment, Enlistment, or Induction,” Change 1, effective September 4, 2020.
As indicated in section 4.2.d of DoDI 6130.03-V1, your Recruiting Service may request a
medical waiver on your behalf, since some medical conditions have a potential to be waived. The
Service Medical Waiver Review Authority will consider each request submitted and make a medical
waiver determination based on all available information regarding the condition, as well as the
specific needs of the Military Service. Therefore, you should contact your recruiter and discuss the
possibility of seeking a medical waiver.
You may be interested to know that approximately 35 percent of individuals desiring to enter
the Armed Forces have some medical condition that is disqualifying. While many of these
individuals have otherwise outstanding qualifications, they are unable to serve in the U.S. Military.
However, the Department of Defense team consists of both military and civilian members.
Individuals who are not eligible for military duty can and do become successful civilian members of
the team. A listing of government job vacancies is available at www.usajobs.gov. In addition, there
are many opportunities for individuals who are medically disqualified from military duty to volunteer
their time and experience. These opportunities are available thru such organizations as USA
Freedom Corps, Citizens Corps, AmeriCorps, and America’s Promise. You can learn more about
these programs through the following websites: www.usafreedomcorps.gov, www.citizencorps.gov,
www.americorps.org, and www.americaspromise.org.
Your interest and desire to serve in the Armed Forces is commendable. Please contact your
recruiter to discuss your options. Best wishes to you on your future endeavors.
Sincerely,
(Insert CMO Name)
Chief Medical Officer
cc:
MEPS Commande

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
155
Appendix F
Supporting Medical Documentation Review Timelines
Supporting medical documents are defined as non-MEPS generated medical documentation, and consist of
the following: 1) Prescreen medical documents, 2) consult/ancillary service result, 3) waiver determination,
and 4) medical read (med read) documents.
F-1. Prescreen:
Prescreen medical documents are submitted prior to the accessions medical examination with the
DD Form
2807-2 by an applicant in order to streamline the accession process. These documents will be processed,
reviewed and considered for authorization of further processing IAW Table F-1. (See USMEPCOM
Medical Prescreen Program for further guidance.)
F-2. Consults:
Consultation results are submitted during or after the accessions medical examination, and will be provided
to the Medical Department either thru the portal from contract providers or via facsimile from non-contract
providers. Consultation results will be reviewed and considered for rendering a qualification determination
within four business days of receipt.
F-3. Medical Waivers:
Medical waiver determinations are submitted to the MEPS by the SMWRA of the sponsoring Service for
an applicant after a disqualification for Service determination has been rendered. All approved SMWRA
waivers will be processed and recorded on the DD Form 2808
and in USMIRS by the MEPS Medical
Department within one business day of receipt.
F-4. Med Reads:
Med read documents are supporting medical documents requested and/or submitted following the
accessions medical examination, but prior to rendering a medical qualification determination. These
documents will be processed, reviewed and considered for rendering a medical qualification determination
IAW Table F-1. (See Paragraph 11-4
for further guidance).

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
156
Table F-1. USMEPCOM Prescreen and Med Read Review Timeline Table
Number of Pages of Supporting
Medical Documents
Maximum Number of Business Days
to Complete the Review by COB
0 - 5
2
6 - 20
3
21 - 26
4
27 - 32
5
33 - 38
6
39 - 44
7
45 - 50
8
51 - 56
9
57 - 62
10
63 - 68
11
69 - 74
12
75 - 80
13
81 - 86
14
87 - 92
15
93 - 98
16
99 - 104
17
105 - 110
18
111 - 116
19
117 - 122
20
123 - 128
21
129 - 134
22
135 - 140
23
141 - 146
24
147 - 152
25
153 - 158
26
159 - 164
27
165 - 170
28
171 - 176
29
177 or >
30
Table F-1. USMEPCOM Prescreen and Med Read Review Timeline Table

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
162
Appendix H
“N” Status Codes
H.1. “N” Status Overview: The following codes are available within the USMIRS Administrative Hold
“N” Status Screen (OQ03) List of Values. The use of the “N” Status will standardize the reporting
requirements for entry in the “Remarks” section of USMIRS Screen OQ03 during QRP.
H.2. “N” Status Purpose: The codes are required for HQ USMEPCOM to identify and count “N” Statuses
captured on an applicant during MEPS processing.
H.3. “N” Status Outcome: The utilization of “N” Statues create a separate “B000N” WKID transaction
for identified discrepancies for a particular applicant. MEPS will also specify the discrepancy as shown in
the examples that must be addressed and resolved by the sponsoring Service.
H.4. “N” Status Code Listing
Codes Literal Text
Q0 Need to take/retake ASVAB
Q1 Ineligible for ASVAB
Q2 Missing Form/Doc; (specify)*
Q3 Expired Form/Doc; (specify)*
Q4 Incorrect Form/Doc; (specify)*
Q5 Projection Issue; (specify)**
Q6 Service has Packet
Q7 Incomplete Form/Doc; (specify)*
Q8 Other Reason; (specify)***
P0 Record Pending Purge
P1 Packet Not Found
P2 Deferred – Not OK to Physical
P3 Data Transaction Missing; (specify)****
P4 Data Reporting Error; (specify)*****
E1 Re-enrollment Due to; (specify)******
E2 Full Re-enrollment Due to; (provide reason)
E3 Service Request Re-enrollment; (last name of Liaison/Counselor)
VA Prescreen Received, No Med Records
VB Prescreen Received, Med Records 5 Pages or Less
VC Prescreen Received, Med Records 6-32 Pages
VD Prescreen Received, Med Records 33-62 Pages
VE Prescreen Received, Med Records 63-92 Pages
VF Prescreen Received, Med Records 93 or More Pages
VG Prescreen Incomplete/Not Reviewed by Med Provider
VH Prescreen In-Review
VI PR Complete; Processing Authorized, Time Line Met
VJ PR Complete; Processing Authorized, Time Line Not Met
VK PR Complete; Processing Not Justified, Time Line Met
VL PR Complete; Processing Not Justified, Time Line Not Met
VM PR Complete; PNJ, SMWRA Requested Exam, Time Line Met
VN PR Complete; PNJ, SMWRA Requested Exam, Time Line Not Met

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
163
NOTES:
1 *; Example – In literal text enter the specific form/document number/name; e.g., Q2 Missing - UMF680-
3A-E, PCN 680-3ADP, DD2807-2, Medical Waiver, DD1966/5,
Medical Paperwork, DD2808, PMS Paperwork, etc.
2 **; Example – In literal text enter a synopsis of the specific issue to assist the sponsoring
Service in identifying what is required to resolve; e.g., Q5 Projection Issue - Special Test not authorized
on selected Processing Date, Processing Date not valid for selected processing, etc.
3 ***; Example – In literal text enter the other administrative hold issue; anything other than what is listed;
e.g., Q8 Other Reason - Issue at Lodging Facility, Disruptive Applicant, etc.
4 ****; Example – in literal text enter the specific WKID that is missing and needs to be reported; e.g., P3
Data Transaction Missing - B300 for Aptitude Not Required, B0M0 for Medical Not Required, DD2808
in Packet w/no Medical Data reported, SAC (ENTNAC) Submission, etc.
5 *****; Example – in literal text enter the specific data error; e.g., P4 Data Reporting Error - DOB in
OP01 does not match UMF680-3A-E; Date of Physical in MD01 does not match DD2808, etc.
6 ******; Example – in literal text enter the specific cause requiring the re-enrollment; e.g., E1 Re-
enrollment - Injured Finger, Problem Verifying Previously Enrolled Finger, Eyes Closed, Looked Away
From Lens, Facial Image Distorted, Traffic In Photo Background, etc.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
164
Appendix I
Encrypted E-mail or Direct Exchange of Cover Sheets
I-1. Encrypted email relations.
MEPS Medical Department Personnel and Selected SLs/GCs will establish secure email traffic
communication or direct exchange of Cover Sheets. To send and receive encrypted email messages, both
the sender and the receiver must share their digital ID certificates with each other and both must add the
other to their Outlook contacts.
a.
Open a message that is digitally signed as indicated in the message list by an encryption or signature
icon.
b.
Right-click the name in the FROM box, and then click – “Add to Outlook Contacts”.
c.
Contact information box will open, click Save
I-2. Set default to encrypt all outgoing emails.
a. Open Outlook and click on the FILE tab. Choose OPTIONS>TRUST CENTER>TRUST CENTER
SETTINGS.
b. Click on the EMAIL SECURITY TAB, under ENCRYPTED EMAIL checkmark the first box
titled: Encrypt contents and attachments for outgoing messages, click OK.
I-3. Create a contact group for each Service.
In Home tab in Outlook, select NEW ITEMS > MORE ITEMS > CONTACT GROUP.
a.
At the Name block give the group a name (Army Prescreen Cover Sheet Distro; Navy Prescreen
Cover Sheet Distro, etc.).
b.
To build your contact group select Add Members in the CONTACT GROUP tab, select, FROM
OUTLOOK CONTACTS > the names of your contacts will display, select personnel for your contact group
accordingly and click MEMBERS > OK.
c.
You will see your built contact group, select SAVE & CLOSE.
d.
When sending Cover Sheets to each Contact Group, open a new email, click the “To…” button in
the Address field, click the ADDRESS BOOK down arrow to access the list of Address Book entries >
scroll or arrow up to “Contacts” (just under your personal email), then select the appropriate Distro list.
e.
You can also type in the “To…Address Field” the name of the Distro group and it will automatically
populate.
I-4. Sort cover sheet by Service.
Medical personnel will need to sort all Prescreen Cover Sheets by Service. Scan Cover Sheets in batches
by Service as follows:
a.
Using your CAC, log onto a Multi-Function Printer (MFP) and select and scan each batch of
Prescreen Cover Sheets.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
165
b.
Scan each Services’ Prescreen Cover Sheets which will show up in your personal folder (H: Drive).
c.
Right click on the file name in your H: Drive and select “Rename”.
d.
Rename all batches of Prescreen Cover Sheets by Service for easy recall (i.e., Army Prescreen
Cover Sheets/current date in YYYY/MM/DD format).
e.
Open the first of your named scanned files (on your H: Drive) to verify the Service you are viewing
then close (i.e., the file you named “Army Prescreen Cover Sheets/current date in the YYYY/MM/DD
format” has only Army Prescreen Cover Sheets only has in the file).
f.
Open a new email and type in the appropriate Contact Group in the “To” line (i.e., Army Prescreen
Cover Sheets Distro).
g.
Attach the appropriate file you scanned to your H: Drive (i.e., Army goes to Army, Navy to Navy
etc.).
h.
In the email, click the OPTIONS tab and select the boxes, “Request a Delivery Receipt”, and
“Request a Read Receipt”.
i.
Email will be sent:
(1) With a subject line titled: Complex Prescreen Cover Sheets.
(2) Encrypted.
(3) Courtesy.
(4) Copied (cc) to the Medical NCOIC/SUP MT.
j.
Immediately after sending encrypted email of Prescreen Cover Sheet, delete electronic copy from
sender’s H drive for PII/PHI security precautions.
k.
Recommend SLs in receipt of encrypted email of the Prescreen Cover Sheets work with their
appropriate staff to ensure the protection of PII/PHI.
I-5. Create an outlook email folder to save sent prescreen cover sheets.
Each MEPS Medical Department will create a Prescreen Cover Sheet folder, by month, in their Outlook
email for saving encrypted sent Prescreen Cover Sheets. The contents of each folder will be deleted every
3 months.

USMEPCOM Regulation 40-1
TOC
166
I-6. Establish a direct prescreen cover sheet exchange between the Medical Department and Service
Liaisons.
a. This method is for the Prescreen Cover Sheets to be manually picked up by the SL. The Medical
Department will establish a specified location in a secure area that the SLs can be given access to.
b. Copies of all Prescreen coversheets will be separated by Service (i.e., in a stackable/hanging paper
tray) and covered with a DD Form 2923
, Privacy Act Cover Sheet.
The Medical Department will be overall responsible for the time(s), place, and the way SLs pick up
Prescreen Coversheet copies as long as Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and Protected Health
Information (PHI) is protected and exchange does not interfere with applicant medical processing.







